Graphic organizers integrate both text and visuals. This has been scientifically proven to be an effective way of teaching and learning. Using them can be extremely useful for both teachers and students as they will make lessons more engaging as well as easily comprehensible.
We have listed below multiple types of graphic organizers you can use during various scenarios, whether you are reading, writing, doing research or studying for exams. Each tool is accompanied by a template that you can use right away.
What is a Graphic Organizer?
A graphic organizer is a powerful teaching and learning tool designed to organize information and ideas visually, making them easier to comprehend and internalize. By integrating text and visuals, graphic organizers illustrate relationships and connections between concepts, terms, and facts, providing a clear and structured way to present complex information. This visual representation aids in simplifying intricate ideas, enhancing understanding and retention for learners of all ages and abilities.
Graphic organizers can be used across all grade levels, serving as effective learning tools for both gifted children and students with special needs. For gifted students, these tools offer a way to explore complex concepts more deeply and independently, encouraging advanced thinking and creativity. For students with special needs, graphic organizers break down information into smaller, more manageable parts, facilitating comprehension and aiding in the retention of new material. By catering to diverse learning styles, graphic organizers provide an inclusive approach to education that can be tailored to meet individual needs.
In the context of adult learners, graphic organizers play a crucial role in bridging the gap between existing knowledge and new information. Adults often enter the learning environment with a rich background of experiences and prior understanding. Graphic organizers help them connect this existing knowledge with newly acquired concepts, fostering a deeper and more integrated learning experience. By visually mapping out information, adult learners can better organize their thoughts, identify areas that require further exploration, and develop a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Benefits of graphic organizers
Graphic organizers are valuable tools for several reasons. They offer numerous benefits that enhance learning and teaching experiences for students and educators alike. Here are some key reasons why you need to use graphic organizers.
1. Simplify complex information
Graphic organizers provide visual clarity by presenting complex information in a way that is easy to understand and process. They break down intricate ideas into smaller, more manageable parts, allowing students to see the relationships between concepts clearly and facilitating comprehension of the big picture.
2. Improve comprehension and retention
The combination of text and visuals in graphic organizers improves memory retention by offering visual cues that reinforce learning. They help students connect new information to prior knowledge, fostering deeper understanding and aiding long-term retention of material.
3. Support diverse learning styles
Graphic organizers cater to different learning styles, including visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners, by providing a structured format that can be customized to meet diverse needs. They are particularly beneficial for students with special needs, offering an inclusive approach that accommodates various learning challenges.
4. Encourage critical thinking and problem solving
By encouraging students to analyze and evaluate relationships between ideas, graphic organizers foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills. They help learners organize their thoughts systematically, enabling them to approach problems strategically and develop effective solutions.
5. Facilitate active learning and engagement
Graphic organizers actively engage students in the learning process, making lessons more interactive and enjoyable. They promote collaborative learning by allowing students to work together to fill in or create organizers, encouraging teamwork and communication in the classroom.
6. Versatile and adaptable
Graphic organizers can be adapted for use in any subject or discipline, making them versatile tools in education. They come in various formats, such as mind maps, Venn diagrams, and flowcharts, providing flexibility to suit different educational needs and learning objectives.
7. Improve instruction and assessment
Teachers can use graphic organizers to present information clearly and assess student understanding efficiently. They serve as valuable tools for formative assessment, allowing educators to gauge student comprehension and identify areas that need further attention, ultimately improving educational outcomes.
Types of Graphic Organizers
Here we have listed 20 types of graphic organizers for teaching and learning. Based on their varied purposes, you can utilize them in reading, writing, researching, brainstorming, and analyzing.
Graphic Organizers for Compare and Contrast
Graphic organizers for comparing and contrasting are a type of graphic organizer that help students visually map out similarities and differences between two or more items, concepts, or ideas. These compare and contrast graphic organizers are designed to clarify and simplify the process of comparison by providing a structured format that highlights the key attributes of each item being examined.
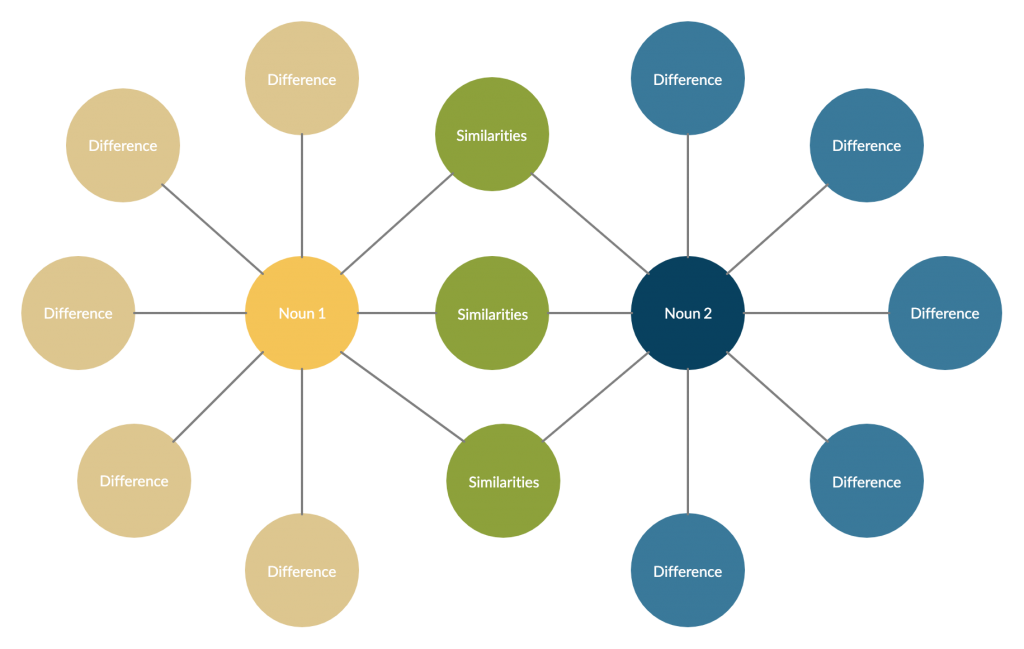
1. Double bubble map
The double bubble map is one of the popular thinking maps and used as a type of graphic organizer. It is much like a Venn diagram and is used to identify similar and different qualities between two things. Students can use bubble map maker to create double bubble map.
How to use it?
Step 1: Write down the two ideas/ topics you are comparing in the two bubbles in the center.
Step 2: As you brainstorm and analyze the topic, write down the differences in the bubbles radiating from the center.
Step 3: Write down the similarities in the bubbles that are common to both topics.
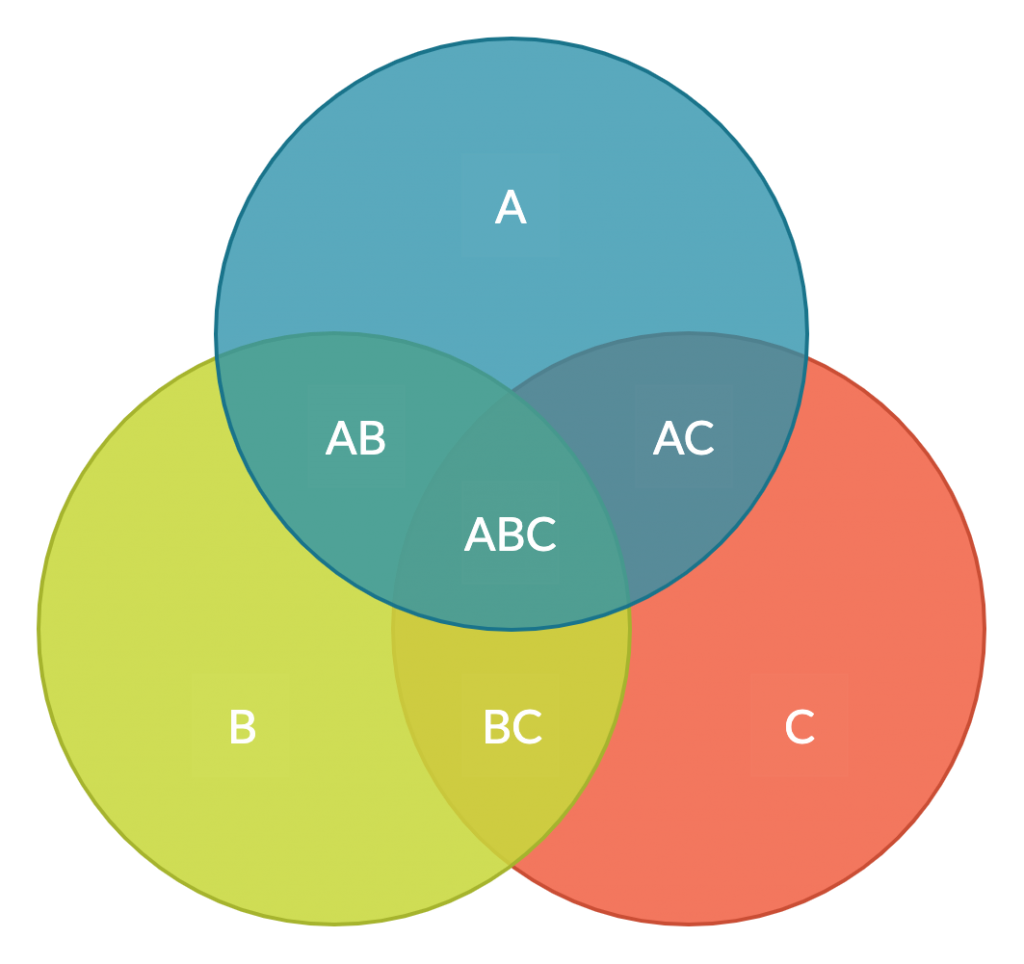
2. Venn diagram
Another graphic organizer that helps you visually represent a comparison of differences and similarities between two subjects, is the Venn diagram. What makes it different from the is that it can include more than two topics and one common area. Using differnt venn diagram templates , student can represent comparions visually.
How to use it
It works similar to the double bubble map.
Step 1: Write down the topics being compared on the top of each circle.
Step 2: Writ down the differences or unique characteristics inside its own sector avoiding the overlapping area.
Step 3: List the similarities in the common area.
Graphic Organizers for Writing
Graphic organizers for writing are a type of graphic organizer that help students plan and organize their ideas before they start writing. These writing graphic organizers provide a visual structure for organizing thoughts, which makes the writing process clearer and more manageable.
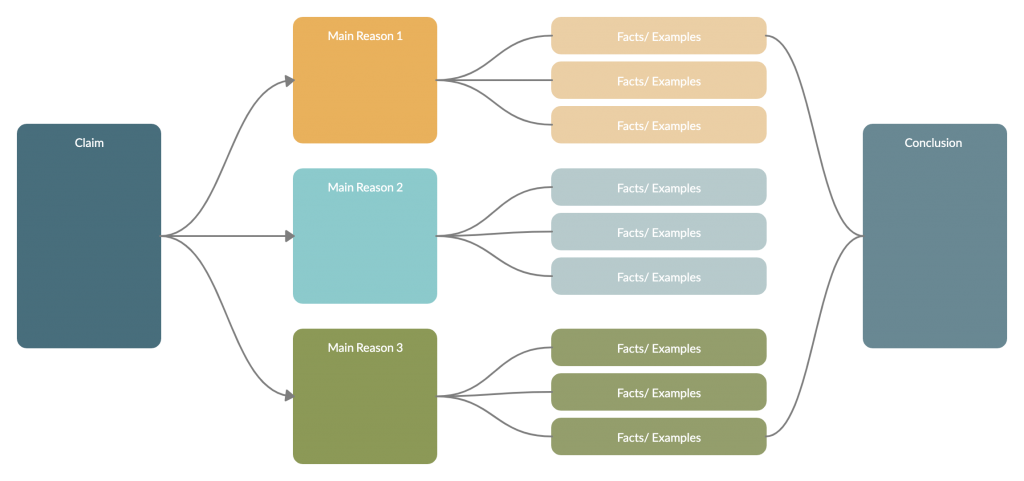
3. Persuasion map
The persuasion map is an interactive graphic organizer that helps students familiarize themselves with the process of persuasive writing . It assists them with outlining and preparing arguments for their essays, speeches, debates, etc.
How to use it
Step 1: Choose a topic of interest for your essay/debate. Do proper research around it to collect enough information.
Step 2: Define the claim that you want to make with your essay. Persuasive writing by writing this down first.
Step 3: Next to it, write down the reasons for making that claim.
Step 4: Then write down facts, examples, and information to back up your reasoning.
Step 5: End your persuasion map with the conclusion of your essay.
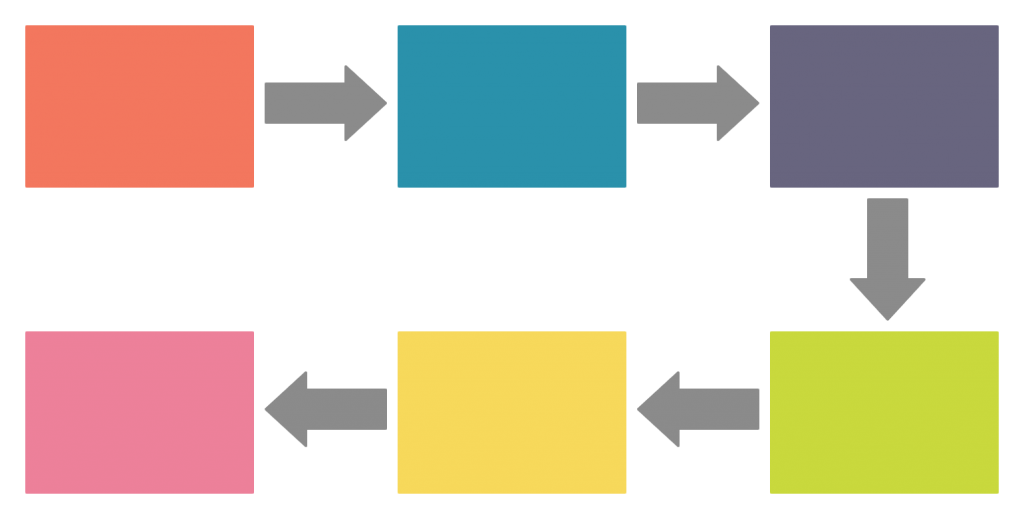
4. Sequence Chart
A sequence graphic organizer is a tool that helps visualize the order of steps of a process or a timeline of events, etc. It can also be used for note-taking, lesson planning, and essay writing.
How to use it
Step 1: Identify the steps in the process or event.
Step 2: Using a sequence chart arrange these steps in sequential order.
Template
Graphic Organizers for Reading
Graphic organizers for reading are a type of graphic organizers that help students understand and analyze texts more effectively. Reading graphic organizer provides visual ways to organize information from a reading passage, making it easier to grasp key ideas and details. Graphic orgnizer for reading provides visual structures to help students break down information, see relationships, and remember key ideas, ultimately enhancing their reading comprehension.
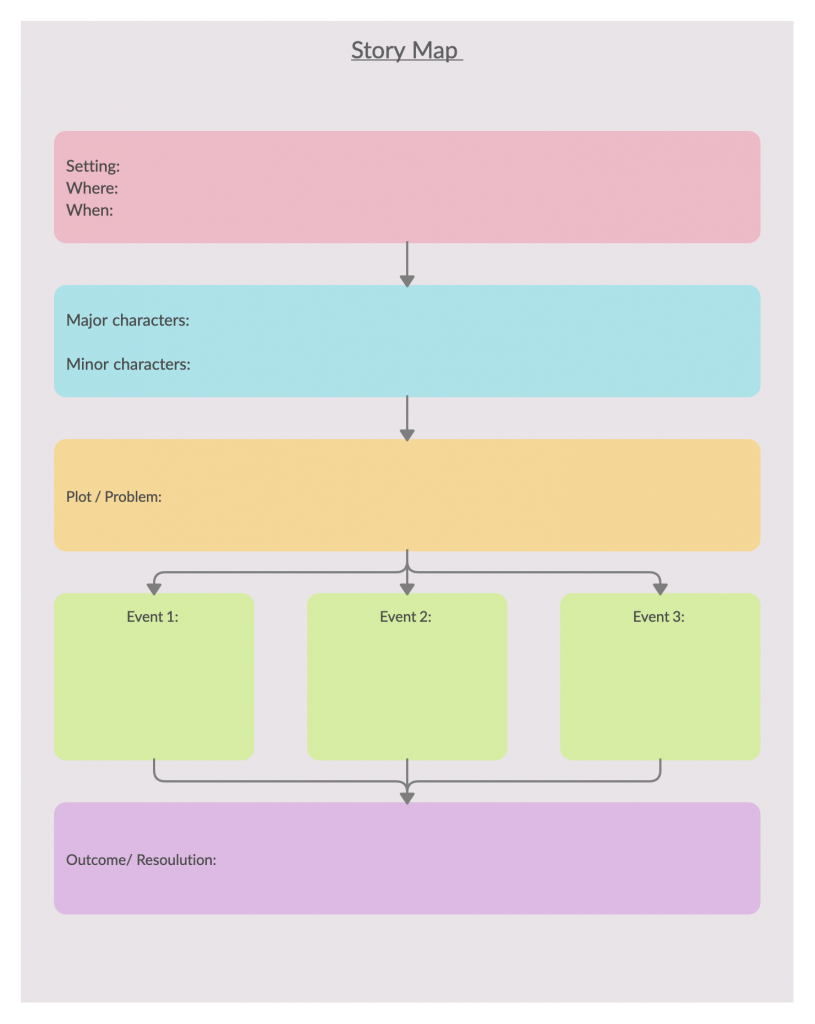
5. Story map
A story map can be used to identify the different elements such as characters, character plots, themes, techniques, etc. in a book students are reading. It’s a useful graphic organizer that teachers can integrate into the lesson to improve students’ comprehension.Teachers can use Storyboard maker to create appealing story maps.
How to use it
Step 1: Read the book and understand it well.
Step 2: Discuss the different significant elements that were involved in the story. These could be the characters, setting, problem and solution, etc. You can fill the story map during the discussion.
Step 3: Once the map is complete you can discuss each element individually.
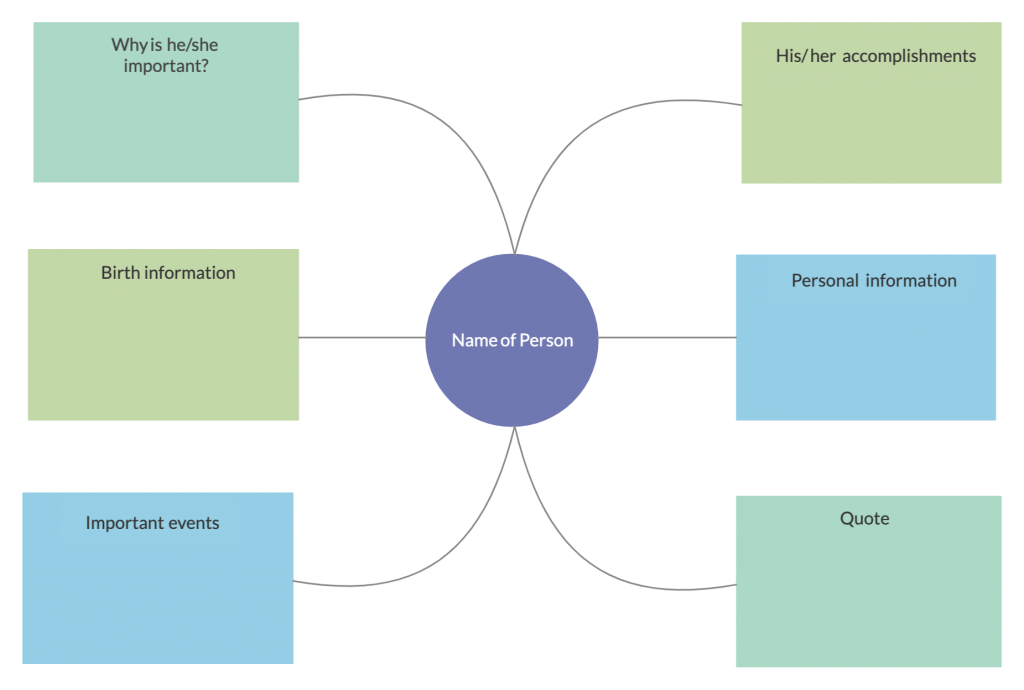
6. Biography graphic organizer
This is a tool that assists with understanding a character from a novel, autobiography or movie or a historical figure more in-depth. It brings attention to various important factors about a person’s life.
How to create it
Step 1: Gather as much information you can about the character you are studying. You can also refer to online resources, or ask from teachers or experts.
Step 2: As you analyze the information you have gathered, isolate the facts that stand out or you think are important.
Step 3: Use your biography graphic organizer to lay out the information in a presentable way. You can add images to make it more comprehensible as well.
7. KWL chart
KWL chart is used for gathering information from student’s prior knowledge or experience. This 3 column chart captures the before (what the reader already knows), during (what the reader wants to learn) and after (what the reader learned) stages of reading. Using KWL templates , students can easily create KWL charts.
How to use it
Step 1: Get students to brainstorm around the selected topic and write down everything they know about it in the K column.
Step 2: Ask them to generate a list of questions about what they want to know in the W column of the chart.
Step 3: During or after reading the book/ lesson get them to answer these questions in the L column.

Graphic Organizers for Teaching
Graphic organizers for teaching are a type of graphic organizers that help educators plan and present lessons more effectively. Teaching graphic organizer provides a structured way to organize information, making it easier for teachers to convey concepts clearly and for students to understand and engage with the material.
8. Learning map
Learning maps visually depict the key takeaways – skills, ideas, knowledge – students should get from a lesson. It usually provides a high-level view of the lesson/ unit/ course that is to be studied and the connection between its different components. Students can also use learning map template in the classroom for note-taking.
How to use it
Step 1: At the center of the map, write down the topic (i.e. name of the lesson or unit)
Step 2: Brainstorm ideas and information related to it. Write these down on branches emerging from the center. Make sure that you place them in a way that makes sense to teach or in a logical sequence around the center.
Step 3: Add connectors between these elements and add labels to highlight the kind of relationship between them.
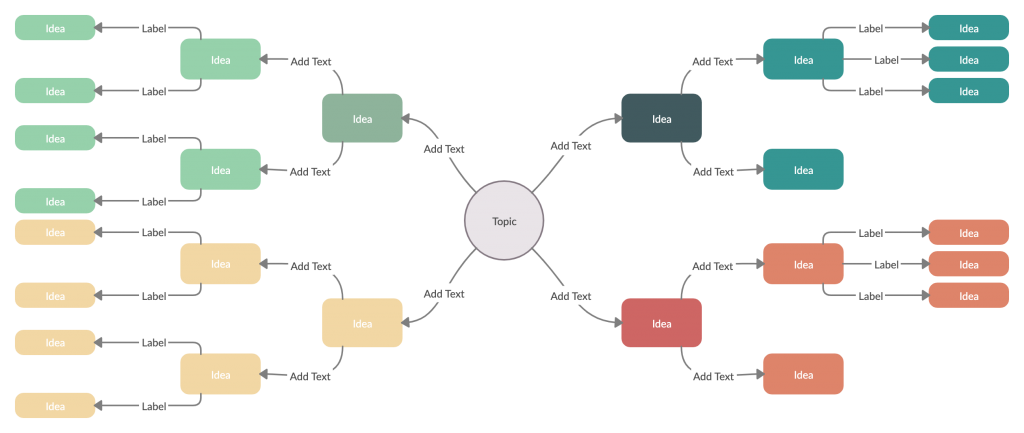
9. Analogy graphic organizer
The analogy graphic organizer uses analogy to help students identify similarities and differences between a new topic and a topic that they are already familiar with.
How to use it
Step 1: Select a topic/ concept that the students already know and is analogous in certain aspects to the new topic
Step 2: Introduce the new concept and get the students to read and discuss it
Step 3: Using an analogy graphic organizer, ask the students to brainstorm and write similarities and differences between the two topics.
Step 4: Based on the completed graphic organizer, ask the students to write a brief description of the new topic

Analogy Graphic Organizer (Click on the template to edit it online)
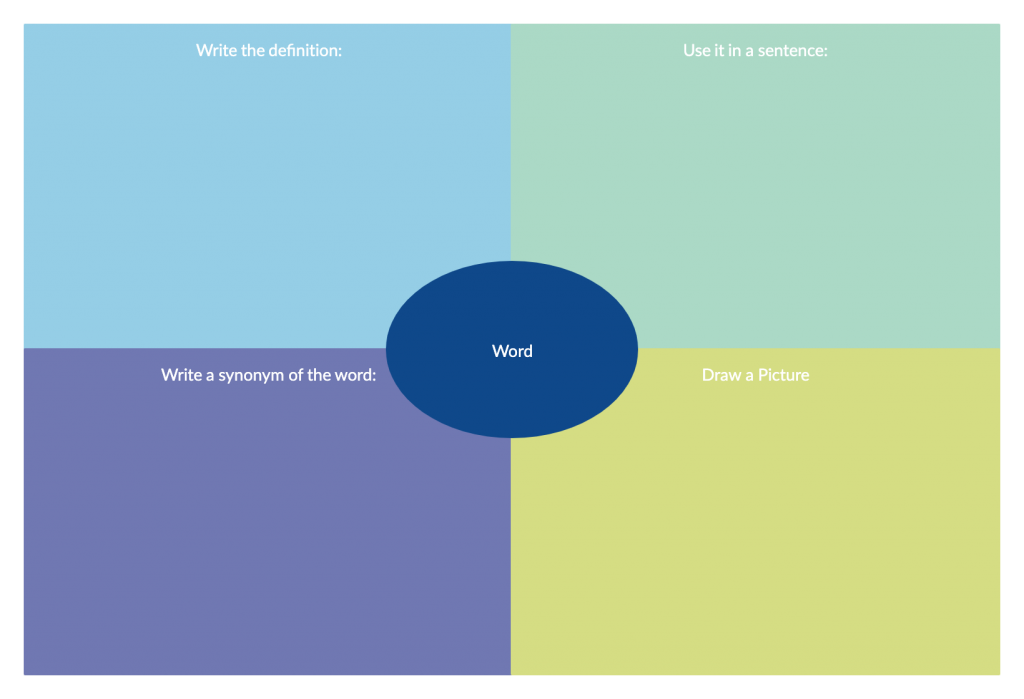
10. Vocabulary graphic organizer
This tool can be used to assess the vocabulary knowledge of students. You can create graphic organizers including various elements to help students learn new words, and learn antonyms and synonyms.
How to use it
Step 1: Write the new vocabulary word at the top of the template. This is the focus of your study
Step 2: Ask students to write down the definition of the Vocabulary in the Definition box
Step 3: List synonyms (words with similar meanings) of the word. This helps you see the word in relation to others
Step 4: Group the students and ask them to use the vocabulary in new sentences
Step 5: Ask students to draw or find an image or symbol that represents the word
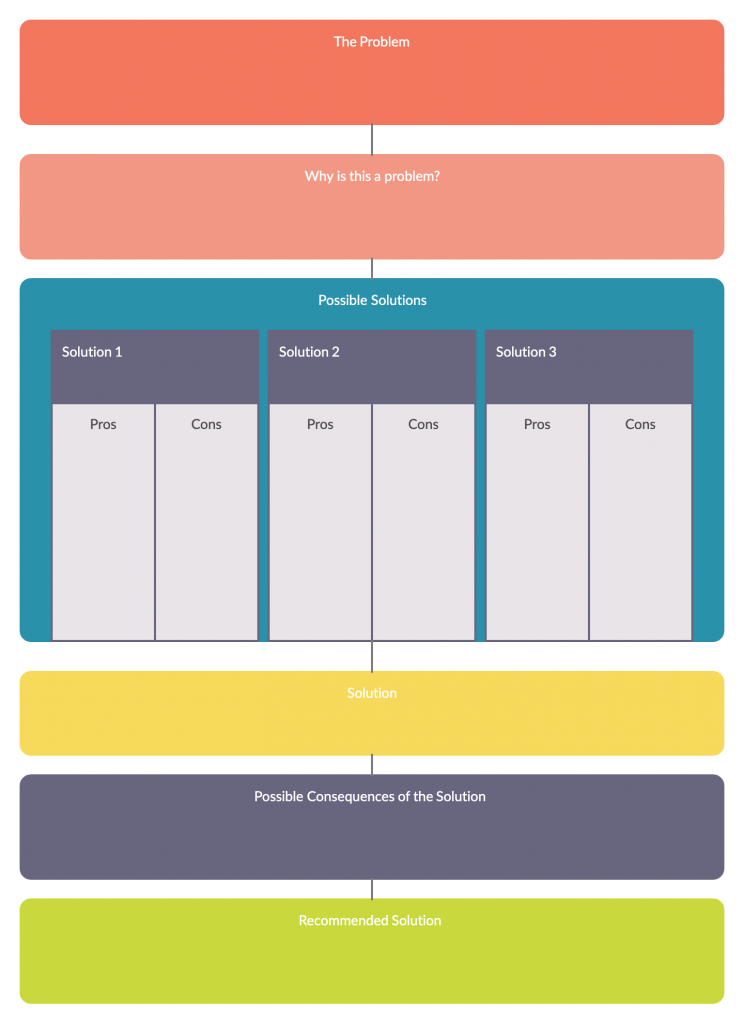
11. Problem-solving organizer
Problem-solving graphic organizers can be used to improve the problem-solving skills of the students. It helps students identify and evaluate solutions to problems.
How to use it
Step 1: Identify the problem and write it in the problem box
Step 2: Ask students to then write down why they think it is a problem in the first place
Step 3: Get them to brainstorm all possible solutions along with the pros and cons relates to them.
Step 4: Once they select the best possible solution, ask them to list down all its possible consequences
Step 5: Students can then make suggestions to improve the selected solution further
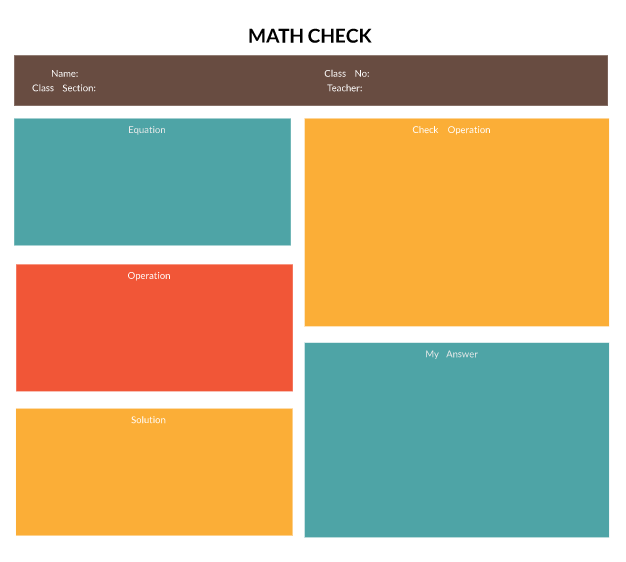
12. Math Graphic Organizer
Math graphic organizers are used to describe math concepts graphically to students. It helps with simplifying and solving complex math problems.
How to use it
Step 1: Select the math problem you want to identify and a relevant math graphic organizer that you can use to solve it.
Step 2: Invite your students or colleagues to collaborate as you wish.
Graphic Organizers for Learning
Graphic organizers for learning are a type of graphic organizers that help students understand, organize, and remember information more effectively. Learning graphic organizer helps break down complex material into manageable parts, illustrate relationships between ideas, and enhance memory retention. By using these tools, students can improve their comprehension, organize their thoughts, and engage more effectively with their learning material.
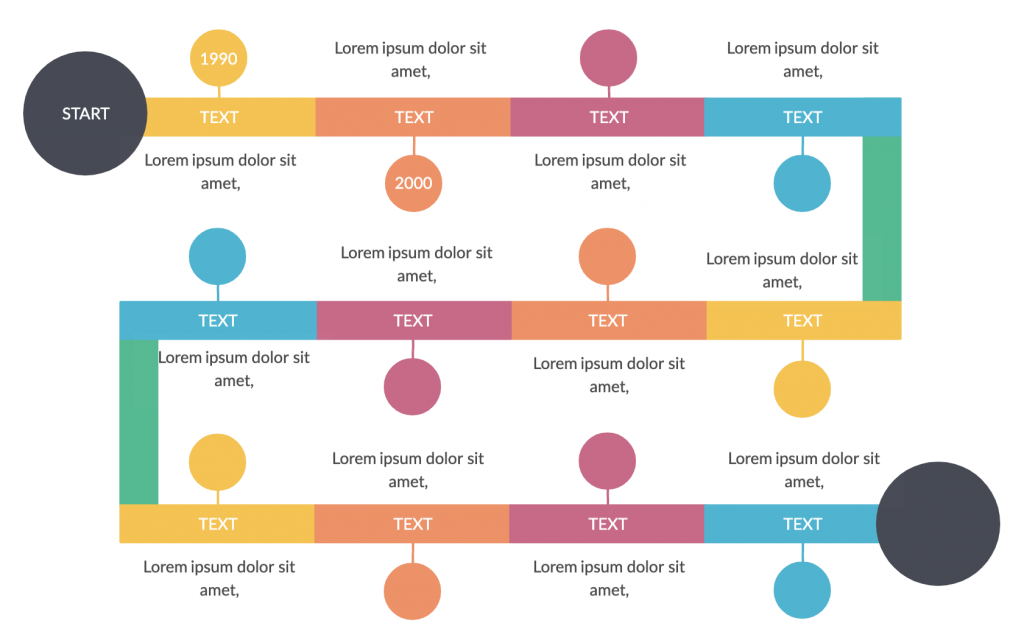
13. Timeline graphic organizer
Timeline diagrams are a type of graphic organizer that shows a sequence of events in chronological order.
They come in handy when studying history as you can use it to display major historical events that occurred during a period of time along with important details such as dates and locations in which they took place. Timeline maker helps to create historical event timleine graphic organizer easily.
In addition, timeline charts can also be used to show the progress of something (i.e. growth of a business) or changes.
How to use it
Step 1: Identify the different events and the sequence of order in which they took place.
Step 2: Use a research on your target audience to arrange them chronologically
Step 3: Include significant details such as dates, locations and other additional information as needed.
14. T chart
T charts allow students to study two facets of a topic. For example, disadvantages and advantages, pros and cons, differences and similarities, etc.
How to use it
Step 1: Draw a T chart using a T chart maker and write down the two areas you want to brainstorm around on each column head.
Step 2: Write down facts on each column as you carry out your brainstorming.

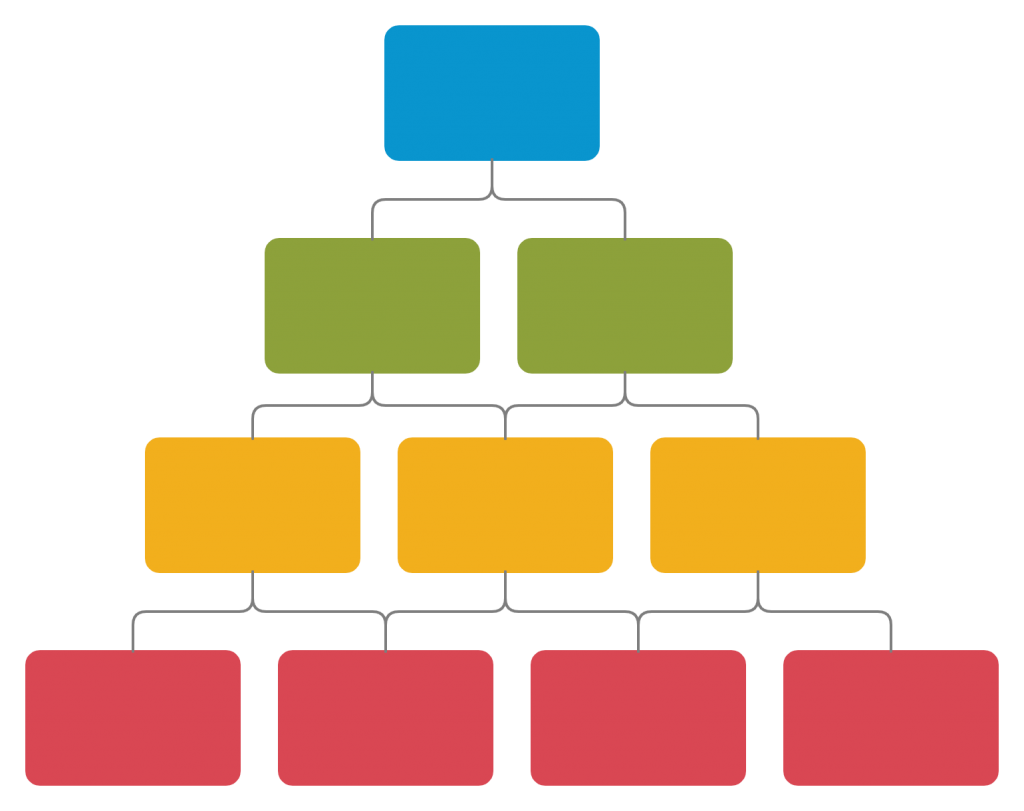
15. Hierarchy chart graphic organizer
Hierarchy charts visualize the elements of a system, organization or concept from its highest position to the lowest. Students can use this tool to understand the superordinate and subordinate categories of a topic and the relationship between them.
How to use it
Step 1: Identify the most important element under the topic you are studying. Write this down at the top of the hierarchy chart.
Step 2: List down the second layer of sub-elements stemming from the first component you have identified. Add a third and fourth as necessary.
Step 3: Connect these with lines to show how they are connected to each other.
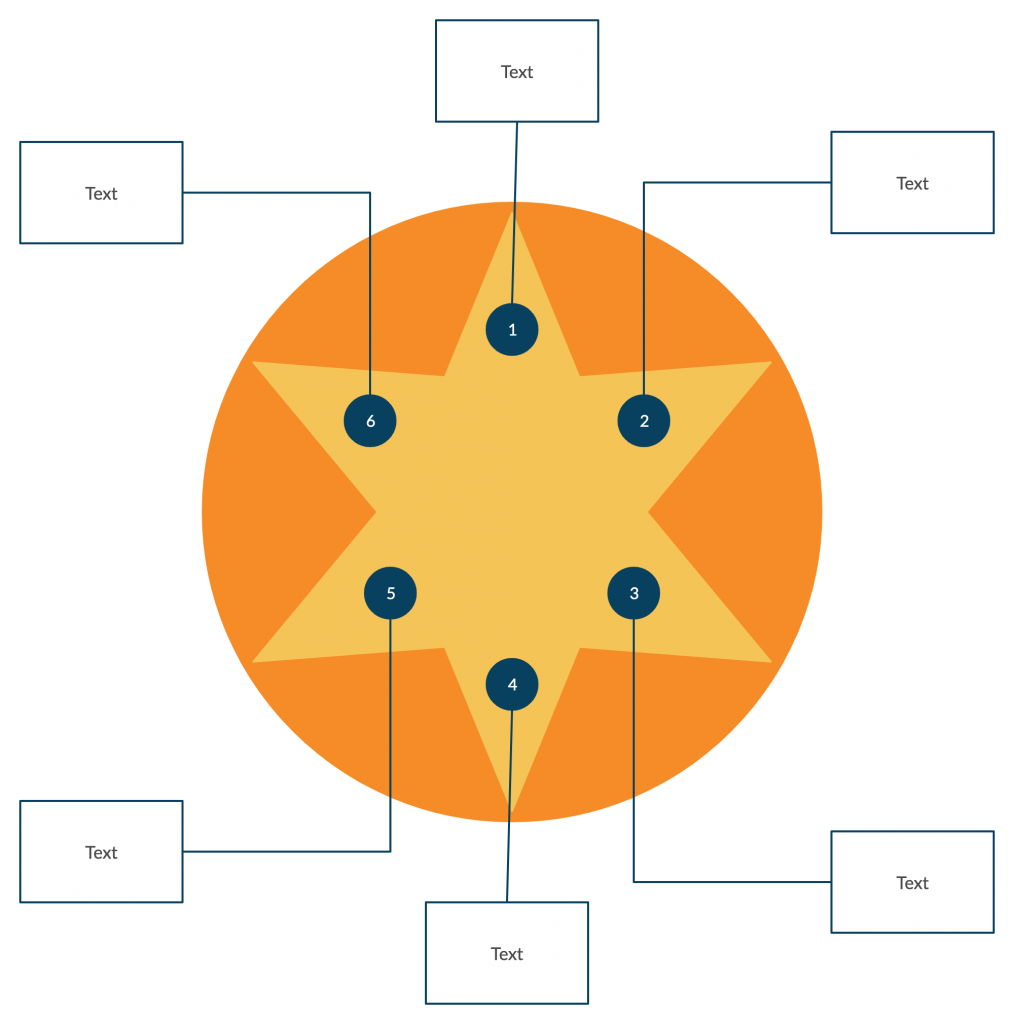
16. Star diagram graphic organizer
Star diagrams are used to organize the characteristics of a chosen topic. It can also be used to brainstorm around new topics.
How to use it
Step 1: Select the topic you want to study and write it down in the center of the star diagram template.
Step 2: Write down the characteristics or attributes related to the central topics on each point of the star. Adjust the points of the star depending on how many traits you write down.
Graphic Organizers for Brainstorming
Graphic organizers for brainstorming are a type of graphic organizers that help students and teams generate, organize, and explore ideas. They help individuals and teams generate and organize ideas more effectively. Brainstorming graphic organizers provide a clear visual structure for exploring various aspects of a topic, making it easier to capture and evaluate creative thoughts. By using these tools, users can improve creativity, streamline idea generation, and better organize their brainstorming sessions.
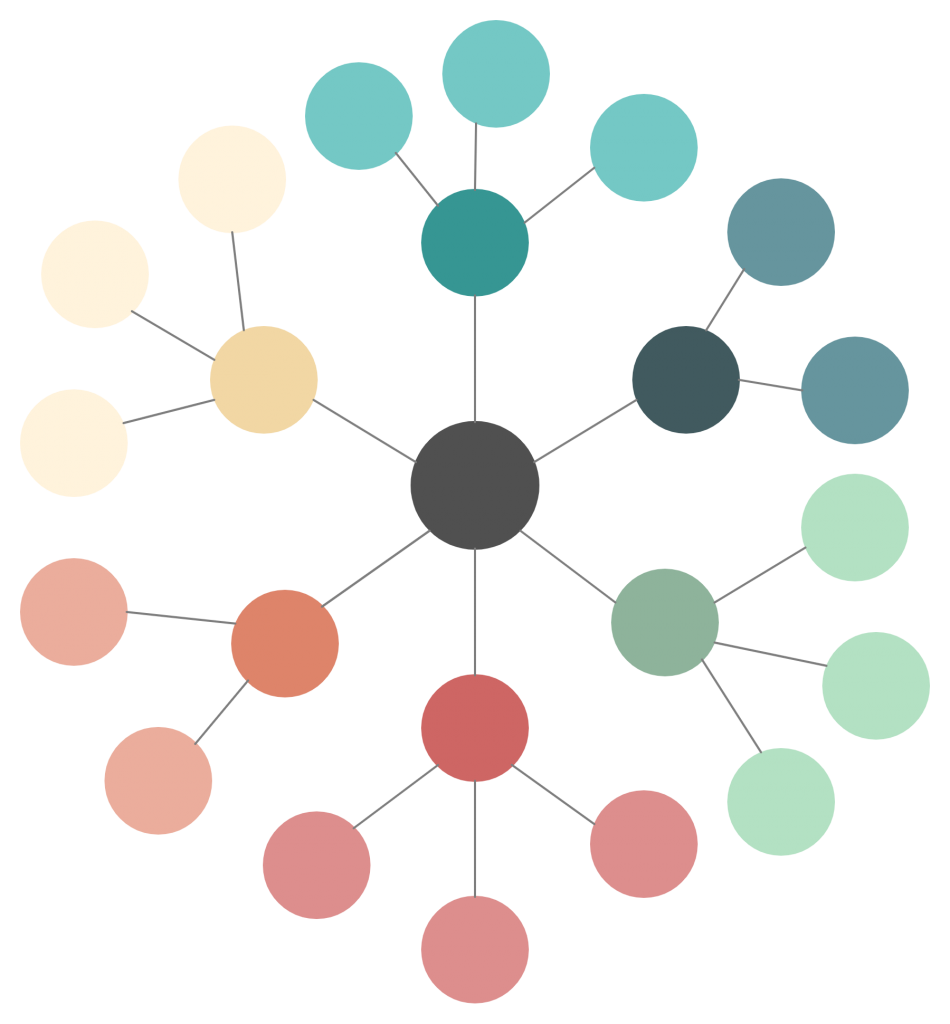
17. Cluster diagram
Cluster diagrams can be used to facilitate a brainstorming session or structure idea generation and even to help with exploring new topics.
How to use it
Step 1: Pick your topic of interest to explore. This should be placed in the middle of the diagram.
Step 2: Brainstorm around this main idea and come up with sub-topics related to it. Place them around the center.
Step 3: Brainstorm around each of the sub-topics and write down related ideas around them.
Step 4: Add as many layers as you want. However, use color-coding to emphasize each branch of thought. This will make it easier for you to read and understand the cluster diagram.
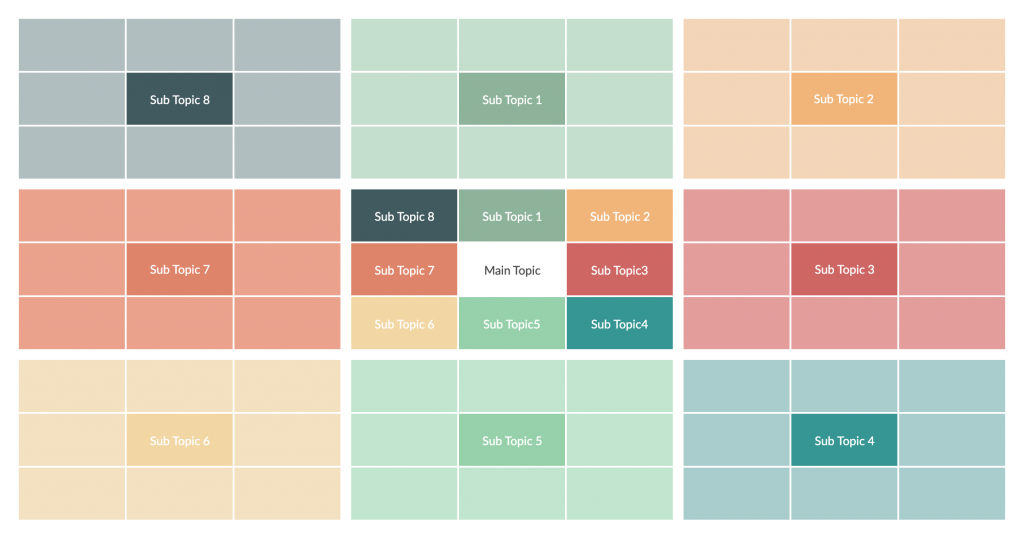
18. Lotus diagram
Lotus diagram is an analytical tool that can be used to breakdown broader and more complex topics into smaller components for easy understanding. It can be used for brainstorming and studying new topics.
How to use it
Step 1: Draw a 3×3 grid in the center. On the square in the center, write down the main topic to be explored.
Step 2: Write down the related sub-topics around it as you brainstorm.
Step 3: Draw 8 more 3×3 grids around the one in the center. Each of these can be used to write down facts that you brainstorm around each subtopic.
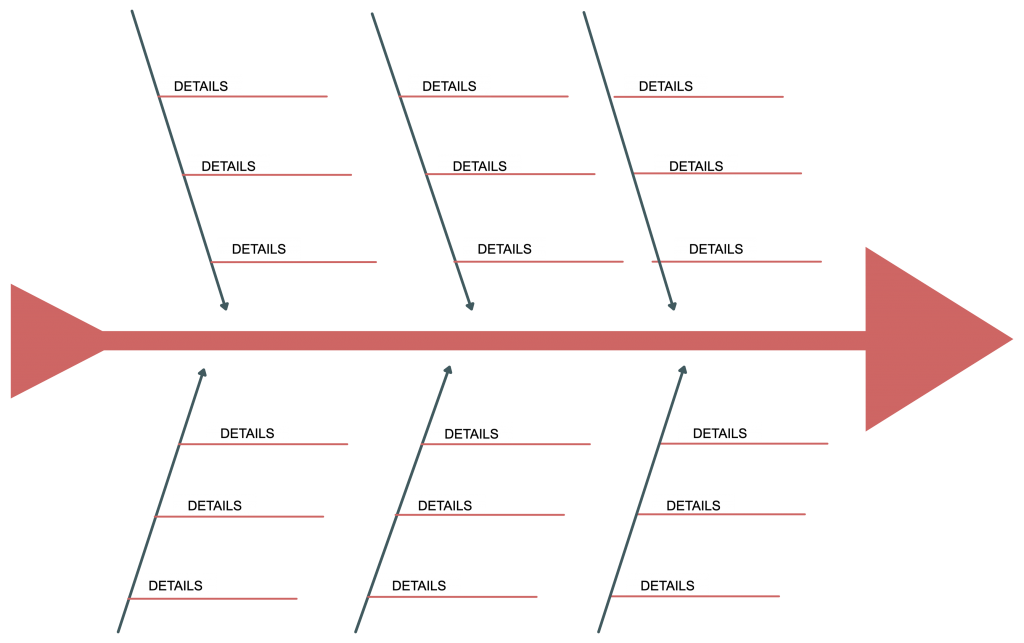
19. Cause and effect graphic organizer
This type of graphic organizer shows the causes and effects of an event. The cause is the reason why something has happened, and effect is the result of what has happened. Visualization helps clearly understand the different cause and effect relationships.
How to use it
Using a cause and effect graphic organizer, identify the causes and effects related to the problem you are studying or writing about. There could be several models of cause and effect events, such as one cause leading to one effect or multiple effects, or multiple causes leading to one effect or multiple effects.
- One cause leading to several effects
- Several causes leading to one effect (You can use a fishbone diagram templates here)
- Each cause having one related effect
- One cause triggering another cause that leads to another
20. Mind map
A mind map is a tool that helps capture the free flow of thought and is widely used for brainstorming around topics. Additionally, it can also be used to organize and group information about a topic.
How to use it
Step 1: Write down the topic you are brainstorming around in the center.
Step 2: On branches emerging from the middle, write down brainstormed ideas/ thoughts.
Step 3: Expand each sub idea with more facts. You can keep on adding more information to your mind map until you have enough.
How to Visualize a Graphic Organizer
To visualize a graphic organizer, follow these easy simple steps. You can use Creately to simplify the process of visualizing a graphic organizer.
1. Decide what you need
Start by determining the purpose of your graphic organizer. Are you organizing ideas for a project, comparing concepts, or planning a story? Understanding what you need will guide the design of your organizer. Decide what information or ideas you need to include. This might involve brainstorming or gathering data from your notes or research to ensure you cover all necessary points.
Use Creately’s graphic organizer maker , templates and brainstorming tools to identify and outline your needs. Explore different graphic organizer templates available in Creately to determine which fits your purpose, whether it’s for organizing ideas, comparing concepts, or planning projects.
2. Pick a type
Choose a graphic organizer type that best suits your purpose. For example:
- Mind maps are great for brainstorming and showing connections between ideas.
- Venn diagrams are useful for comparing and contrasting two or more items.
- Flowcharts help illustrate processes or sequences of steps. Think about who will use the graphic organizer. Choose a type that will be easy for them to understand and interact with. Creately offers a wide range of graphic organizer templates, such as mind maps, Venn diagrams, flowcharts, and T-charts. Choose a template that suits your purpose from its collection.
3. Start with the main idea
Begin by placing the main idea or central topic in a prominent position, such as the center of a mind map or the top of a flowchart. This will be the focal point of your organizer. Use Creately’s formatting tools to make the main idea stand out with colors, fonts, or different shapes. This ensures that it is immediately noticeable and serves as the anchor for other information.
4. Add details
Include supporting information: Add related ideas, details, or subtopics around the main idea. For a mind map, these will branch out from the central topic. In a Venn diagram, they will be placed in the appropriate circles.
Use connections: Draw lines or arrows to connect related details. This helps to show how different pieces of information are linked to each other and to the main idea.
Be clear and concise: Use brief phrases or keywords rather than long sentences to keep the organizer easy to read and understand.
5. Organize and arrange
Arrange logically: Position the elements in a logical order. For instance, in a flowchart, arrange steps sequentially. In a mind map, place related ideas close to each other.
Ensure clarity: Make sure the connections between elements are clear and not overlapping. Arrange the elements in a way that avoids clutter and makes the organizer easy to follow.
Use visual aids: Incorporate colors, shapes, or symbols to differentiate between types of information or to highlight important points.
6. Review and adjust
Check for completeness: Review the organizer to ensure that it includes all relevant information and that nothing important is missing.
Simplify if needed: If the organizer looks too crowded or confusing, simplify by removing unnecessary details or reorganizing elements.
Seek feedback: If possible, ask someone else to review the graphic organizer. They can provide insights on clarity and suggest improvements. Creately allows for real-time collaboration and feedback, making it easy to review and adjust your graphic organizer. You can also use version history to track changes.
Limitations of Graphic Organizer
While graphic organizers are valuable for organizing and understanding information, they have limitations. It’s important to use them thoughtfully and consider other methods when needed.
1. Oversimplification
Graphic organizers can sometimes oversimplify complex information. By breaking down ideas into visual formats, they might leave out important details or nuances, which can lead to incomplete understanding.
2. Limited scope
They often focus on specific aspects of information and might not capture the full scope of a topic. This can limit their effectiveness if you need a more comprehensive view or in-depth analysis.
3. Reliance on visuals
Graphic organizers rely heavily on visual representation, which might not suit all learners. Some people may find it challenging to translate visual information into a coherent understanding or prefer different methods of organization.
4. Time-consuming
Creating and filling out graphic organizers can be time-consuming, especially if they are complex. This can be a drawback if time is limited or if a simpler approach would be more efficient.
5. May not fit all subjects
Not all subjects or topics are well-suited for graphic organizers. Some areas of study may require different methods or tools to effectively convey information and facilitate learning.
6. Potential for confusion
If not designed clearly, graphic organizers can become cluttered or confusing, which may hinder rather than help the learning process. It’s important to ensure that the organizer is well-structured and easy to understand.
Add to Our List of Graphic Organizers for Teachers and Students
Although we have covered 20 types of graphic organizers in this post, there are plenty more that can be useful to our users. Know more? Mention in the comments section below to keep expanding the list of ultimate graphic organizers.
FAQs About list of Graphic Organizer
What are the 6 types of graphic organizers?
Graphic organizers are designed to help with various tasks, from comparing and contrasting to planning writing and enhancing learning. Each organizer offers a visual method for structuring and understanding information effectively. Here are the 6 types of graphic organizers;
- Graphic organizers for compare and contrast
- Graphic organizers for writing
- Graphic organizers for reading
- Graphic organizers for teaching
- Graphic organizers for learning
- Graphic organizers for brainstorming
What is the easiest graphic organizer?
What is a 5 W’s graphic organizer?
How to select the right graphic organizer for a specific project?
When selecting a graphic organizer for a specific project, you should consider the type of information you need to organize and the purpose of the project. Here are some tips on how to select the right graphic organizer:
Identify the type of information: Before selecting a graphic organizer, consider the type of information you need to organize.
Determine the purpose of the project: Consider the purpose of the project and what you want to achieve.
Consider the audience: Think about who the audience is for the project. If the audience is young children, a simpler graphic organizer like a picture web might be more appropriate. If the audience is adults, a more complex graphic organizer like a timeline or a chart could be suitable.
Evaluate the effectiveness of different graphic organizers: Try out different graphic organizers and see which ones work best for you. Creately has different graphic organizer editable templates that you could use to create your graphic organizer based on the purpose.
Be creative: Don’t be afraid to create your own graphic organizer or adapt an existing one to meet your needs. Graphic organizers are flexible tools that can be customized to fit different projects and purposes.
What are the common mistakes to avoid when creating a graphic organizer?
Avoid these common mistakes that you make to ensure that your organizer is effective in conveying information.
Avoid overcomplicating the design of your graphic organizer: It should be easy to read and understand, therefore avoid using too many colors, fonts, or shapes which make the organizer confusing and difficult to read.
Consistency is important in creating a graphic organizer. Use the same formatting, color scheme, and font throughout the organizer to ensure that it is easy to follow and understand.
The purpose of a graphic organizer is to simplify and organize information. Including too much information can defeat the purpose and make the organizer overwhelming. Stick to the most important information and use the organizer to highlight key concepts and relationships.
Use clear and appropriate labels for each section of the organizer. Avoid using labels that are too vague or unclear, as this can cause confusion and make it difficult to understand the relationships between the different elements.
Consider who the audience is for the graphic organizer and use appropriate language and images. Avoid using jargon or technical terms that may not be familiar to the audience.
Test your graphic organizer to ensure that it effectively conveys the intended information. Ask for feedback from others and make revisions as needed.