Process mapping is a powerful tool that helps businesses visualize and improve their workflows. By creating a clear map of each step in a process, teams can see how work flows, identify bottlenecks, and pinpoint opportunities to make things run smoother. But there isn’t just one way to map a process—different process mapping techniques are available, each suited to various types of tasks and levels of detail.
In this guide, we’ll explore the most popular process mapping techniques, from simple flowcharts to detailed value stream maps. Each technique has unique strengths, helping teams break down processes, clarify responsibilities, and drive efficiency. Whether you’re managing a small project or overseeing complex workflows across departments, there’s a process mapping method to match your needs.
What Are Process Mapping Techniques?
Process mapping techniques are specific methods used to create visual diagrams of a workflow or process. These diagrams, called process maps, break down tasks, decision points, and the flow of work from start to finish. Process mapping techniques help teams clearly see every step of a process, making it easier to understand and analyze. By choosing the right technique, you can create a map that’s detailed, easy to follow, and fits the specific needs of your team.
The purpose of these techniques is to bring clarity to how things are done. They help identify where steps can be streamlined, responsibilities clarified, and tasks improved. Ultimately, using process mapping techniques is about boosting efficiency and making sure every part of the workflow adds value.
Why Use Different Process Mapping Techniques?
Not every process is the same, and neither are the teams or goals behind them. That’s why there are various process mapping techniques to choose from. Each technique serves a slightly different purpose, which makes it easier to find the one that best fits your needs.
For example, some techniques, like flowcharts, are great for simple, straightforward processes with few steps. Others, like value stream mapping, are better for complex workflows where you need to track every step’s impact on time and resources. Additionally, different teams may have unique preferences and requirements. A project manager might need a high-level view of the process, while an operations team may need a detailed breakdown of every step. By choosing the right technique, you ensure your process map is useful, effective, and tailored to both the complexity of the workflow and the needs of the team.
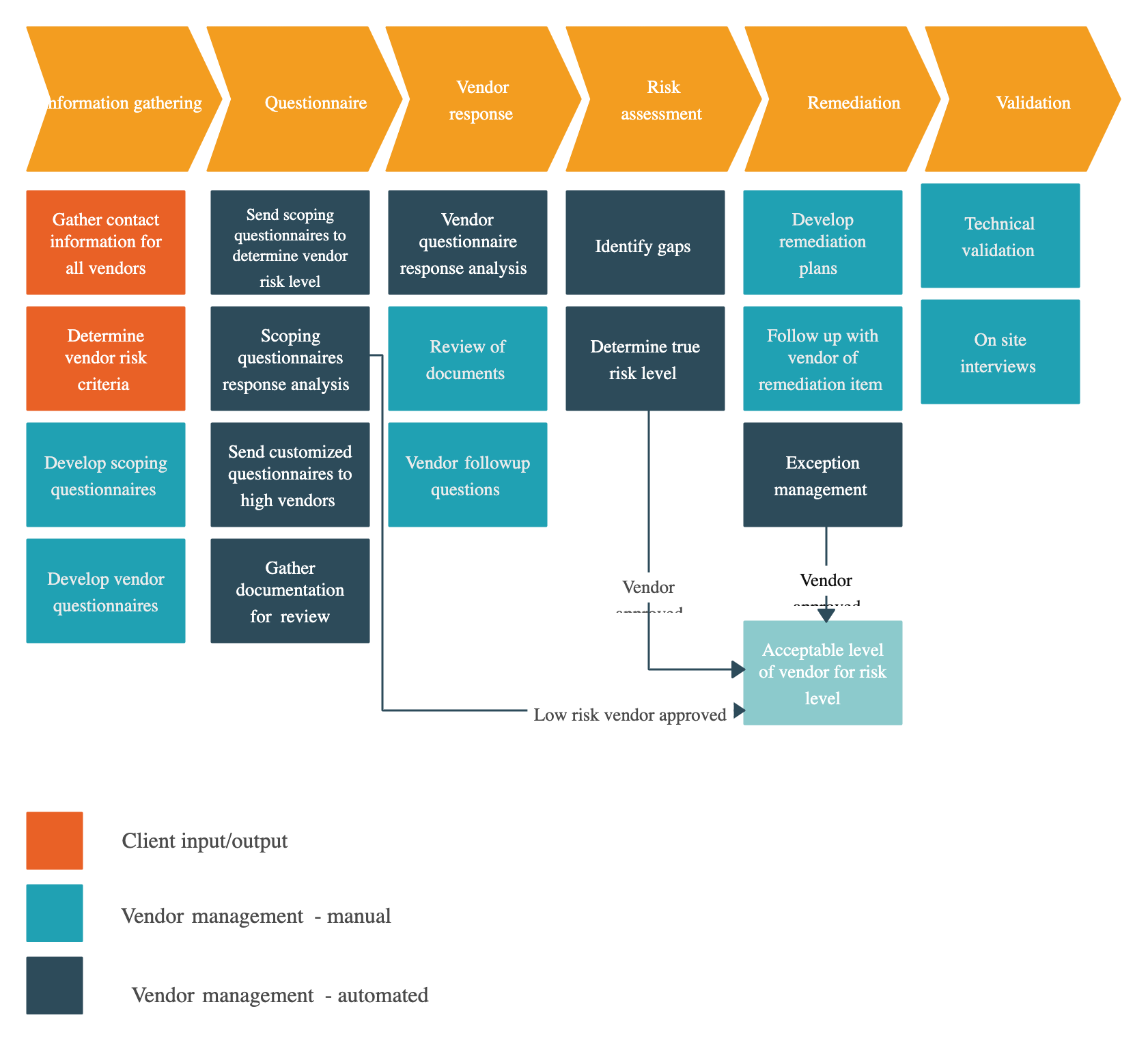
Common Process Mapping Techniques and Their Uses
Flowcharts
Flowchart is one of the simplest and most widely used process mapping techniques for visualizing processes step by step. A flowchart lays out each task, decision, or action in a process using a sequence of shapes and arrows. Each shape has a specific purpose—for instance, ovals typically represent the start and end points, rectangles show actions or tasks, and diamonds indicate decision points where different paths might occur.
Flowcharts are easy to understand and are an excellent way to map out workflows for people at all levels of a team. Because they break down processes into straightforward steps, flowcharts can help quickly highlight where tasks might be getting delayed or where handoffs happen between team members.
When to use flowcharts
Flowcharts are ideal for mapping simple processes and workflows that don’t have a lot of complex steps or decision points. They work well for:
- Basic workflows: Processes that follow a clear sequence, like onboarding a new employee or handling a customer service request.
- Training and documentation: Flowcharts can help new employees quickly understand how to complete tasks.
- Troubleshooting guides: They make it easy to show a step-by-step decision-making path, like diagnosing a technical issue.
Flowcharts are most effective when you need a quick, clear view of how a process flows. By visually breaking down tasks into manageable steps, flowcharts help teams follow procedures accurately and identify areas for improvement.
SIPOC diagrams
A SIPOC diagram is a high-level process mapping technique that outlines the key elements of a process from start to finish, focusing on the flow from suppliers to customers. “SIPOC” stands for Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers—the five components that the diagram captures. This approach helps teams see the full picture of a process and understand how each part connects to the final outcome.
In a SIPOC diagram:
- Suppliers are the sources providing necessary materials or information.
- Inputs are the resources (such as data, parts, or tools) required to start the process.
- Process represents the actual steps taken to complete the workflow.
- Outputs are the results produced by the process, like products or services.
- Customers are the end users or recipients of the process output.
Use cases in quality control and process improvement
SIPOC diagrams are commonly used in quality control and process improvement because they give a clear, end-to-end view of how a process flows. By mapping out each part from suppliers to customers, teams can pinpoint where issues arise and identify areas for improvement. Key use cases include:
- Identifying bottlenecks: By clearly outlining each step, SIPOC diagrams help highlight where delays or issues might be occurring, allowing teams to troubleshoot effectively.
- Ensuring consistency and quality: Teams can use SIPOC diagrams to ensure that each part of the process aligns with quality standards and that inputs meet the necessary requirements before work begins.
- Setting improvement goals: With a full view of the process, SIPOC diagrams make it easier to identify specific areas where small adjustments could improve quality, reduce waste, or increase efficiency.
Because they provide a structured look at each stage, SIPOC diagrams are valuable tools for teams focused on continuous improvement and delivering high-quality results.
Value stream mapping (VSM)
Value stream mapping (VSM) is a process mapping technique focused on maximizing value and reducing waste. It’s a tool that helps teams visualize each step in a process, from start to finish, and identify which parts truly add value to the end product or service. In VSM, “value” refers to activities that contribute to the customer’s needs, while “waste” includes steps that slow down or complicate the process without adding real value.
By using VSM, teams can track and analyze time, resources, and effort spent at each step. This helps in spotting and avoiding bottlenecks, redundancies, and non-essential actions, ultimately improving the process to be faster and more efficient.
Suitable industries and applications
Value stream mapping is especially popular in Lean manufacturing, where reducing waste and maximizing value is a core focus. However, it’s also highly applicable in other fields where efficiency is critical, including:
- Healthcare: Streamlining patient flow, reducing wait times, and improving overall care quality.
- Logistics and supply chain management: Optimizing order processing, delivery routes, and inventory management.
- Software development: Mapping development cycles to reduce lead times and eliminate bottlenecks in Agile workflows.
- Service industries: Enhancing customer service processes to deliver quicker, more effective responses.
By focusing on what truly matters to the customer, VSM helps teams align their efforts to produce the best results while cutting out wasted time, effort, and resources. It’s a powerful technique for any industry that prioritizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
Swimlane diagrams
Swimlane diagrams are a type of process map that organizes tasks by roles or departments, showing who is responsible for each part of a workflow. In these diagrams, “lanes” represent different people, teams, or functions, and each task or decision is placed within the lane of the group responsible for it. This structure makes it easy to see not only what needs to be done but also who is accountable for each step.
Swimlane diagrams are especially useful for visualizing cross-functional processes, where multiple teams or departments are involved. By separating tasks by role, swimlane diagrams help prevent confusion and clarify responsibilities, ensuring each team knows when they need to step in and when the process is in someone else’s hands.
Ideal for cross-functional processes and team-oriented workflows
Swimlane diagrams work well in scenarios where multiple people or teams contribute to a process, including:
- Project management: Showing how different departments (e.g., marketing, sales, operations) work together on a project.
- Customer service: Mapping the handoffs between support, technical teams, and billing to streamline issue resolution.
- Product development: Outlining the roles of design, engineering, and quality assurance in bringing a product from idea to launch.
- Compliance processes: Ensuring each role involved in a regulatory workflow (like approvals or audits) is aware of their specific tasks.
By clearly assigning roles to each step, swimlane diagrams help teams work together smoothly, reduce communication gaps, and create accountability. They’re an effective tool for any workflow where coordination across different roles is key.
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN)
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a standardized system for mapping out complex workflows in detail. BPMN uses a specific set of symbols and shapes—like circles, rectangles, and diamonds—that represent tasks, events, decision points, and the sequence of actions in a process. This system makes it easy to create highly detailed and structured maps that anyone familiar with BPMN can understand, regardless of their background or industry.
BPMN is more technical than basic flowcharts, making it ideal for processes that require precise detail and consistency. It’s often used by teams where accurate mapping is crucial, such as in highly regulated industries or in workflows where every action needs to be clearly documented and understood.
Best for detailed, technical processes and regulatory compliance
Because of its precision, BPMN is especially valuable in:
- Detailed, technical processes: It captures complex workflows with multiple steps, departments, or decision points, ensuring every aspect is documented. This is common in fields like software development, engineering, and financial services.
- Regulatory compliance: For industries bound by strict regulations (such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing), BPMN provides a clear record of each step, ensuring that all necessary actions are followed and tracked.
- Cross-departmental workflows: BPMN’s structured approach helps teams with specialized roles coordinate their work, minimizing misunderstandings and maintaining consistent standards.
With its clear and universal notation, BPMN is a powerful tool for organizations that need to maintain accuracy, comply with regulations, and handle complex processes that require a high level of detail and clarity.
Spaghetti diagrams
Spaghetti diagrams are a process mapping technique used to visualize the physical movement of people, materials, or equipment in a workspace. The diagram shows the path taken within a specific area, often resulting in a “spaghetti-like” look when there are many crisscrossing lines. By mapping these movements, teams can see exactly where people or resources are moving inefficiently, allowing them to identify ways to minimize travel time and create a more organized workspace.
Use cases in workspace organization and efficiency
Spaghetti diagrams are commonly used in production floors, warehouses, and offices where efficiency and organization are essential. Key applications include:
- Manufacturing: Mapping the movement of workers and materials on the production floor to reduce unnecessary travel, improve layout, and increase productivity.
- Warehouse management: Visualizing the path workers take to retrieve or store items, helping teams adjust layouts to make high-demand items easier to access and optimize storage locations.
- Healthcare facilities: In hospitals or clinics, mapping nurse or doctor movement can help identify opportunities to bring supplies and equipment closer to patient rooms, improving response times.
- Office spaces: Understanding how employees move around the office to redesign layouts, minimizing time spent walking between common areas, equipment, and workstations.
Spaghetti diagrams provide a simple but effective way to understand physical workflows, eliminate wasted motion, and optimize space for smoother operations. They’re a valuable tool for any environment where reducing movement can save time and boost efficiency.
UML activity diagrams
UML (Unified Modeling Language) activity diagrams are visual tools used to model workflows, focusing on the flow of activities or tasks within a system. They show how different actions, decisions, and outcomes progress from one step to the next, making them ideal for representing both software and business processes with a focus on user or system actions.
Activity diagrams use standardized symbols—such as arrows for transitions, diamonds for decision points, and rounded rectangles for activities—to provide a clear view of process flows. This helps teams visualize the order of operations, identify dependencies, and clarify possible decision points.
Common uses of UML activity diagrams
- Software Development: Useful for designing software workflows, activity diagrams help developers visualize how users or system components interact through various steps, ensuring each action is accounted for and logically sequenced.
- Business Process Modeling: Activity diagrams are widely used to model business workflows, especially when human tasks intersect with automated steps. They can help in understanding complex processes and ensuring all necessary actions are included.
- System Integration: These diagrams illustrate how data and actions flow through integrated components, making it easier to map interactions between databases, applications, and other systems.
UML activity diagrams offer a structured way to capture both high-level processes and detailed workflows. By using this technique, teams can ensure a clear, standardized understanding of workflows, supporting accurate development, seamless integrations, and efficient business processes.
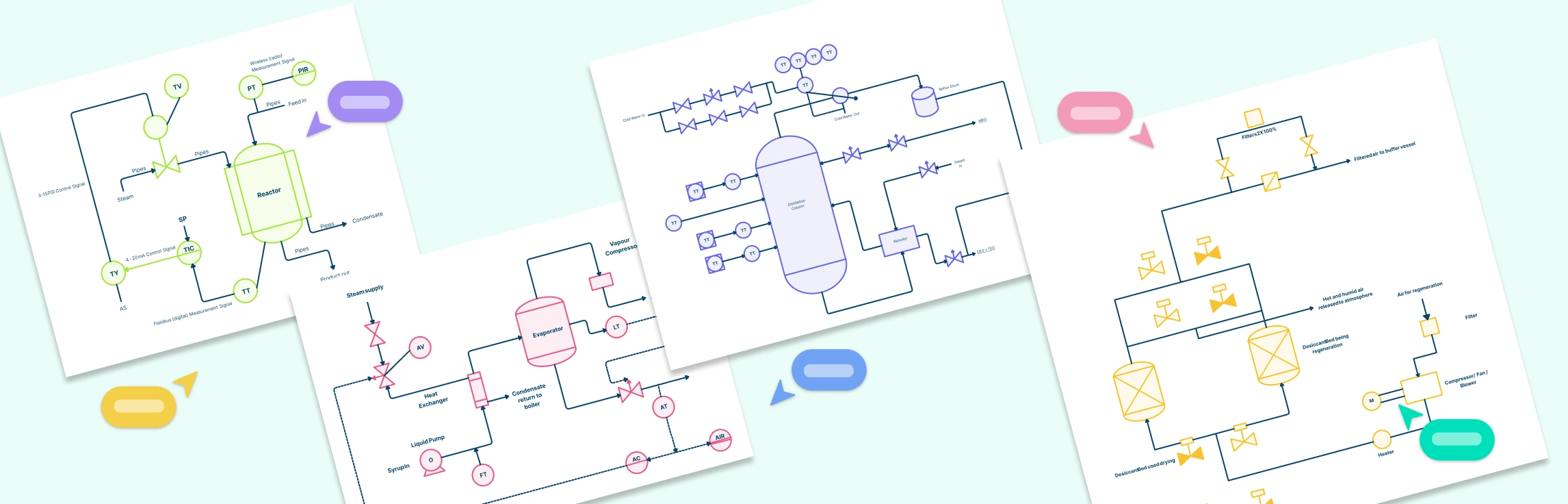
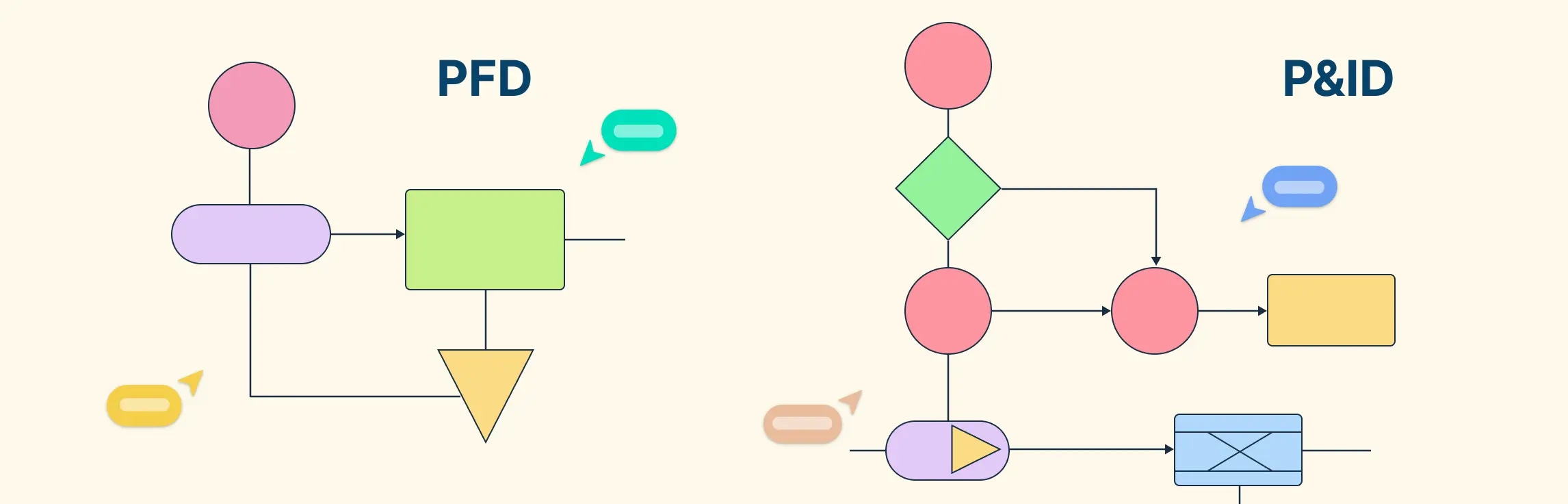
Process Flow Diagrams (PFDs)
Process flow diagrams (PFDs) are a process mapping technique commonly used in engineering and manufacturing to show the main steps, equipment, and flows within a technical process. Unlike basic flowcharts, PFDs often include specific symbols for machinery, pipes, and other technical components, making them highly detailed and informative for teams familiar with the process.
PFDs provide an overview of the process, showing how materials, chemicals, or other elements move from one stage to the next. This helps engineers and operators understand how each part of the system connects and where potential issues might occur, such as bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
Suitable for processes with many technical components
Process flow diagrams are ideal for complex systems with multiple technical parts and flows, such as:
- Manufacturing processes: Outlining each stage in a production line, including machinery, material inputs, and outputs.
- Chemical and petrochemical industries: Showing how chemicals move through equipment like reactors, tanks, and separators, essential for safety and efficiency.
- Energy and utility plants: Mapping how resources like water, gas, or electricity move through a facility, ensuring smooth operations and risk management.
- Pharmaceutical production: Detailing equipment and flows in drug production to maintain strict standards and avoid contamination.
With their technical focus, PFDs help teams in engineering and manufacturing visualize and control intricate processes, ensuring that each part functions correctly and that the system as a whole operates efficiently.
Data Flow Diagrams (DFD)
Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) are used to represent the flow of data within a system, showing how data is processed, stored, and transferred between different components. They provide a clear picture of where data originates, where it goes, and how it is handled at each stage of a process.
DFDs are especially useful in understanding complex systems by focusing on the movement of data rather than the tasks or actions themselves. They break down the process into easy-to-understand steps, allowing for a clear visual representation of data flow. This makes them an essential tool for system analysis, particularly in software development and database design.
Common uses of DFDs
- System design: DFDs help design information systems by mapping out data flows, making it easier to understand how systems interact.
- Database management: They are used to visualize how data is processed and stored across different parts of a database, improving database architecture.
- Process analysis: DFDs are valuable in identifying inefficiencies in data handling and processing, which is essential for improving system performance.
By focusing on the flow of information, DFDs provide clarity on how data moves through a system, helping identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for optimization.
Deployment flowcharts
Deployment flowcharts are a variation of swimlane diagrams that focus specifically on task delegation across multiple roles or departments. Like swimlanes, they use separate lanes or sections to represent each person, team, or department involved in a process. However, deployment flowcharts put a stronger emphasis on who is responsible for each task, making it clear where each action needs to be executed.
This focus on task ownership is especially useful in processes that require coordination among different departments, as it helps prevent confusion about who is handling each part of the workflow. Deployment flowcharts also help visualize the handoffs between roles, showing how tasks move from one team to the next.
Common in multi-departmental processes
Deployment flowcharts are particularly valuable in scenarios where multiple departments need to work together, such as:
- Project management: Breaking down complex projects into tasks assigned to various teams, ensuring clarity on each team’s responsibilities.
- Product launches: Coordinating roles across departments like marketing, product, and customer support, so that each team knows its part in the launch plan.
- Hiring and onboarding: Mapping out the steps involved in bringing a new employee on board, from HR to department managers.
- Compliance processes: Ensuring that each department understands its specific compliance-related duties within a larger regulatory framework.
With their clear focus on task delegation, deployment flowcharts make it easy to manage responsibilities, streamline communication, and keep cross-departmental workflows organized. They’re an effective tool for ensuring accountability and smooth handoffs in team-oriented processes.
Workflow diagrams
In process mapping, highlighting workflows with roles, inputs, and outputs provides a structured view of who does what, with what resources, and what results each step produces. This approach makes it clear how each role contributes to the process and what is required to complete each task. Inputs include any resources, information, or materials needed to perform an action, while outputs are the results or deliverables that the task generates.
Mapping roles, inputs, and outputs is especially useful when there are multiple participants in a process. It helps ensure that everyone understands their part, what they need to accomplish it, and what they are expected to deliver.
Widely used for automated and semi-automated processes
This approach is often applied in automated and semi-automated processes because it simplifies tracking and management. When machines or software handle some or all of the tasks, it’s crucial to define each role’s input requirements and expected output. Key applications include:
- Manufacturing: Mapping machine tasks, human oversight, materials, and finished product requirements in automated production lines.
- IT and software workflows: Assigning roles and defining data inputs/outputs in processes like data processing, user management, or software deployment.
- Financial services: Outlining roles, inputs, and outputs in automated transactions or compliance checks to ensure regulatory standards are met.
- Customer support systems: Setting up workflows where automated systems (like chatbots) handle initial inputs and transfer outputs (like unresolved queries) to human agents.
By emphasizing roles, inputs, and outputs, these workflows help ensure consistency and accuracy, reduce misunderstandings, and enable seamless interactions between human and automated tasks. This structure is key for managing complex processes efficiently, especially in automated environments.
Benefits of Business Process Mapping Techniques
Business process mapping techniques are essential for understanding and improving the way work gets done within an organization. They provide a clear visual representation of workflows, making it easier to see how different tasks, people, and resources are connected. By using process maps, businesses can identify inefficiencies, reduce errors, and streamline operations.
1. Improved clarity and understanding: Process mapping techniques make complex workflows easy to understand. Whether you’re working with a team or communicating with stakeholders, clear maps help everyone see how a process works and what each step involves.
2. Identifying inefficiencies: By visualizing a process, you can spot bottlenecks, unnecessary steps, or areas where things slow down. This allows teams to make changes that improve efficiency and reduce waste.
3. Better decision-making: process mapping techniques provide the data needed to make informed decisions about where improvements are needed. With clear visuals, it’s easier to analyze performance and choose the best course of action.
4. Standardization of processes: Mapping processes helps standardize how work is done across teams or departments. This ensures consistency, reduces errors, and makes it easier to train new employees.
5. Enhanced communication and collaboration: process mapping techniques act as a common language that teams can use to discuss workflows. They help bridge gaps between different departments and ensure that everyone is on the same page.
6. Easier compliance and documentation: In industries that require regulatory compliance, process maps are crucial for documenting how tasks are performed. They provide a clear record of procedures, making it easier to meet legal and industry standards.
7. Continuous improvement: Process mapping techniques help businesses continually evaluate and refine their workflows. By regularly updating process maps, organizations can keep improving their operations and stay competitive.
Selecting the Right Process Mapping Technique
Choosing the best process mapping technique is crucial for making workflows clear and effective. Here’s how to select the right method by matching it to process complexity, stakeholder needs, and available tools.
Match complexity to technique
Simple Processes: For basic, step-by-step workflows, use straightforward techniques like:
- Flowcharts: Ideal for linear processes with few decision points.
- Workflow diagrams: Suitable for outlining tasks in order without many layers.
Complex Processes: For processes with multiple decision points, team roles, or complex stages, consider techniques like:
- Value stream mapping (VSM): Focuses on waste reduction and process efficiency.
- Business process model and notation (BPMN): Provides a standardized approach with symbols for complex workflows, making it easier to follow intricate steps and interactions.
Consider stakeholder needs and roles
For team members
- Swimlane Diagrams: Clearly outline each person’s role, making it easy for team members to see where they fit in the workflow.
- Flowcharts: For tasks that don’t require cross-functional details, flowcharts provide a simple, direct map.
For managers and process owners
- BPMN or value stream mapping: These give a high-level view, showing how each stage impacts the workflow as a whole, which is useful for strategic decision-making.
- SIPOC diagrams: Useful for understanding supplier-customer relationships and overall process input-output.
Evaluate tools and resources
Basic tools: If only basic software (e.g., Google Drawings, PowerPoint) is available, stick with simple techniques like flowcharts or basic workflow diagrams.
Specialized software: For advanced mapping needs, tools like Creately offers templates and symbols suited to:
- BPMN: Creately’s BPMN tool comes with standardized symbols for comprehensive process details.
- Value stream mapping: Creately’s value stream mapping tool has tailored templates that make it easier to map detailed processes.
Helpful Resources
Learn the essentials of process mapping with our comprehensive guide. Discover techniques, best practices, and tools to streamline workflows and improve efficiency.
Explore various business process modeling techniques with real-world examples. Learn how to visualize, analyze, and improve workflows for greater efficiency and clarity.
Master business process analysis with our complete guide. Learn key techniques, best practices, and tools to optimize workflows and enhance organizational efficiency.
Create, analyze, and optimize workflows effortlessly with Creately's process mapping software. Visualize processes, collaborate in real-time, and improve efficiency with intuitive, easy-to-use tools.
Practical Tips for Applying Process Mapping Techniques
Using process mapping techniques effectively takes attention to detail and a few key best practices. Here are some tips to ensure your maps are clear, easy to understand, and adaptable over time.
- Keep it straightforward: Make your maps as clear and simple as possible. Avoid adding unnecessary details, as this can overwhelm viewers, especially in cross-functional processes where multiple teams are involved.
- Focus on key steps: Include only essential steps and decision points. This helps everyone quickly understand the overall flow without getting lost in extra details.
- Use standardized symbols: Stick to recognized symbols for common actions (like circles for start/end, diamonds for decisions) so everyone understands them easily.
- Maintain a uniform layout: Ensure similar elements are placed consistently across maps. For example, always show start points at the top or left and follow a clear direction. This consistency helps users quickly interpret the map’s flow.
- Update for process changes: Processes evolve over time, so make it a habit to review and update your maps regularly to reflect any changes.
- Encourage feedback: Invite team members who use the maps to provide feedback on any unclear areas. This helps you keep the maps accurate, relevant, and valuable for day-to-day use.
Simplifying Process Mapping with Creately
Creately makes process mapping straightforward by providing a clear, visual way to organize complex workflows. Here’s how it helps streamline the process:
- Drag-and-drop interface: Quickly add shapes, connectors, and annotations with Creately’s easy-to-use interface. No more wrestling with complex software—just focus on building clear, accurate, and efficient maps.
- Real-time collaboration: Creately allows you to invite team members to contribute and edit in real time. This is especially useful for cross-functional workflows where input from various roles ensures a comprehensive map.
- Ready-made templates: Choose from templates for flowcharts, swimlanes, SIPOC diagrams, and more. Templates save time and create consistent, professional maps tailored to your needs.
- Beyond mapping – for documentation, planning, and training: Process maps aren’t just for workflows—they also aid in documentation, planning, change management, and training. Bring all related information into one place with Creately’s additional features:
- Notes feature: Add detailed notes to each process step. Attach screenshots, PDF forms, or other resources for quick access, making it easy to reference everything you need.
- Attachments and centralized Iinformation: Add documents, instructions, or screenshots directly to the process map. This centralizes information, reduces time spent searching for resources, and simplifies processes for everyone involved.
- Interlinked maps for centralized access: Creately lets you create interlinked process maps that serve as a gateway to all processes. This central discovery workspace provides quick access to interconnected workflows, making it easy to navigate complex systems.
Conclusion: Process Mapping Techniques for Improving Workflows
Process mapping techniques are powerful tools for understanding, analyzing, and improving workflows. Whether you’re simplifying a process with a basic flowchart, identifying value with value stream mapping, or assigning roles in a swimlane diagram, each technique offers a unique approach to clarifying how work gets done.
Selecting the right technique for your needs depends on factors like complexity, team roles, and specific process goals. From managing daily tasks to ensuring compliance in complex operations, these tools help make processes more transparent, organized, and effective.
By using process mapping techniques thoughtfully, teams can streamline workflows, improve communication, and ultimately create a more efficient and collaborative environment. In today’s fast-paced work settings, a well-designed process map is not just a visualization—it’s a pathway to achieving better outcomes with clarity and purpose.
References
Al-Fedaghi, S. and Mohamad, Y. (2019). Business Process Mapping: A Case Study. 2019 IEEE/ACS 16th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA). doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/aiccsa47632.2019.9035277.