Bringing a product to life—from idea to launch and beyond—is no small task. That’s where product management comes in. It’s the structured process that helps businesses create, improve, and sustain products that meet customer needs while driving growth.
In this guide, we’ll break down the product management process, making it easy to understand and apply. Whether you’re a startup founder, product manager, or business leader, you’ll get clear steps, practical tips, and ready-to-use templates to guide you through each stage.
By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp of how to turn an idea into a successful product—without the confusion or overwhelm.
What Is the Product Management Process
The product management process is the structured approach businesses use to develop, launch, and refine products that solve real problems. It ensures that every product decision—from the initial idea to continuous improvements—is backed by research, strategy, and customer needs.
A strong product management process helps teams stay focused, make informed choices, and bring valuable products to market efficiently. It bridges the gap between business goals, customer expectations, and technical feasibility, ensuring a smooth journey from concept to success.
In the next sections, we’ll break down the process step by step, with templates to help you apply it effectively.
Product Management Process: 7 Stages Explained
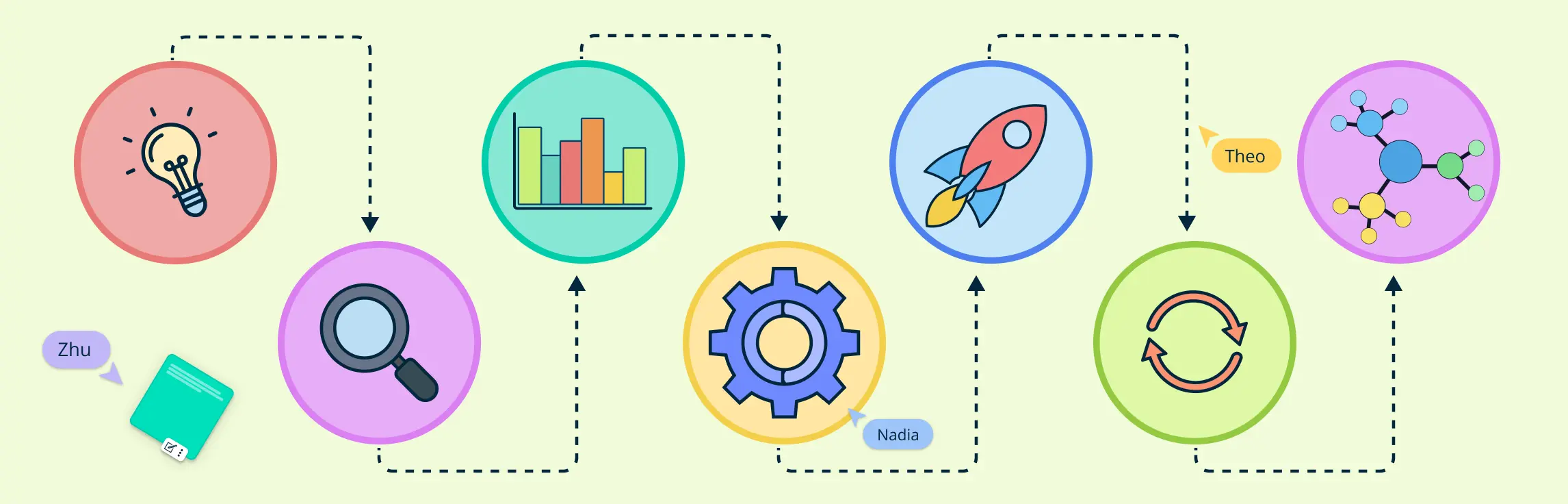
The product management process is a structured approach that guides a product from its initial concept to its launch and beyond. While the specific steps can vary across different organizations, a commonly accepted framework includes the following seven product management stages:
- Step 1: Identifying the problem
- Step 2: Defining the vision
- Step 3: Translating ideas into technical specifications
- Step 4: Developing a product roadmap
- Step 5: Prioritizing Features and Initiatives
- Step 6: Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
- Step 7: Launching and Continuous Improvement
Step 1: Identifying the problem
Before you start building a product, you need to clearly understand the problem you’re trying to solve. If you skip this step or misunderstand the problem, you risk creating something that no one needs or cares about.
Listen to your customers
The most reliable way to identify a problem is by talking to your customers. They’re the ones who experience the customer pain points, so their insights are invaluable. Use methods like customer surveys, interviews, and focus groups to learn about the challenges they face. Pay attention to common themes in their feedback.
Analyze customer complaints and support tickets
If you already have a product or service, your customer support team can be a goldmine of information. Look through past support tickets, chat logs, and social media comments. What issues do customers mention most often? What problems seem to frustrate them the most? This can point you toward areas where your product might fall short or where there’s a clear unmet need.
Study competitors and market gaps
Look at what your competitors are offering. Are there areas where they’re missing the mark or opportunities to improve their solutions? Competitive analysis can help you identify weaknesses or gaps in the market that your product can address.
Pay attention to industry trends
Sometimes, the problems people face aren’t always obvious—they’re influenced by broader shifts in technology, behavior, or the economy. Stay up to date with industry trends, news, and emerging technologies. Often, new problems arise as industries evolve, and spotting these early on gives you a competitive edge.
Understand the root cause of the problem
Don’t just look at surface-level symptoms. To create a truly impactful product, you need to dig deeper and understand the root cause of the problem. For example, if people are struggling with managing time, the real issue might be a lack of organization or inefficient tools. Identifying the root cause helps you offer a more effective solution.
Ideation: generating and refining ideas
Before finalizing your product vision, you need to explore different solutions through ideation. This stage involves brainstorming, validating concepts, and refining ideas to ensure you develop the best possible product.
- Brainstorming solutions – Gather your team and generate multiple ideas on how to solve the identified problem. Use methods like mind mapping, design thinking workshops, or collaborative whiteboarding to encourage creativity.
- Validating ideas – Not every idea will be practical or marketable. Conduct quick validations through surveys, interviews, or prototype testing to understand which concepts have real potential.
- Using structured frameworks – Tools like the Business Model Canvas or Value Proposition Canvas help refine ideas into viable product strategies.
- Collaborating with stakeholders – Engage product managers, designers, engineers, and even customers to gain diverse perspectives before moving forward.
Step 2: Defining the vision
Once you’ve identified the problem you’re solving, it’s time to define what your product will do and why it matters. This is where you craft a clear and compelling vision for your product. A well-defined vision will serve as your guiding light throughout the development process, keeping your team focused and aligned.
Describe the product’s mission
Start by clearly articulating the mission of your product. What change will it bring to users’ lives? For example, if you’re building a task management app, your mission might be to help people get organized and increase productivity. Be specific about what your product will help customers achieve.
Identify the core value proposition
What makes your product stand out? Your value proposition answers the question, “Why should customers choose your product over others?” Think about the unique benefits your product provides. Does it save time, reduce costs, improve efficiency, or enhance the user experience? This is the reason your product will attract and retain users.
Set measurable goals
A vision without measurable goals is just a dream. Define how you’ll measure success—whether it’s user adoption, revenue growth, customer satisfaction, or market share. Setting goals helps you track progress and keeps the team motivated as you work toward achieving them.
Ensure alignment with business strategy
Your product vision should be in line with your company’s overall mission and goals. Ask yourself: How does this product fit into the broader business objectives? Is it aimed at expanding your customer base, driving revenue, or improving customer retention? Ensuring alignment with your company’s strategy helps prioritize resources and keeps the team on the same page.
Keep it inspiring and clear
Your product vision should not only make sense to your team, but it should also inspire them. A clear and compelling vision motivates everyone involved, from developers to marketers. It should be easy to communicate to anyone, whether they’re part of the product team or an external stakeholder. If people are excited about your product’s vision, they’re more likely to be invested in its success.
Step 3: Translating ideas into technical specifications
Once you’ve identified the problem you’re solving and brainstormed potential solutions, it’s time to turn those ideas into actionable plans. This involves translating the insights gathered during market research and product discovery into technical specifications that guide the development process. This step ensures that everyone involved in the product development process is on the same page and that the product’s functionality is clear.
Work with cross-functional teams
At this stage, the product manager, along with the product owner, project manager, or Scrum master (who may be the same person in smaller teams), work together to define the technical specifications. This is done through collaboration with the development team to create a list of requirements. These requirements are then transformed into user stories, which are concise descriptions of product features from the perspective of the end user. User stories help ensure that each feature meets a specific user need and aligns with the product vision.
Close collaboration with the UX team
User experience (UX) is a critical aspect of the product management process. During this step, close cooperation with the UX team is essential. The UX team will design UI mockups and wireframes, providing a visual representation of how the product will look and function. These early prototypes offer a way to test different ideas and help determine the feasibility and value of potential solutions before moving into development.
Define product requirements
This stage also involves defining and refining product requirements. Product specifications should be short, clear, and focused on answering the following key questions:
- What are we building, and why? It’s important to explain the core problem the product is solving and the specific solution it provides.
- What should this product achieve? Define the desired outcome or impact for users and the business.
- How do we measure success? Establish metrics that will help you track the product’s performance, such as user adoption, customer satisfaction, or revenue growth.
These specifications give the team a shared understanding of what needs to be built, why it matters, and how success will be measured.
Step 4: Developing a product roadmap
Now that you’ve identified the problem, defined the vision, and tested potential solutions, it’s time to create a product roadmap. This step is where you outline the path forward, detailing how your product will evolve over time. A well-developed roadmap helps you plan, prioritize, and communicate your product’s journey to your team, stakeholders, and customers.
Set clear goals and milestones
Before creating your product roadmap, define clear and measurable goals for your product. These should be aligned with your product vision and business strategy. For example, your goals might include increasing user adoption, launching new features, or hitting revenue targets. Once your goals are set, break them down into smaller milestones—specific achievements that mark progress along the way. These could include completing design phases, releasing new features, or reaching a set number of active users.
Prioritize features and tasks
Not all features or improvements are created equal. Some will have a bigger impact on your users and business goals than others. In this step, you’ll prioritize the features that will bring the most value. You can do this by using a framework like the MoSCoW method (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have) or RICE framework (Reach, Impact, Confidence, and Effort) to rank and assess each feature. This helps ensure that your team focuses on what matters most.
Organize the roadmap into timeframes
Once you’ve prioritized features, you’ll need to assign them to specific timeframes. Typically, roadmaps are divided into short-term, medium-term, and long-term phases. The short-term phase might focus on launching an MVP or completing the first few features, while the long-term phase might include more advanced features or growth objectives. Be realistic about the time it will take to complete each task—underpromise and overdeliver to keep things on track.
Align with stakeholders
A product roadmap is not just for the product team. It’s a tool for all stakeholders, including marketing, sales, and leadership. Make sure you regularly align with these groups to get their input on priorities, timelines, and any potential roadblocks. Having everyone involved ensures that the roadmap reflects company-wide objectives and helps avoid any surprises later on. Regularly communicate updates to stakeholders to keep them informed about the product’s progress.
Stay flexible and adjust as needed
A product roadmap is a living document—it’s not set in stone. While it’s important to have a plan, be prepared to make adjustments based on new information, market changes, or user feedback. Product development is rarely linear, and sometimes priorities shift. Your roadmap should be flexible enough to accommodate these changes without losing sight of your overall vision.
Step 5: Prioritizing Features and Initiatives
At this stage of the product management process, it’s time to figure out which features and initiatives to focus on first. With a long list of potential ideas, it’s crucial to prioritize what will have the biggest impact on your users and business goals. This step ensures that your team is working on the right things at the right time, making the best use of available resources.
Understand your users’ needs
Start by looking at your users—they are the key to understanding what features matter most. Based on feedback, user testing, and data, identify the pain points or needs that will have the biggest impact. Ask yourself: Which features will make users’ lives easier or more enjoyable? For example, if your users struggle with navigation in your app, improving the user interface (UI) should be a top priority.
Align with business goals
Prioritize features that support your business strategy. Are you focused on increasing user engagement? Driving revenue? Improving customer satisfaction? Make sure the features you prioritize align with your company’s broader objectives. This alignment ensures that every decision supports the overall success of the product and the company.
Use a prioritization framework
There are several frameworks you can use to rank features based on their value and impact. Some common frameworks include:
- RICE (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort): This method helps you score each feature based on how many people it will reach, how much impact it will have, how confident you are in your estimates, and the effort it will take to implement. The higher the score, the higher the priority.
- MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have): This method categorizes features into four groups based on their importance. “Must-have” features are essential, while “Could-have” features are less critical and can be deferred.
- Kano Model: The Kano model helps categorize features into basic needs, performance needs, and delightful features. Basic needs must be met, while delightful features can enhance user satisfaction but are not always essential.
By using one of these frameworks, you can evaluate the potential value of each feature and make data-driven decisions on where to invest your resources.
Consider technical constraints and resources
While it’s important to focus on user needs and business goals, you also need to take into account the technical feasibility and resource availability. Some features might be technically challenging or resource-intensive, which could delay the project. Be realistic about what can be delivered based on your team’s capabilities, budget, and timeline.
Factor in dependencies
Some features may depend on others to work, meaning one feature must be completed before another can be started. For example, a new payment gateway feature might need backend infrastructure to be set up first. Map out these dependencies and consider them when deciding which features to tackle first. It will help you avoid delays and ensure smooth development.
Communicate with stakeholders
Make sure to involve key stakeholders, such as your sales, marketing, and customer support teams, when prioritizing features. They can provide insights into what customers are asking for or what will drive the most value for the business. Regularly communicate your prioritization decisions to keep everyone aligned and set clear expectations for what’s coming next.
Stay flexible and adjust as needed
Feature prioritization is not a one-time task. As market conditions, user feedback, or business goals evolve, you may need to reassess and adjust your priorities. Keep your process flexible to ensure that you’re always working on the most valuable features and responding to changes in a timely manner.
Step 6: Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
At this point in the product management process, you’ve done the groundwork—defined your product vision, tested solutions, developed a roadmap, and prioritized features. Now, it’s time to bring your idea to life by creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). An MVP is a simplified version of your product that includes just enough features to solve the problem and test your assumptions with real users.
Focus on the core value proposition
The goal of an MVP is not to create a fully-featured product but to deliver the core value that your product promises. Start by identifying the most important feature(s) that solve the main problem for your users. For example, if you’re building a task management app, focus on basic features like task creation, due dates, and notifications. Everything else can be added later.
Keep it simple
When building an MVP, simplicity is key. Cut down on any non-essential features and focus only on what’s absolutely necessary to demonstrate your product’s core value. This doesn’t mean your product should be bare-bones or unusable, but rather that it should provide a streamlined user experience with the most important functions.
Develop iteratively
Building an MVP doesn’t mean you’re stuck with just one version. In fact, the best approach is to develop it in iterations. Start with a basic version, release it to users, gather feedback, and make adjustments. Repeat this process, improving the product over time based on real user insights. This iterative development helps you make smarter decisions and deliver a better product.
Test with real users
Once your MVP is ready, it’s time to put it in front of your users. Whether you choose a beta test, a soft launch, or a limited release, gathering feedback from real users is essential to understanding if your product solves the problem effectively. Pay attention to how users interact with the product, what features they use the most, and where they struggle.
Measure success and iterate
Your MVP should include key performance indicators (KPIs) that help you track whether it’s meeting your goals. These might include user engagement, retention rates, or conversion rates. Use this data to determine whether the MVP is hitting the mark or if adjustments are needed. Feedback is your best friend at this stage—keep listening to your users, making improvements, and refining your product.
Avoid overcomplicating things
It’s tempting to keep adding new features or over-designing the MVP, but remember: the goal is to test the core functionality. Resist the urge to go all-in at this stage. Focus on delivering a simple product that allows you to gather valuable insights. You can always add more features and polish later.
Step 7: Launching and Continuous Improvement
The final step in the product management process is the launch and the continuous journey of improvement that follows. By now, you’ve spent time building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), gathering feedback, and refining the product. But the work doesn’t stop once your product hits the market. In fact, launching is just the beginning of a long-term process where your focus shifts to monitoring performance, listening to users, and continuously enhancing the product.
Plan for a smooth launch
A successful launch requires careful planning. Make sure you have the necessary marketing, sales, and support systems in place. Create a go-to-market strategy that details how you’ll introduce the product to your target audience. This can include email campaigns, product demos, press releases, or social media announcements. Clear communication is key to ensuring your users know about the product and how to get started.
Monitor performance closely
Once the product is launched, it’s time to track how it’s performing. Use analytics tools to gather data on key metrics such as user engagement, retention, and conversion rates. These insights help you understand how well the product is meeting user needs and if there are any areas where it’s falling short. Pay attention to early user feedback and monitor customer support channels to spot issues quickly.
Gather feedback from users
Even after launch, your users remain the best source of insights. Continuously ask for feedback through surveys, user interviews, or by observing how users interact with your product. You can also look for patterns in user complaints or feature requests. This helps you identify areas for improvement, new features to add, or bugs to fix.
Prioritize improvements and new features
As you collect feedback, it’s important to decide which areas need attention first. Not all issues or feature requests are equally important. Use the same prioritization methods (like RICE or MoSCoW) that you applied earlier in the process to assess what to tackle next. You may find that some changes require urgent fixes, while others can wait until future updates.
Continuously iterate
Product development doesn’t end at launch. Based on the feedback and data, you should keep refining and enhancing your product. This means releasing updates, fixing bugs, adding new features, or improving user experience over time. The more you iterate, the better your product becomes, and the more you’ll keep your users happy and engaged.
Communicate updates to users
As you make improvements and launch new features, it’s essential to keep users informed. Make sure your users know when there’s a new update, a bug fix, or a new feature they can take advantage of. You can use in-app notifications, emails, or blog posts to communicate these updates. Transparency builds trust and keeps your users engaged.
Keep an eye on the competition
The market is always evolving, and so are your competitors. After launch, continue monitoring competitors’ products to stay ahead of the curve. This means understanding new trends, features they’re releasing, and shifts in user needs. By staying proactive and being aware of the competitive landscape, you can make better decisions for your product.
Product Management Process Challenges
Here are some common challenges in the product management process and ways to overcome them:
1. Aligning stakeholders
One of the biggest challenges in product management is aligning all stakeholders—whether it’s your marketing team, developers, or executives. Everyone has different goals and priorities, and it can be tough to ensure that everyone is on the same page.
Solution: Regular communication is key. Hold meetings or create clear, shared documents (like product roadmaps or vision statements) to ensure that everyone understands the same objectives and progress. It’s important to listen to different perspectives while keeping the overall product goals in mind.
2. Understanding customer needs
Customer needs are at the core of any successful product, but figuring out exactly what your customers want can be tricky. Without a deep understanding of their problems, desires, and behaviors, it’s easy to create a product that misses the mark.
Solution: Engage directly with your customers through surveys, interviews, or user testing. Use analytics tools to track how users are interacting with your product. The more insights you gather, the better you’ll be at identifying what your customers truly need. And you can use a customer profile to visualize the data.
3. Balancing features vs. time and resources
It’s common for product managers to face pressure to pack as many features into a product as possible. However, doing so without considering time, budget, or resources can lead to delays or a subpar product. Striking the right balance between a great product and the available resources can be difficult.
Solution: Prioritize the features that directly address customer pain points or business goals. Use frameworks like MoSCoW or RICE to evaluate and rank features based on their importance. Focus on building a solid MVP that can be refined over time, based on feedback.
4. Managing product roadmap changes
A product roadmap is meant to provide a clear plan for what’s coming next. However, as market conditions, customer feedback, and business priorities shift, it’s not uncommon for product roadmaps to change. This can be frustrating for teams and stakeholders who are relying on the initial plan.
Solution: Stay flexible and prioritize clear communication when changes are necessary. Regularly update the roadmap, and ensure that everyone understands why adjustments are being made. Keep stakeholders involved in the process to minimize any confusion.
5. Handling scope creep
Scope creep happens when the project’s requirements keep growing over time, often leading to delays, cost overruns, or lost focus. This usually happens when new features or changes are added without proper evaluation or approval.
Solution: Create a scope statement to clearly define the scope from the beginning and keep track of all proposed changes to avoid scope creep. Establish a process for evaluating the impact of new features or changes, including their impact on time and budget. Don’t be afraid to say no to features that don’t align with your product’s core goals.
6. Competing priorities
As a product manager, you’re constantly juggling multiple tasks and priorities, from strategic planning to day-to-day operations. It can be overwhelming when you have to manage both urgent issues and long-term goals, often from different teams or departments.
Solution: Time management and strong organizational skills are crucial. Break tasks into smaller, manageable pieces and set realistic deadlines. Delegate when possible, and stay focused on the key priorities that align with your product goals.
7. Managing cross-functional teams
Product managers often work with cross-functional teams (marketing, engineering, design, etc.), and coordinating these teams can be challenging. Different teams may have different working styles, communication preferences, and priorities.
Solution: Foster a collaborative culture and ensure that all teams understand their role in the product’s success. Regular check-ins and clear communication help avoid misunderstandings. Use tools like Creately, Slack or Trello to streamline collaboration and keep everyone aligned.
8. Dealing with uncertainty
The world of product management is rarely predictable. There are always uncertainties about customer behavior, market shifts, and how the product will be received once launched. These uncertainties can lead to hesitation or delayed decision-making.
Solution: Embrace an iterative approach. Use an MVP to gather early feedback, then refine the product based on real-world data. Trust your research and stay agile to adapt to new information as it becomes available.
Product Management Process Best Practices
Product management is both an art and a science. While each team and product may have its own approach, some best practices can help make the process smoother, more effective, and more aligned with business goals.
1. Stay customer-centric
Always keep the customer at the heart of every decision. Gather insights through user feedback, surveys, and analytics to ensure you’re building something that truly meets their needs. A product that doesn’t solve a real problem won’t succeed, no matter how well it’s built.
2. Validate before you build
Avoid wasting time and resources by testing ideas early. Use prototypes, MVPs, or market research to validate demand before fully committing to development. This helps ensure that what you’re building is valuable and minimizes the risk of failure.
3. Prioritize ruthlessly
Not every feature request or idea deserves equal attention. Use frameworks like RICE (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort), MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have), or the Impact-Effort matrix to determine what’s truly important. Focus on what delivers the most value with the least complexity.
4. Keep your roadmap flexible
A product roadmap should provide direction, not be set in stone. Market trends, user feedback, and business goals evolve, so be prepared to adapt. Communicate changes transparently to stakeholders and keep the team aligned on priorities.
5. Encourage cross-team collaboration
Product management sits at the intersection of business, design, and engineering. Foster open communication and collaboration between teams to ensure alignment. Regular check-ins, shared documentation, and visual collaboration tools can help break silos.
6. Use data, but don’t ignore intuition
Metrics like customer retention, engagement, and Net Promoter Scores help track success, but numbers don’t tell the whole story. Balance quantitative data with qualitative insights from customer interviews, sales teams, and industry trends to make well-rounded decisions.
7. Continuously improve
Product management is an ongoing cycle of learning and improvement. Regularly review what’s working and what’s not, gather team and customer feedback, and iterate. Small, continuous improvements often lead to big long-term gains.
Simplify Product Management with Creately
Creately is a powerful tool for product managers, offering visual and collaborative features that streamline the product management process. It allows you to create, manage, and track your product development work with ease, all while improving team collaboration. Here’s how you can leverage Creately throughout your product management journey.
1. Brainstorm and define the problem
Every great product starts with identifying the right problem to solve. Product managers need to gather insights, collaborate with teams, and explore different angles before setting a clear direction.
- Open-ended brainstorming boards in Creately allow teams to capture ideas freely. You can start with a blank canvas or use templates like the brainstorming templates to organize thoughts.
- Use sticky notes to jot down pain points, customer feedback, and feature ideas.
- Build on ideas collaboratively in real time, ensuring every stakeholder has a say in shaping the product vision.
By making brainstorming sessions more structured yet flexible, Creately helps product managers refine raw ideas into well-defined problem statements.
2. Develop the product vision and strategy
Once the problem is clear, the next step is to define the vision and align stakeholders on the direction of the product. A well-articulated product vision keeps teams focused and ensures that every decision contributes to the long-term goal.
- Use a business model canvas in Creately to outline key components like customer segments, value propositions, and revenue streams.
- Map out positioning strategies using the positioning map to understand where your product fits in the market.
- Embed documents, screen recordings, and customer interviews to keep all research and insights in one place.
Having a visual representation of your strategy makes it easier to communicate the vision across teams and stakeholders.
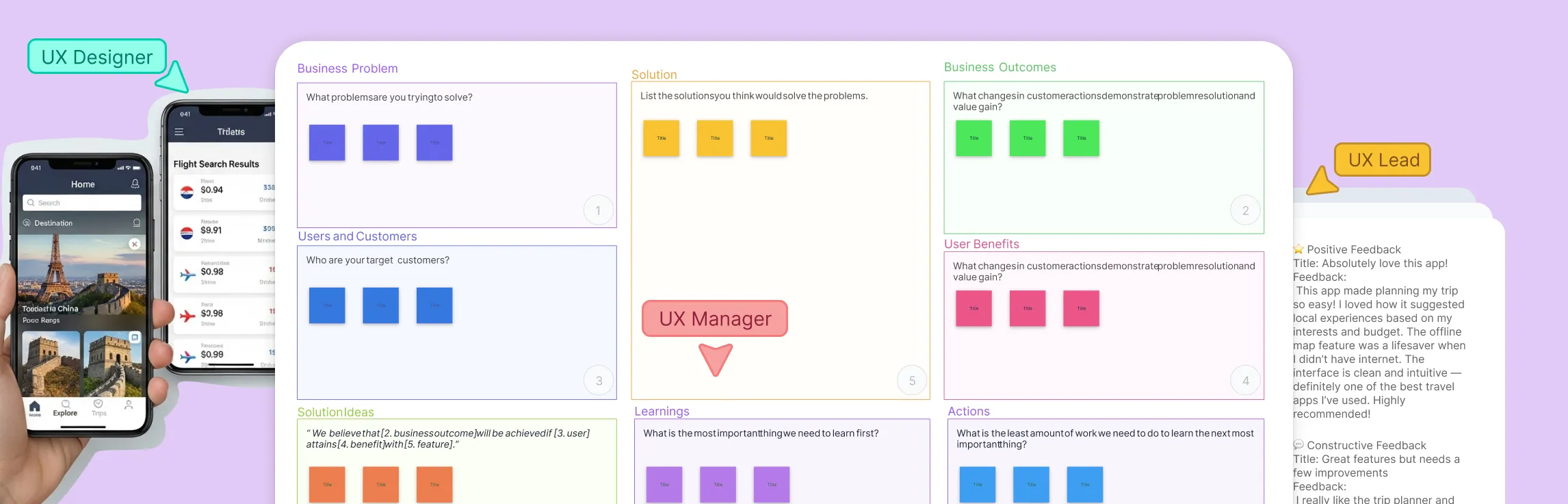
3. Understand customer needs with user journey mapping
A deep understanding of your customers’ experiences is key to building a product that truly meets their needs. Customer journey maps help visualize how customers interact with your product, from discovery to ongoing use.
- Map out customer touchpoints and pain points using customer journey map templates in Creately.
- Identify moments of friction and opportunities for improvement.
- Collaborate with cross-functional teams, including UX designers and customer success teams, to refine the user experience.
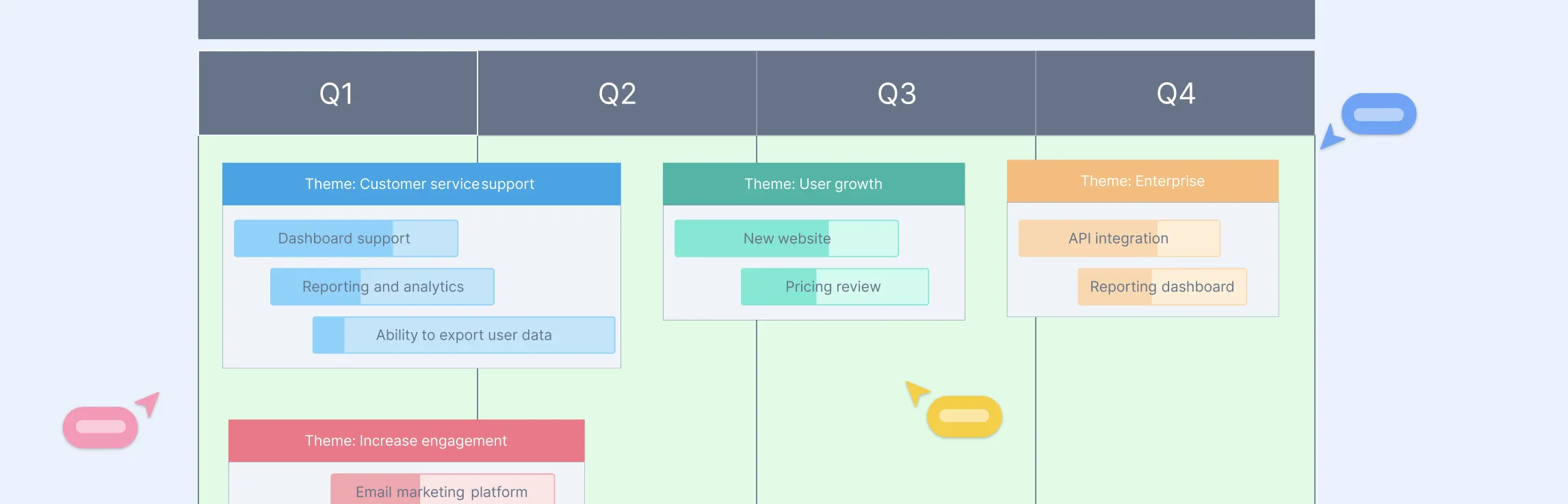
4. Build a product roadmap
A product roadmap provides a clear plan for how features and improvements will be delivered over time. It helps teams stay aligned, set priorities, and manage expectations.
- Use Creately’s product roadmap templates to organize upcoming features, releases, and strategic initiatives.
- Customize the roadmap based on time-based (quarterly/yearly) or goal-based (themes, objectives) roadmapping approaches.
- Share the roadmap with stakeholders to ensure alignment and transparency.
5. Prioritize features and initiatives with decision frameworks
Deciding what to build next is one of the biggest challenges in product management. Product managers need structured frameworks to evaluate and prioritize features effectively.
- Use prioritization matrices like:
- RICE (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort) to evaluate features based on strategic impact.
- Impact-Effort Matrix to balance effort vs. value.
- MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have) to categorize features based on necessity.
- Host voting sessions within Creately where stakeholders can visually weigh in on feature priorities.
- Integrate with Microsoft Teams to run collaborative discussions and decision-making workshops.
6. Manage execution with Kanban boards
Once features are prioritized, they need to be broken down into tasks and managed effectively across teams. Kanban boards in Creately provide a simple way to track progress.
- Organize tasks into columns like To Do, In Progress, and Done to visualize workflow.
- Assign tasks, set deadlines, and move work across different stages effortlessly with integrated shape data.
- Use color-coded labels to differentiate task types (e.g., bugs, new features, improvements).
Compared to spreadsheets or static lists, a visual Kanban board helps teams stay organized and quickly adapt to changing priorities.
7. Integrate with GitHub for development tracking
For technical teams, managing the engineering backlog efficiently is critical. Creately’s two-way integration with GitHub allows product managers to keep track of development work while maintaining a high-level visual overview.
- Sync tasks between Creately and GitHub in real-time so updates reflect in both places.
- Use Creately to group and categorize GitHub issues visually, making it easier to see relationships between different tasks.
- Combine data from GitHub, Jira, or spreadsheets into a single visual workspace.
This integration bridges the gap between planning and execution, ensuring that development teams stay aligned with product goals.
8. AI-powered product management with Creately VIZ
Creately VIZ enhances the product management process by turning ideas into structured visuals, offering expert insights, and automating workflows.
- Instant visualization – Convert product concepts, roadmaps, and user journeys into mind maps, flowcharts, or Kanban boards with AI-generated visuals.
- Smart frameworks – Use AI-powered templates for feature prioritization, competitive analysis, and go-to-market planning.
- Workflow automation – Streamline product development by automatically categorizing feedback, updating task trackers, and transforming discussions into action plans.
Conclusion: Product Management Process
The product management process is a journey, not a checklist. From identifying problems to launching and continuously improving, each stage plays a crucial role in turning an idea into a successful product.
Great product management isn’t just about following steps—it’s about staying flexible, making data-driven decisions, and keeping the customer at the center of everything. Challenges will come up, priorities will shift, and markets will change. The key is to adapt, collaborate, and focus on delivering real value.
By using the right tools, like Creately, and following best practices, product managers can streamline workflows, make informed decisions, and bring better products to life faster. Whether you’re building a new product or refining an existing one, a well-structured process will set you up for success.