Change is never easy. Especially in a context of business, as it affects a lot of aspects. In order to ensure a smooth transition from the current state to the desired state of business, you need the correct change management tools and resources at hand.
What is Change Management?
In the simplest of terms, change management is a systematic approach towards dealing with change. It’s a structured way of applying tools, knowledge, and resources to effectively drive organizational success.
Change management enables the navigation of organizational transitions and ensures successful adoption of new initiatives, processes, or technologies. It involves understanding the need for change, planning the implementation, and guiding individuals and teams through the transformation process. Change management aims to minimize resistance, manage risks, and maximize the benefits of change.
Change Management Tools
Change management tools help organizations effectively manage transitions—be it technological, structural, or cultural—by offering strategies, frameworks, and techniques to guide the process. These tools promote transparency, collaboration, and employee engagement through platforms for communication and project management, enabling organizations to adapt and succeed in a constantly evolving environment.
1. Flowcharts/ Process Maps
Flowcharts and process maps help visualize organizational processes, making them accessible to everyone—even those not directly involved. During the readiness assessment stage of change management, they are useful for mapping the current state. Any proposed changes can be added using flowchart software, allowing for clear documentation and future reference.

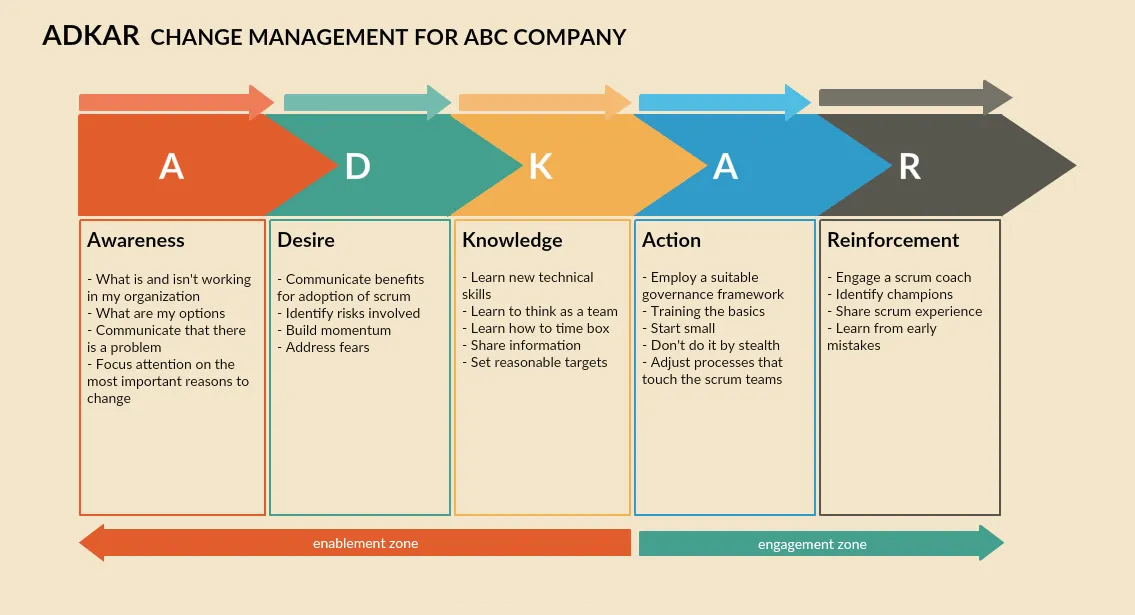
2. ADKAR Analysis
The ADKAR model in change management is used as a coaching tool to make sure that the people or employees involved in the process support and believe in the change. ADKAR stands for,
Awareness - Clearly communicate to the employees what change is occurring and why.
Desire - Build desire in your employees to support the change so they would do their part naturally rather than forcing them to do so.
Knowledge - Make sure to help employees learn how to support the change through training programs, job aids, tutorials, coaching programs and checklists provided by the company.
Ability - Help employees further improve their ability through feedback and evaluations.
Reinforcement - Make sure that employees don’t go back to their old ways. In order to reinforce the changes, give incentives and rewards to employees.
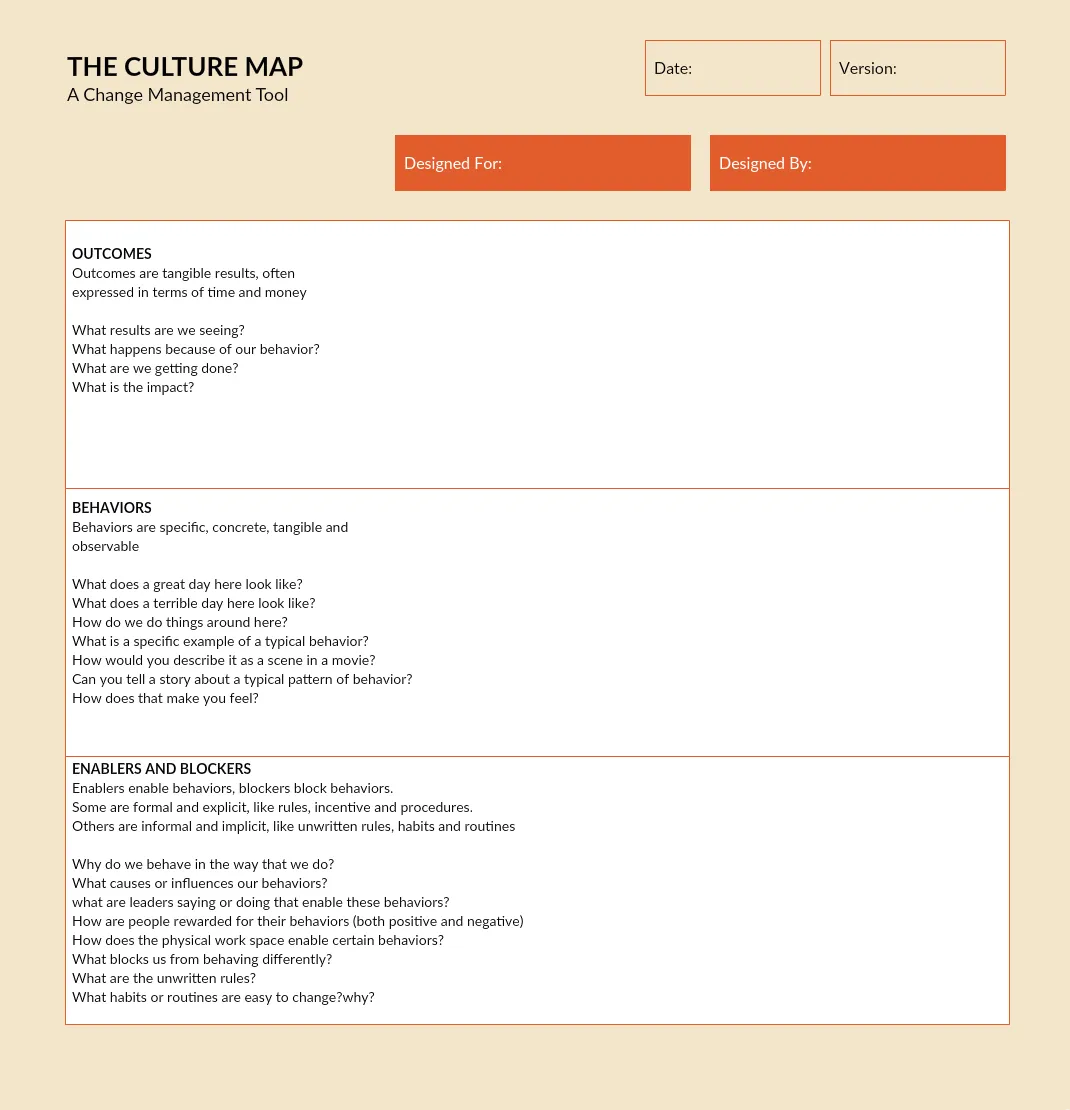
3. Culture Mapping
A culture map is one of the change management tools that is used to visualize the company culture, which is influenced by values, norms, employee behavior etc. It helps you discover information that is crucial to your change initiative, such as who are the positive enablers and how you can minimize risks during a project.
Step 1: Identify the subcultures - Identify the groups that belong to the different subcultures in your organization. These could be IT, finance, marketing, sales, etc teams in your organization. Identify 5-6 people that can best represent these subcultures.
Step 2: Carry out interviews - Interview each group to know the cultural blockers and enablers reinforced intentionally or unintentionally by the management.
Step 3; Organize the information - Organize the information such as the behaviors, enablers, blockers, current and desired outcomes etc. in a cultural map like the one below for quick analysis.
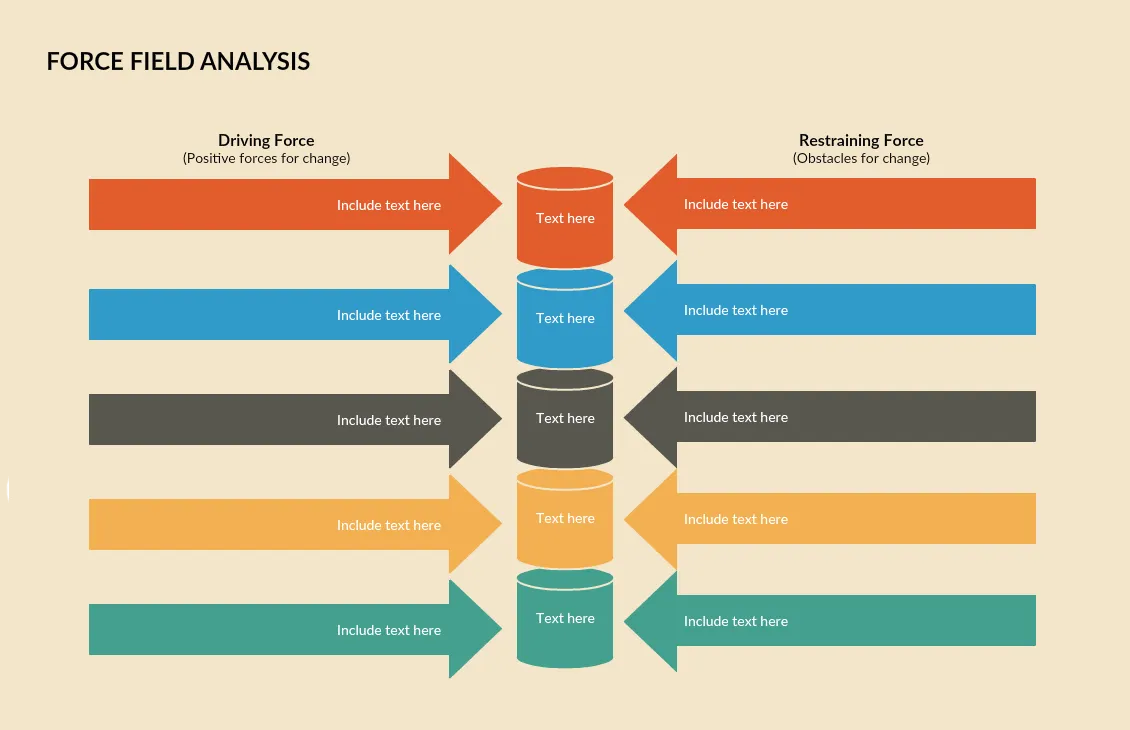
4. Force Field Analysis
Force field analysis, also known as a barrier and aids analysis, is a useful decision-making tool. It helps you identify and analyze forces for and against change or the implementation of a proposed solution.
Step 1: Define your plan for change - What is your goal for the change?
Step 2: Brainstorm forces for change - What are the forces you can think of that would help you move forward with your plans? Remember to look at factors in both the internal and external environment.
Step 3: Brainstorm forces against change - What are the forces that are blocking you from implementing the changes? Fill out these sections for the analysis using the template below.
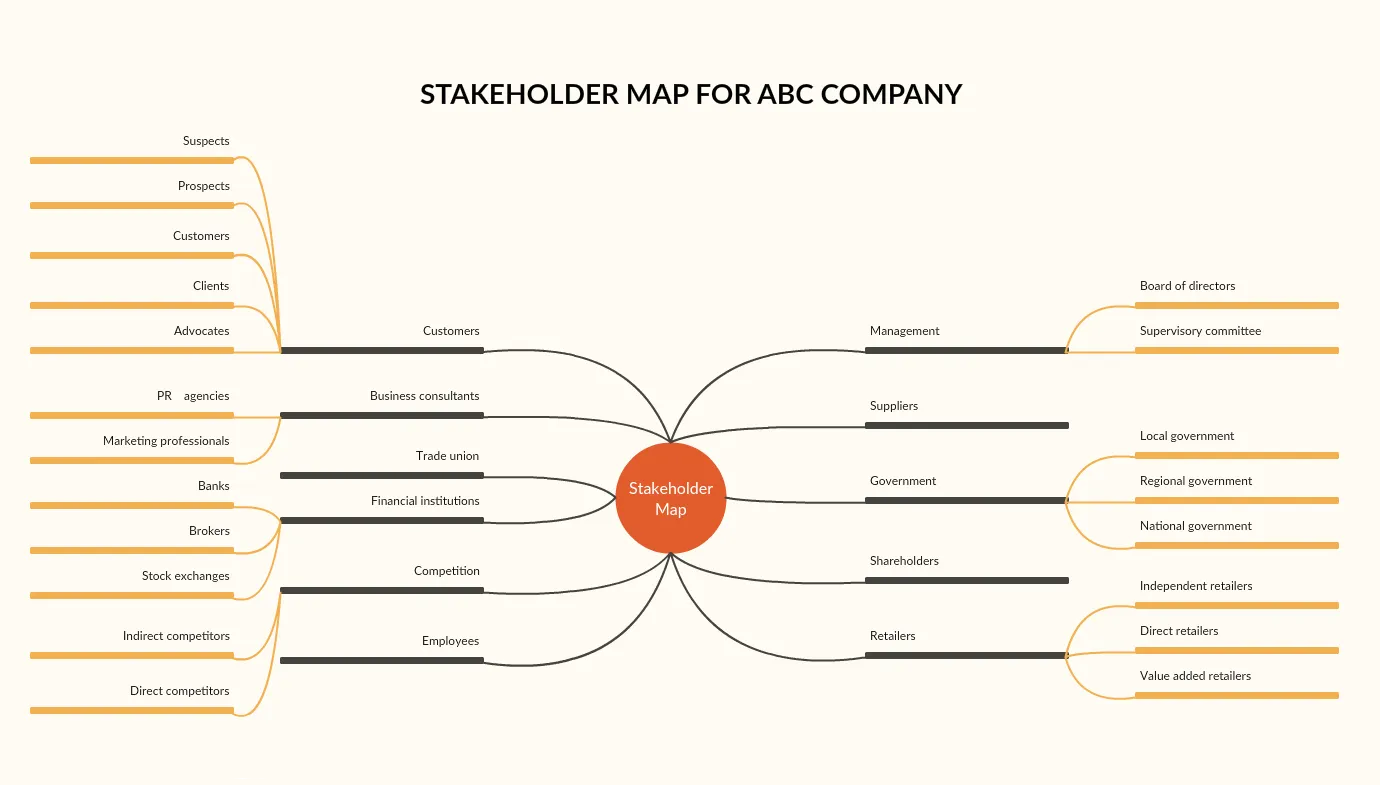
5. Stakeholder
In the stakeholder analysis, you identify stakeholders and categorize them based on different factors such as geography, income groups, occupation, legal requirements etc.
At the end of the analysis, you’ll have found out who your project’s stakeholders are and why the project is important to them.
Step 1: Identify the stakeholders - Think of all the people who might be affected by your project. Remember to consider those who come from outside of your company as well.
Step 2: Prioritize the stakeholders - Your list of stakeholders may include people who may be affected by and care about your project and, who may be unaffected by and be not that interested in your project.
Using a Power/interest grid for stakeholder analysis like the one below, you can prioritize your stakeholders based on their stake in the project and their engagement.

Step 3: Stakeholder map - Now that you have prioritized your stakeholders, you can use a stakeholder map to easily categorize them.
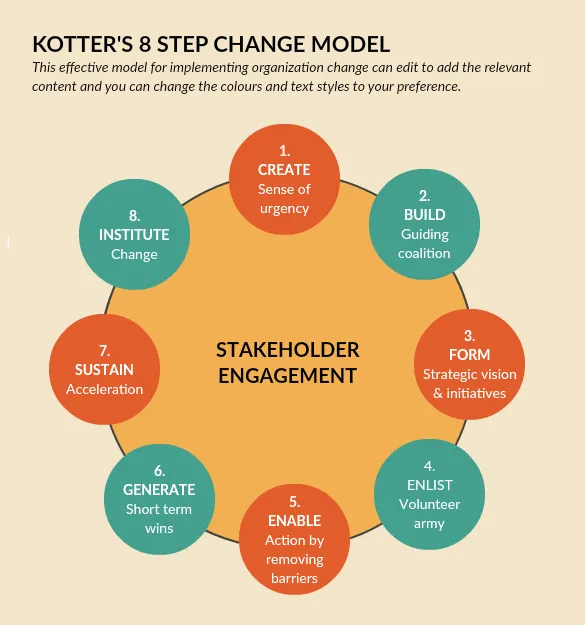
6. Kotter’s 8 Step Change Model
Kotter’s change model is an 8-step method to manage change. These steps include,
Step 1: Create a sense of urgency - Creating a sense of urgency helps motivate people to embrace change. SWOT analysis can highlight external threats and opportunities, while a threat vs. opportunity matrix can illustrate the potential impact on stakeholders—reinforcing the need for timely change.
Step 2: Build a guiding coalition - Build a strong team made up of influential people from all statuses and expertise and who can convince others that change is necessary.
Step 3: Form a strategic vision and initiatives - Create a clear vision as to why change is necessary or as to why you are asking your employees to do something. Determine the values that are linked to the change and create a strategy to get to your vision.
Step 4: Clearly communicate the said vision - Communicate your vision frequently so that it will be embedded within everything your team does. Not only during special meetings but every chance you get, try to remind the vision to your team.
Step 5: Enable action by removing any obstacles - Identify barriers that are blocking the implementation of change. Help those who are resisting change see what’s needed. Reward people to support change.
Step 6: Generate short-term wins - If your staff can see short-term wins that will motivate them. Create short-term targets so you can celebrate quick wins.
Step 7: Build on the change - If something worked, identify what went right and improve it. Set goals and continue to work on it, building momentum.
Step 8: Make it part of the culture - Make sure that any change you gain, you make it part of your culture.
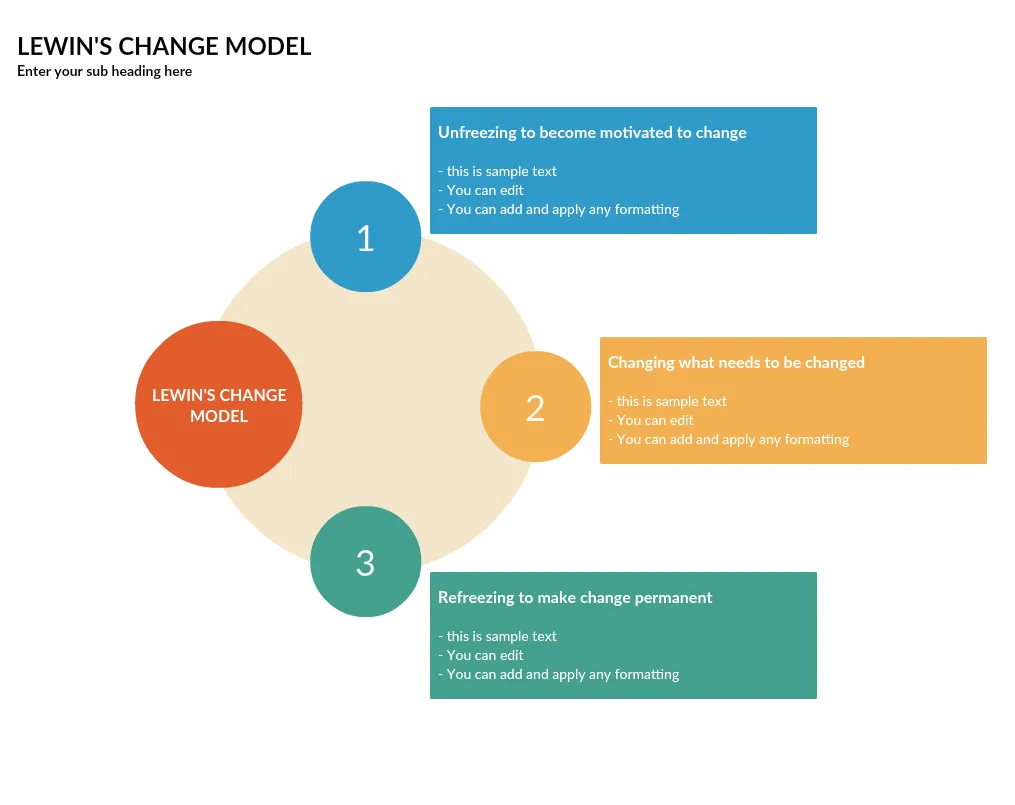
7. Lewin’s Change Model
According to Kurt Lewin’s change model, successful change is achieved through a 3-step process;
Unfreezing - In the preparation stage of change, it’s crucial to raise awareness about why the change is needed. Reviewing and sharing key elements like processes and organizational structures with employees helps build understanding and encourages acceptance of the change.
Changing - This is the stage where real change occurs. Employees will learn new behaviors, processes, and ways of thinking during this time.
Refreezing - It’s time to solidify the new behavior, processes, goals etc. You must make sure that the change implemented is not lost and is incorporated into the culture of your organization.
8. Gantt Chart
Any change management project includes a large number of tasks, and to complete them successfully you must make sure that they are completed on schedule. Gantt charts help teams stay on track, identify potential risks early, and ensure better collaboration and resource allocation. With clear steps—like defining scope, breaking down tasks, setting timelines, and tracking progress—Gantt charts make complex projects easier to manage and more transparent for all stakeholders.
FAQs About Change Management Tools
What are the benefits of using change management tools?
- Streamlined Communication
- Improved Collaboration
- Enhanced Accountability
- Data-Driven Decision Making
- Risk Mitigation
What are the benefits of change management?
- Minimizes Resistance
- Maximizes Adoption and Engagement
- Enhances Benefits Realization
How do I choose the right change management tools for my organization?
Choosing the right change management tools involves several considerations:
Identify Your Needs: Begin by understanding your organization’s specific change management requirements. What are the key challenges you face during change initiatives?
Features and Compatibility: Evaluate the features offered by different tools. Ensure they align with your organization’s goals and that the tool can integrate with your existing systems.
Ease of Use: Look for a tool that is user-friendly and can be adopted by team members with varying levels of technical expertise.
Scalability: Consider whether the tool can accommodate the scale of your organization’s projects and future growth.
Cost: Determine your budget and select a tool that offers a reasonable cost-benefit ratio.
User Feedback: Research user reviews and seek recommendations from other organizations that have used the tool.
Vendor Support: Assess the level of customer support and training offered by the tool’s vendor.



Dr. Chris
which of the following change management tools are designed to visualize your project’s development process?
Amanda
Great question! All these tools are helpful for visualizing your project’s development during change management, and you can create them easily with Creately’s ready-made templates:
Kanban boards - let you track tasks through each stage of change and spot bottlenecks quickly. Flowcharts and process maps - helps redesign workflows and clarify new processes. Gantt charts - keep your changes plan on schedule with clear timelines and dependencies. Roadmaps - align everyone on long-term change goals and priorities. Value stream maps - helps you identify and eliminate inefficiencies during transitions.