Traditional organizational hierarchies often leave teams frustrated, decisions get stuck in approval loops, responsibilities overlap, and clarity is lost across departments. Enter the holacratic structure: a modern, role-based approach that distributes authority, clarifies responsibilities, and makes decision-making faster.
In this guide, we’ll explore what a holacracy is, how a holacratic organizational structure works, the advantages and disadvantages of adopting this model, and practical holacratic org chart templates to help teams visualize and implement it effectively.
What Is a Holacratic Structure?
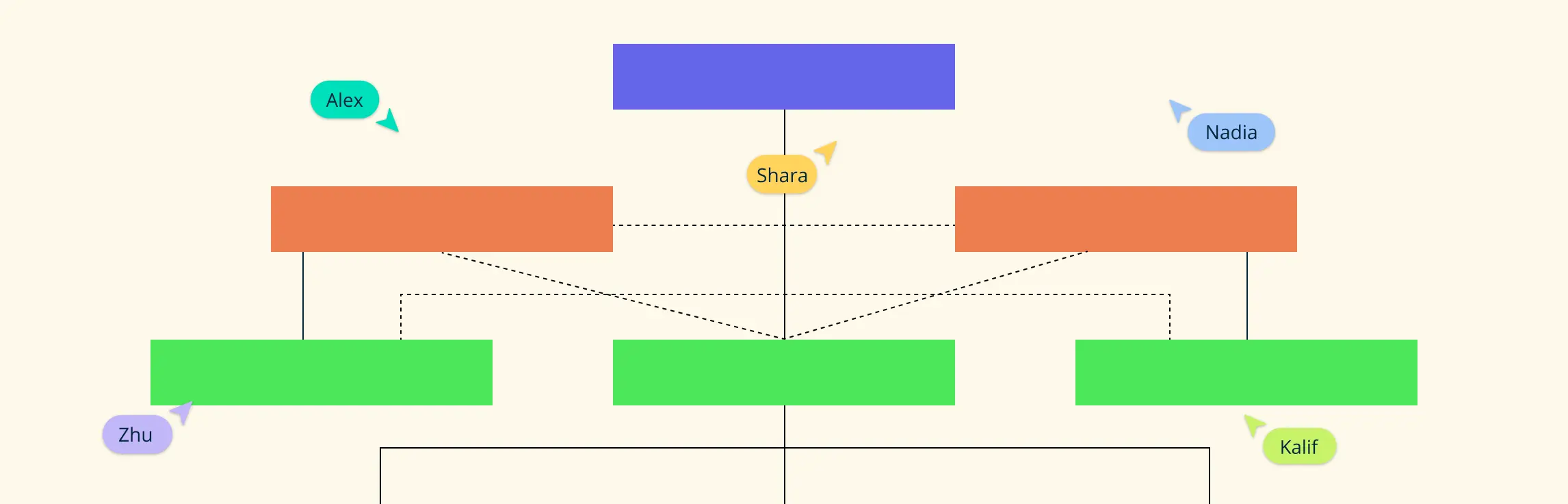
A holacratic structure is an organizational model where authority is distributed across clearly defined roles rather than concentrated in a traditional management hierarchy. It’s essentially a system that organizes teams into flexible units called circles, each responsible for specific functions and outcomes.
In the holacracy model, people don’t operate based on job titles. Instead, they work through multiple roles, each with its own purpose and accountabilities. These roles sit within circles, and circles connect to one another to form a responsive, adaptable structure. Decision-making is guided by structured governance processes, ensuring clarity without relying on top-down control.
Key Elements of a Holacratic Org Structure
A holacratic organizational structure is built on a set of core elements that replace traditional hierarchy with clarity, adaptability, and distributed authority. Together, these elements allow teams to self-organize, respond quickly to change, and operate with greater transparency.
Dispersed Management System
In a holacratic structure, management authority is not concentrated at the top. Decision-making is distributed across roles and circles, allowing team members closest to the work to contribute meaningfully. This dispersed approach reduces bottlenecks, strengthens ownership, and encourages collaboration across the organization.
Roles Instead of Job Descriptions
Rather than fixed job descriptions, holacracy relies on roles. Each role has a clear purpose and defined accountabilities, created based on current business needs. When priorities shift, roles can be updated, reassigned, or retired, allowing individuals to move fluidly into new areas where they add the most value. It’s common for people to hold multiple roles across different circles.
Responsiveness and Flexibility
A key strength of the holacracy structure is its ability to respond quickly to change. Actions are guided by outcomes rather than rigid reporting lines. Within each circle, the Lead Link helps prioritize work, assign roles, and allocate resources, ensuring the team remains aligned while staying flexible.
Distinct Governance Process
Holacracy uses a formal governance process to evolve the organization over time. Team members can propose changes to roles, responsibilities, or structures, which are reviewed and integrated through structured governance meetings. This ensures the holacratic organization continuously adapts without relying on static job definitions or top-down directives.
Integrative Decision-Making
Decisions in a holacratic org structure follow an integrative approach. Relevant input is gathered, tensions are addressed, and solutions are shaped to serve the organization’s purpose. This method avoids slow consensus-building while still ensuring decisions are informed, practical, and aligned with operational needs.
Role Fluidity and Self-Organization
Roles in a holacratic organization are not permanent. They can be combined, split, or redefined as work evolves. Teams self-organize around projects that align with organizational goals, enabling skill-sharing, job rotation, and cross-functional contribution without formal titles.
Circles as Core Structural Units
Circles are the foundational building blocks of a holacracy organizational structure. Each circle focuses on a specific purpose and contains multiple roles. Circles can exist independently or within larger circles, forming a scalable and interconnected system aligned with the company’s overall mission.
Built-In Agility
By minimizing hierarchy and formal bureaucracy, holacratic structures are designed for agility. Teams can adapt faster, experiment more freely, and operate with greater efficiency, making this model particularly effective for organizations navigating constant change.
Together, these elements create a holacratic org structure that prioritizes clarity, adaptability, and empowered teamwork, while remaining structured enough to scale and sustain growth.
Examples of Holacratic Org Structure
Holacratic org structures can look very different depending on an organization’s size, industry, and way of working. Below are practical examples that show how a holacratic structure is applied in real-world scenarios, using roles, circles, and distributed authority instead of traditional hierarchies.
Startup Product Organization
In a startup environment, a holacratic org structure often consists of a small number of circles focused on product development, growth, and operations.
- A Product Circle may include roles such as Product Strategy, UX Design, Development, and Quality Assurance.
- Team members hold multiple roles across circles, allowing the organization to stay lean and highly responsive.
This structure works well for agile teams that need to iterate quickly without management bottlenecks.
Design and Marketing Organization
In creative teams, a holacratic organizational structure supports collaboration while maintaining clarity.
- A Marketing Circle might include roles like Content Strategy, Brand Design, Campaign Management, and Analytics.
- Sub-circles can be formed for specific initiatives, such as product launches or seasonal campaigns.
This approach enables self-organizing teams to move faster while keeping responsibilities visible.
Distributed Remote Organization
For remote-first companies, a holacratic org structure helps maintain alignment across locations.
- Separate circles may exist for Engineering, Customer Support, Sales, and Operations.
- Lead Links connect circles to ensure priorities remain aligned with the company’s overall purpose.
Distributed authority allows teams in different time zones to make decisions independently while staying coordinated.
Mid-Sized Scaling Organization
As organizations grow, holacracy helps manage complexity without adding layers of management.
- Circles are created around core business functions, with nested sub-circles handling specialized work.
- Governance processes ensure roles and responsibilities evolve as the company scales.
This structure supports growth while preserving agility and accountability.
Project-Based or Innovation-Focused Teams
Organizations focused on innovation often use a holacratic structure to form temporary circles around projects.
- Teams self-organize based on skills and interests.
- Roles are reassigned or dissolved once projects are completed.
This model encourages experimentation while maintaining operational clarity.
These examples show how a holacratic org structure can adapt to different organizational needs. Visualizing these structures with clear org charts makes it easier to understand role ownership, circle relationships, and decision-making flow, especially when teams are growing or distributed.
How a Holacratic Organizational Structure Works
A holacratic organizational structure operates through a set of interconnected elements that replace traditional hierarchy with clarity, distributed authority, and structured collaboration. Instead of relying on job titles or managerial chains of command, a holacracy structure uses well-defined roles, circles, and processes to keep teams aligned and adaptive.
Roles vs. Job Titles
In a holacratic organization, individuals don’t function based on broad job titles. Instead, they take on multiple roles, each with a specific purpose, clear accountabilities, and defined boundaries.
- A job title tells you who someone is in the hierarchy.
- A role tells you what work they own and what decisions they’re empowered to make.
This shift removes ambiguity and ensures that responsibilities are visible and actionable.
Circles
Roles are grouped into circles, self-organizing units that operate like mini-organizations within the broader holacracy model.
Each circle:
- Has its own purpose
- Contains roles aligned to that purpose
- Manages its own processes and improvements
Circles sit within wider circles, creating a flexible structure that can expand or evolve as the organization grows.
Lead Links
Instead of traditional managers, a holacratic structure uses Lead Links.
A Lead Link:
- Assigns roles within the circle
- Ensures the circle’s purpose aligns with the organization’s overall direction
- Helps balance priorities and resources
However, they do not micromanage or control decision-making. Authority still remains distributed across roles.
Governance Meetings
Governance meetings are where the structure itself is updated. These sessions focus on:
- Adding or removing roles
- Updating role accountabilities
- Adjusting role expectations or links between circles
Governance ensures the holacracy organizational structure remains responsive, not static. Teams adapt their structure as work evolves.
Tactical Meetings
Tactical meetings address day-to-day execution. They’re designed for:
- Reviewing metrics
- Resolving operational obstacles
- Assigning next actions
- Sharing quick updates
This clear separation between governance (structure) and tactical (execution) keeps teams focused, efficient, and aligned.
Together, these components create a holacratic organizational structure that is both structured and flexible, supporting faster decision-making, clearer ownership, and more adaptive teamwork than a traditional hierarchy.
Holacratic Org Chart Templates
1. Startup Product Team Template
Visualize a fast-moving product team with roles like Product Owner, UX Designer, Developer, and QA Lead grouped into a single circle. This template highlights clear ownership, agile workflows, and distributed authority, making it ideal for small teams aiming for rapid iteration and accountability.
2. Design & Marketing Circle Template
Map a creative team with roles such as Graphic Designer, Copywriter, Social Media Manager, and Marketing Strategist. This template shows how roles collaborate within a circle, encouraging cross-functional creativity while maintaining clarity and autonomy. Perfect for teams managing campaigns, sprints, or branding projects.
3. Distributed Remote Company Template
Designed for fully remote organizations, this template illustrates multiple circles for engineering, support, marketing, and operations. Roles are assigned by function rather than hierarchy, with lead links connecting circles for alignment. Ideal for showcasing distributed authority, self-organizing teams, and agile collaboration across regions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Holacratic Structure
A holacratic structure offers a modern alternative to traditional hierarchies, but it comes with its own set of strengths and challenges. Here’s a clear, balanced look at the holacratic structure advantages and disadvantages, and where this model works best, or becomes difficult to manage.
Advantages of Holacratic Structure | Disadvantages of Holacratic Structure |
| 1. Clearer Ownership and Accountability Because work is defined through roles—not job titles—teams gain clarity on who is responsible for what. This reduces confusion, overlap, and the “I thought someone else owned it” problem. | 1. Steep Learning Curve for Teams New to Distributed Authority Shifting from a traditional hierarchy to a holacratic organization can be overwhelming at first. Teams need time to understand roles, governance processes, and decision-making rules. |
| 2. Faster, Decentralized Decision-Making Authority sits with the roles closest to the work, enabling decisions to be made quickly without lengthy approval chains. This is especially useful in fast-moving environments where teams need to adapt continuously. | 2. Governance Can Feel Process-Heavy While governance meetings help maintain clarity, they can feel rigid or time-consuming if teams aren’t used to structured discussions. Without discipline, these meetings can become bottlenecks. |
| 3. Higher Organizational Agility Holacratic structures evolve through governance meetings, allowing teams to update roles, responsibilities, and processes as work changes. This makes the organization more responsive and resilient. | 3. Role Proliferation and Over-Engineering It’s easy to create too many roles or overly detailed accountabilities. When this happens, the system becomes complex instead of empowering. |
| 4. Improved Transparency Across Teams Roles, accountabilities, and processes are documented and visible. Teams know how different circles operate and how decisions flow, reducing internal friction and misalignment. | 4. Requires Strong Communication and Documentation Habits A holacracy model depends on transparency. If teams don’t document changes or communicate clearly, confusion can spread quickly. |
| 5. Encourages Cross-Functional Collaboration Since individuals often hold multiple roles across circles, collaboration becomes more fluid. Work naturally crosses team boundaries without the limiting effects of rigid hierarchical silos. | 5. May Not Suit Highly Traditional or Top-Down Cultures Organizations that rely on strong managerial control or clear chains of command may struggle to adopt holacratic principles. The system works best where autonomy and distributed ownership are already culturally supported. |
How to Draw a Holacratic Org Chart with Creately
Creating a holacratic org chart can be complex if done manually, but with Creately, the process becomes visual, structured, and collaborative. Here’s a step-by-step guide to designing your holacracy organizational structure efficiently, highlighting key Creately features that make it easier.
Step 1: Define Circles and Roles
- Start by mapping the main circles in your organization, such as Product, Marketing, or Operations. Then, define roles within each circle.
- Use pre-built holacratic templates in Creately and drag-and-drop shapes for roles and circles. This ensures your chart stays structured and visually clear from the start.
Step 2: Connect Roles and Circles
- Show relationships between roles and circles. Indicate which roles report to Lead Links or interact with other circles.
- Smart connectors automatically link roles and circles, keeping relationships clear even when you reorganize the chart.
Step 3: Assign Role Details
- Add descriptions, accountabilities, and responsibilities for each role. Include key performance indicators or decision-making authority if needed.
- Use customizable text fields and tooltips to embed role-specific information directly in the chart, making it easy for teams to reference.
Step 4: Visualize Governance and Tactical Flows
- Include governance processes and tactical meeting structures where applicable. Highlight which roles are responsible for proposing or approving changes.
- Flowchart and process shapes help represent governance flows alongside the org chart, giving a complete view of the holacracy model.
Step 5: Customize and Iterate
- Adjust shapes, colors, and layouts to match your team’s structure and branding. Update roles and circles as your organization evolves.
- Real-time collaboration lets multiple users edit and update the chart simultaneously. Version history ensures you can track changes and iterate safely.
Step 6: Share and Collaborate
- Share the final holacratic org chart with your team or stakeholders. Collect feedback and make adjustments.
- Cloud sharing and export options allow you to share the chart as PDFs, images, or interactive diagrams, keeping everyone aligned.
Using Creately’s org chart software, teams can transform the abstract concept of holacracy into a clear, visual structure. By combining roles, circles, and governance flows in a dynamic chart, organizations gain clarity, transparency, and agility while reducing the frustration of scattered responsibilities.
Difference Between a Holacratic Structure and a Hierarchical Structure
| Aspect | Holacratic Structure | Hierarchical Structure |
| Decision-Making | Authority is distributed. Individuals can make decisions within the scope of their roles. | Decision-making is centralized, with senior leaders having the final say. |
| Roles | Employees hold multiple, evolving roles based on organizational needs. | Each employee typically has one fixed role or job title. |
| System Type | Decentralized system built around roles and circles. | Centralized system based on reporting lines and levels of authority. |
| Collaboration Style | Cross-functional and flexible collaboration across circles. | Department-based collaboration, often resulting in silos. |
| Organizational Flexibility | Highly adaptable and responsive to change. | More rigid, with slower structural changes. |
| Best Suited For | Agile teams, startups, creative teams, and organizations facing rapid change. | Large, traditional organizations that require stability and control. |
Final Thoughts: A Structure Built for Modern, Visual Teams
A holacratic structure transforms traditional hierarchies into clear, adaptable systems that empower teams to make decisions where the work happens. By focusing on roles, circles, and distributed authority, organizations gain clarity, transparency, and agility, while avoiding the confusion of overlapping responsibilities. With the right visual tools, you can map your holacracy organizational structure, experiment with roles and circles, and maintain an evolving, high-performing team design. Start creating your holacratic org charts today in Creately and see how visual thinking can make your organization more aligned, efficient, and responsive.
Helpful Resources
Explore rules for drawing organizational charts and org chart best practices to make your org chart more meaningful and useful.
Easily make organizational charts to visualize the reporting structure of your organization for effective HR planning and management with org chart maker.
Learn simple steps to create an org chart that fits your business, along with tips and tools to make it easy to build and update.
FAQs About Holacratic Structure
Can a holacratic structure work in large enterprises?
How does a holacratic structure handle promotions or career growth?
Do teams need special training to adopt holacracy?
How flexible is a holacratic structure during organizational changes?
What industries benefit most from a holacratic organizational structure?