A go to market strategy is an essential part of a product launch. It defines how a business should reach out to its customers and gain a competitive advantage. It focuses on the market segments that should be pursued, the channels that should be used and the solution that should be offered to them.
In this post, we will guide you through the process of building a go-to-market strategy for launching your new product.
We’ve created several templates to simplify some of the steps as well. Click on the templates to open them in the editor so you can modify them according to your needs.
What is a Go To Market Strategy
A go-to-market (GTM) strategy is an action plan. It outlines the steps a company needs to take to succeed in a new market or with a new audience.
It outlines the steps a company needs to take to succeed in a new market or with a new audience.
It specifies why you are launching a new product as well as who it’s for and how you are going to do it. The GTM strategy also focuses on the issues the customers will face once presented with the product, which will, in turn, help you work on improving their experience.
A GTM plan can be used for launching a new product or service as well as for marketing existing products.
What differentiates a GTM strategy from the typical marketing strategy is its place in the product’s lifecycle. Whereas the marketing strategy focuses on the continuing campaigns and programs the company runs to increase demand for the product or service after it’s been introduced to the market, the go-to-market strategy is about creating the plan to introduce that offer to the market.
For startups, these two strategies might be one and the same, but for more mature businesses, these two involve different steps, teams, and goals.
A solid go-to-market strategy aims to answer;
- What are you selling?
- Who are your potential customers?
- How will you connect with your audience?
- What are the channels you will use to reach them?
Benefits of a go-to-market strategy
The advantages associated with an effective GTM strategy are many. Among them, these stand out the most
- Minimizes customer acquisition costs
- Improves customer experience
- Ensures successful product launches (reduce costs associated with failed launches)
- Brings everyone in the team on the same page and guides them throughout the process
- Increases the company’s ability to adapt to changes in the market
- Helps reinforce brand position
How to Build a Go to Market Strategy
We have outlined 8 steps to building a go-to-market strategy in this guide. Follow them to formulate your own strategy.
1. Identify Your Target Market
The effectiveness of a go-to-market strategy depends on how well you know your market. That’s why building one should begin with a detailed analysis of your target market.
Your product may not be appropriate for everyone, which is why you need to identify the ideal and the most profitable market to sell it to. Areas you need to consider here are demographics, geography, psychographics, ethnographic, buyer personas, competition, etc.
You can brainstorm a list of possible markets you can thrive in and compare their attractiveness in terms of market size, competition, growth trends, barriers to entry and so on.
An ideal framework to incorporate into your research here is Porter’s Five Forces. The analysis focuses on five factors that a business planning to introduce a new product to a new market should be aware of;
- Power of suppliers
- Power of the buyer
- Rivalry between competitors
- Threat of substitute products
- Threat of new entrants
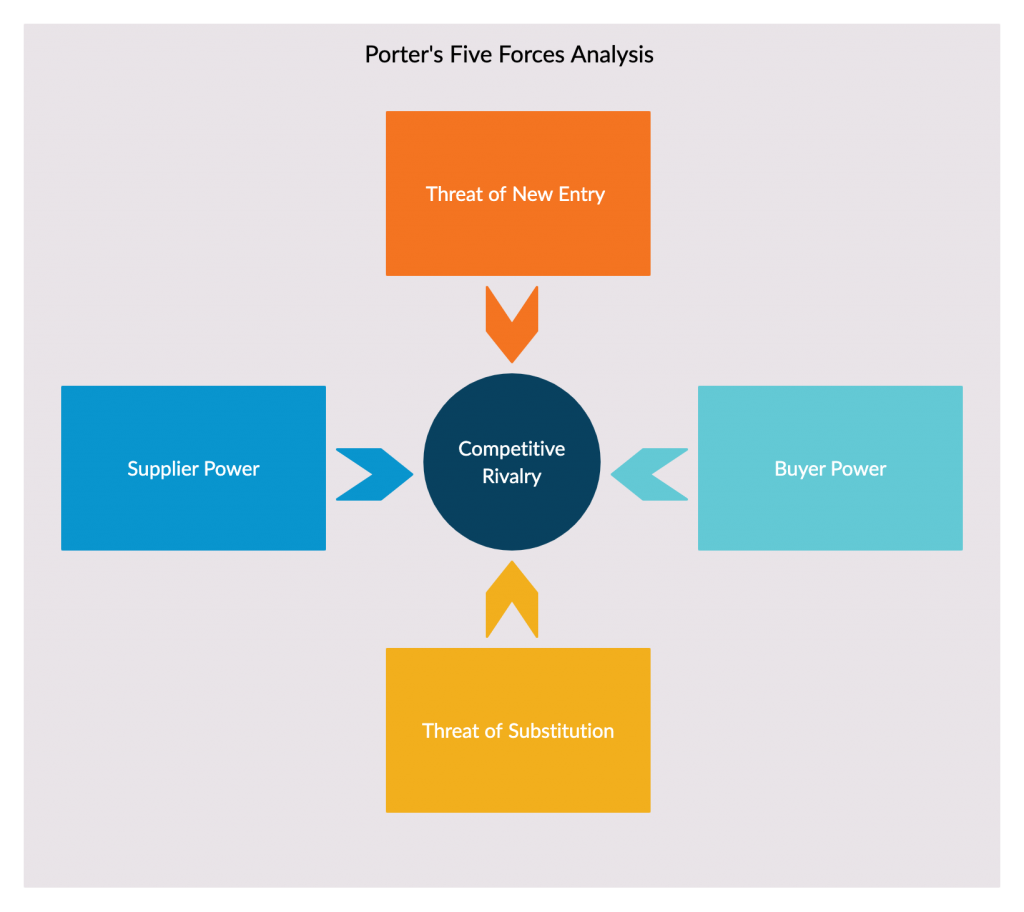
In addition, refer to our guide on how to conduct a competitive analysis to learn about more handy tools for understanding your competitive landscape.
2. Know Your Target Customers
The second step of developing a go-to-market strategy is understanding your ideal customer. Once you have defined your target market, you are a step closer to identifying who they are.
Here you have to gather as much insight as possible on your target audience. Some of the methods you can rely on here are, online surveys, one-on-one interviews, focus groups, in-store interactions, research, etc.
At the end of this step, you should have a customer persona based on extensive knowledge about the behavior, preferences, challenges, attitudes, goals, and needs of your target customer.
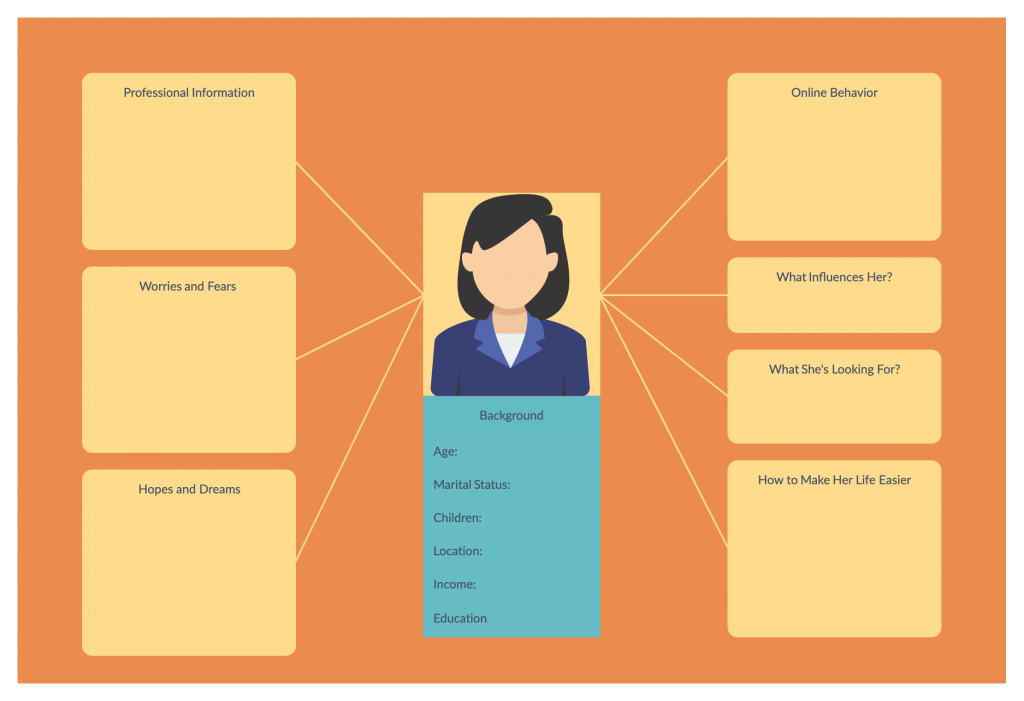
Refer to our easy guide to creating a buyer persona to learn about conducting audience research and developing a buyer persona with editable templates in more detail.
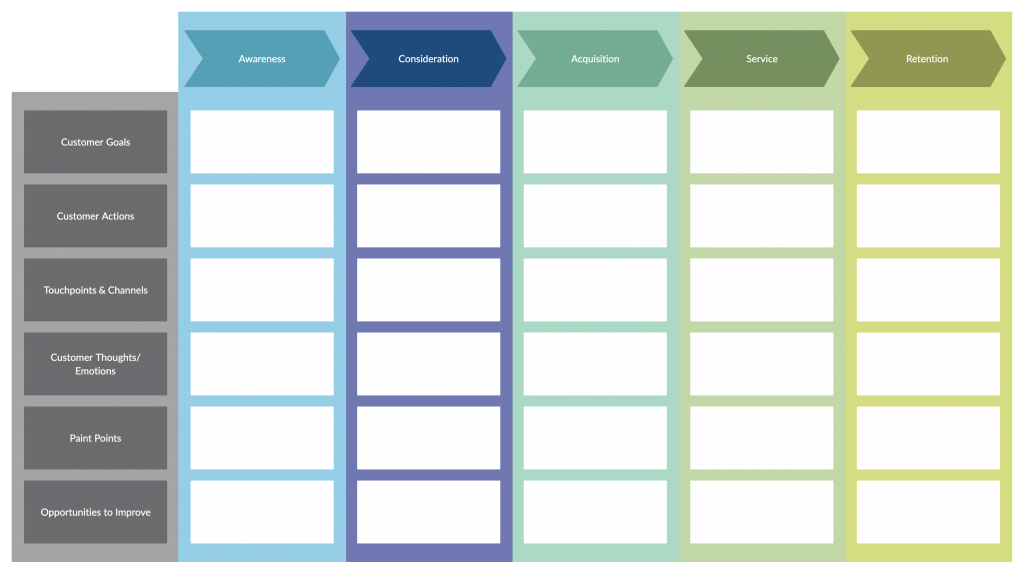
Understanding the customer’s journey here is equally important. This will further inform you about how your customer becomes aware of your brand, how they interact with it, and what they experience throughout the process.
Using a customer journey map, you can map this out making it easier for the entire team to refer to and understand.
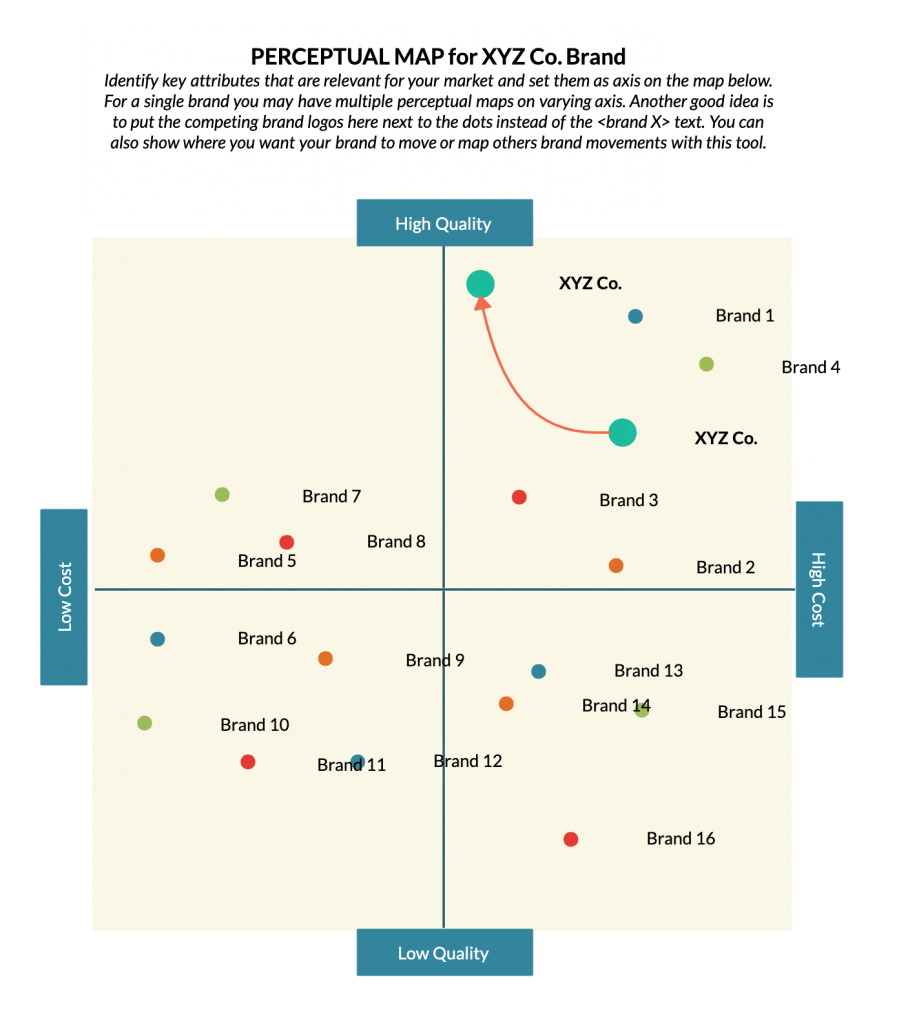
3. Understand Your Brand Position
How do you want your customers to view you in relation to the products/ brands of your competitors? Do you want to be the one who offers high-quality, premium products or an affordable alternative?
Here you can use a perceptual map, to assess the strengths and weaknesses related to your competitor products based on criteria that are important to your customer. And it will help you identify the competitive advantage for your own brand in the market as well.
4. Define Your Unique Value Proposition
This is where you need to understand your product in terms of its key features and user benefits. Focus on what your product does to solve the problems of the customers in order to understand how your offering differs from that of your competitor.
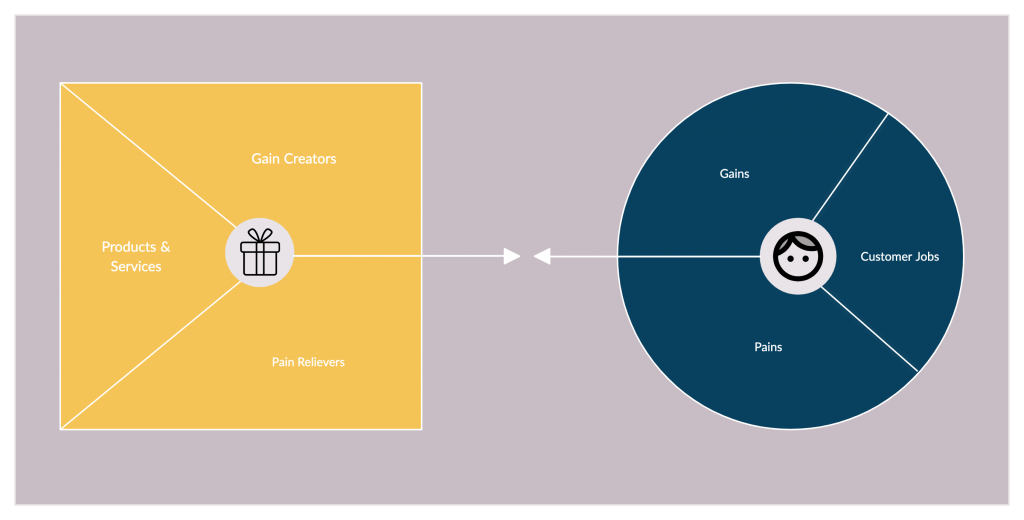
You can base your analysis on the value proposition canvas which helps you understand the value of your product from the perspective of the customer. It sheds light on what features or functionalities your product should have to meet the needs of the customer.
5. Select Your Marketing Channels
What is the most efficient way of reaching your customers? These could include both outbound (newspaper ads, TV ads, flyers, etc.) and inbound (newsletters, websites, social media, blogs, online videos, podcasts) forms of marketing.
Although you use different channels, your messaging, content or branding material utilized should be consistent throughout.
6. Set Your Budget
In this step, you need to focus on defining your product/ service pricing strategy as well as estimating costs associated with your overall GTM strategy.
When determining your pricing model you need to consider the expectations of your customers, the prices of the products of your competitors and how it will help you gain a competitive advantage in the industry.
Your pricing strategy should be based on your business model and it should indicate to your customers the value of your product or service at the same time.
7. Outline Your Sales Strategy
If your product is more sales-intensive, you need to have a well-defined sales process. Here you need to define how your sales team is going to find, reach out to and acquire customers. This might entail finding the right tools and giving the right training to the sales team as necessary.
At the same time, your support team should be well-equipped with tools and knowledge to handle the requests from the new customers who might struggle with using the new product.
8. Put Together Your Marketing Strategy
Now that you know what you are selling, who you are selling to, and what channels to use, it’s time to decide how you are going to market and promote it when it eventually launches.
If you are promoting it to an existing market, you can start with consistent customers. However, if you are entering a new market, you’ll have to identify ways to bring your product in front of them through different means.
Once your new product is out in the market, it doesn’t mean the end of your efforts. As the product team should focus on adding new features and fixing bugs, the marketing and sales teams should consider more new ways to attract customers and sell the product.
Any More Tips?
The steps we have outlined here are a great starting point for formulating your own go-to-market strategy. Make use of the templates provided to make your plan easy-to-understand. On your journey, new marketing trends may arise and conditions may change, and it’s important to revise your strategy from time to time to adapt accordingly.
Got anything to share with us? Let us know in the comments section below.




