In the field of biology, classification plays a major role. With new species being discovered every day, it’s important to have techniques in place to identify and classify them. One such tool is the dichotomous key. It helps identify organisms by directing the user to look at the known organisms.
In this simple guide, we will explain what is a dichotomous key and how to create one. Some examples are provided in the dichotomous key examples section; you can use any template to start your project right away. Download them as PNGs, JPEGs, SVGs or PDFs for publishing, printing, and sharing.
Dichotomous Key Definition
A dichotomous key is a tool used in biology and other scientific fields to help identify and classify organisms, objects, or other items based on their characteristics. Simply put, it is a method used to identify a species by answering a series of questions based on contrasting features (eg: physical characteristics) that have two possible outcomes.
“Dichotomous” means divided into two parts, hence the dichotomous keys always present two choices based on the key characteristics of the organism in each step. By correctly selecting the right choice at each stage, the user will be able to identify the name of the organism at the end. The further you divide the key, the more you learn about the specimen you are trying to identify.
Students and professionals use the dichotomous key to identify and classify objects (i.e. people, animals, plants, bacteria, etc.) into specific categories based on their characteristics. It’s the most commonly used form of classification or type of identification key used in biology as it simplifies identifying unknown organisms.
Simply put, it is a method used to identify a species by answering a series of questions based on contrasting features (eg: physical characteristics) that have two possible outcomes.
When creating a dichotomous key, both qualitative (i.e. physical attributes such as how the organism looks, what color it is, etc.) and quantitative (i.e. the number of legs, weight, height, etc.) factors are considered.
It can be done in both a graphical (as a branching flowchart or written format - series of paired statements organized sequentially). Most often, they are used to identify plant and animal species, although it can be used to classify any object that can be identified by a set of observable characteristics.
To easily draw connections between species to better establish proposed phylogeny create Cladograms.
What is the dichotomous key used for
A dichotomous key is usually used for
- Identifying and categorizing organisms
- Helping students easily understand harder scientific concepts
- Organizing large amounts of information to make identification of an organism much easier
How to Make a Dichotomous Key
Below we have listed the steps you need to follow when creating a dichotomous key.
Step 1: List down the characteristics
Pay attention to the specimens you are trying to identify with your dichotomous key. List down the characteristics that you can notice. For example, say you are trying to classify a group of animals. You may notice that some have feathers whereas others have legs, or some have long tails and others don’t.
Step 2: Organize the characteristics in order
When creating your dichotomous key, you need to start with the most general characteristics first, before moving to the more specific ones. So it helps to have identified the more obvious and less obvious contrasting characteristics among the specimen before creating your dichotomous key.
Step 3: Divide the specimens
You can use statements (i.e. has feathers and no feathers) or questions (does it have feathers?) to divide your specimens into two groups. The first differentiation should be made on the most general characteristic.
Step 4: Divide the specimen even further
Based on the next contrasting characteristic, divide the specimen further. For example, first, you may have grouped your animals as have feathers and have no feathers, in which case the ones with feathers can be categorized as birds while you can further subdivide the ones that have no feathers as having fur and having no fur. Continue to subdivide your specimen by asking enough questions until you have identified and named all of them.
Step 5: Draw a dichotomous key diagram
You can either create a text-based dichotomous key or a graphical one where you can even use images of the specimen you are trying to identify. Here you can use a tree diagram or a flowchart as in the examples below.
Step 6: Test it out
Once you have completed your dichotomous key, test it out to see if it works. Focus on the specimen you are trying to identify and go through the questions in your dichotomous tree to see if you get it identified at the end. If you think the questions in your dichotomous key needs to be rearranged, make the necessary adjustments.
Best practices to keep in mind
- Consider only one characteristic at a time
- Use morphological or observable characteristics as much as you can
- Use major characteristics when dividing the organisms in the beginning and use lesser or less obvious characteristics to divide them into smaller groups
- When writing contrasting statements, rely on similar word formats (i.e. have feathers and don’t have feathers)
- Be specific in your statements and avoid repeating the same characteristics
- Use questions that lead to yes or no answers rather than statements
To draw connections between species to better establish evolutionary connections use a Phylogenetic Tree Maker
Dichotomous Key Examples
Let’s look at some examples to make more sense of what is a dichotomous key.
Dichotomous key for animals
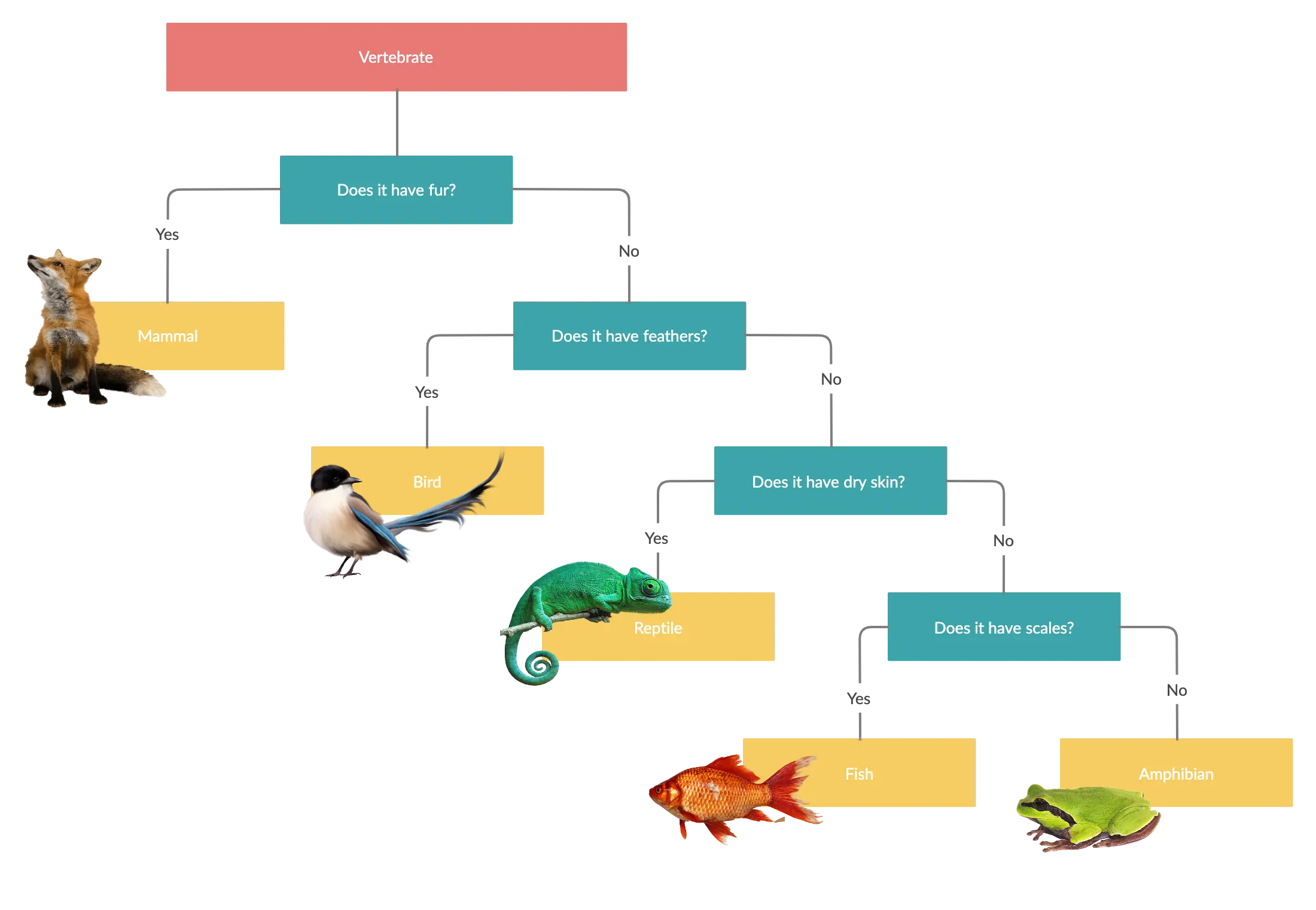
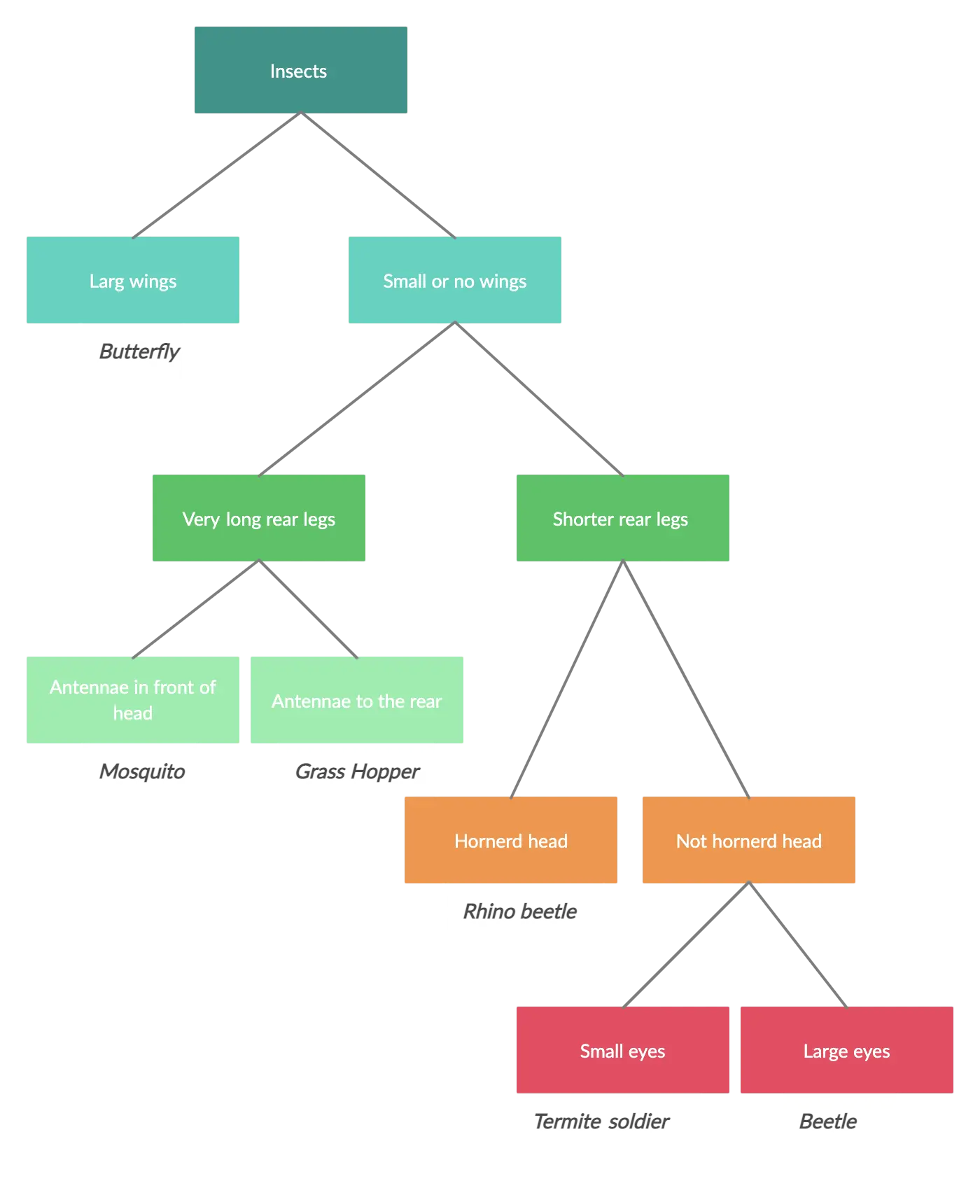
Dichotomous key for insects
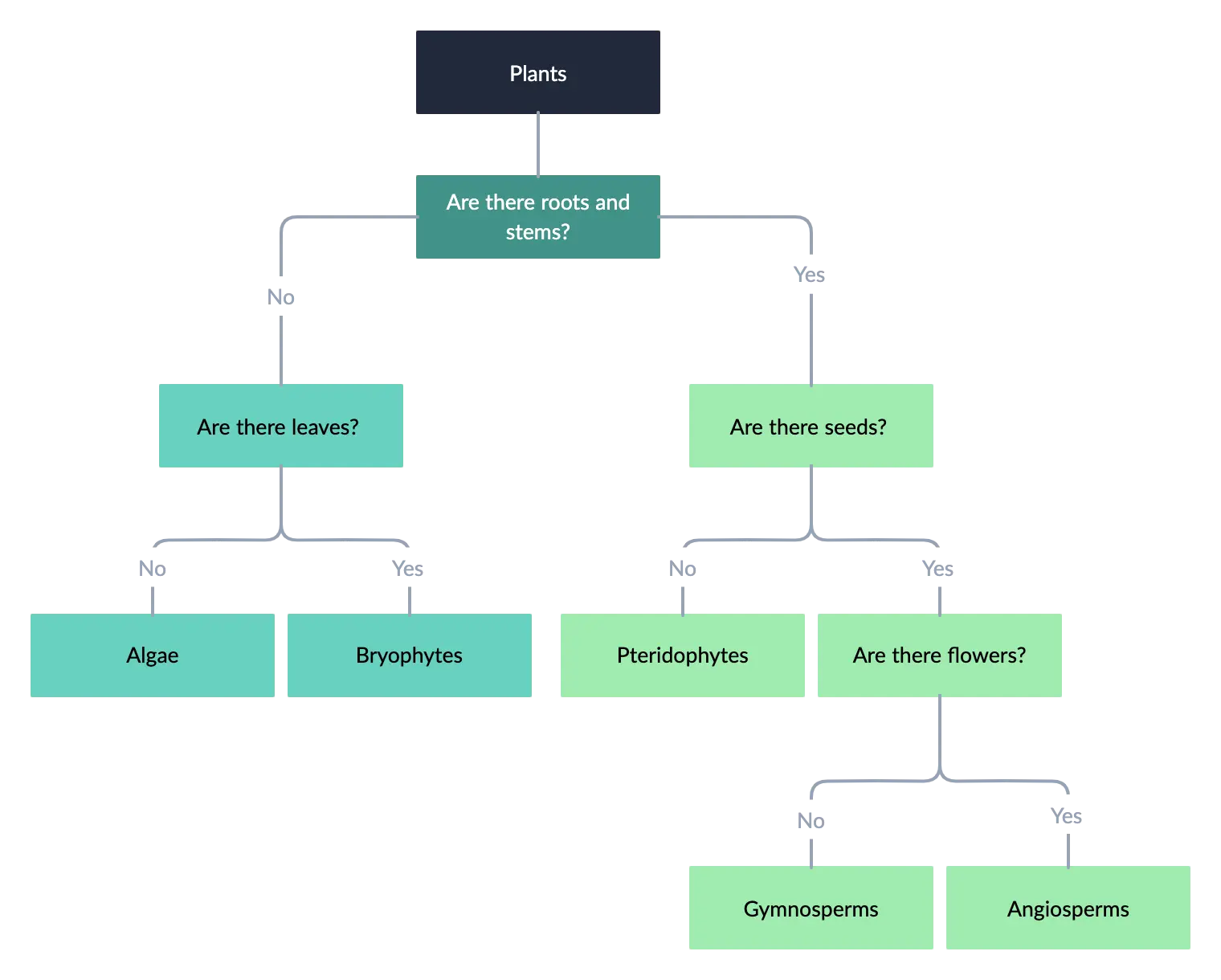
Dichotomous key for plants
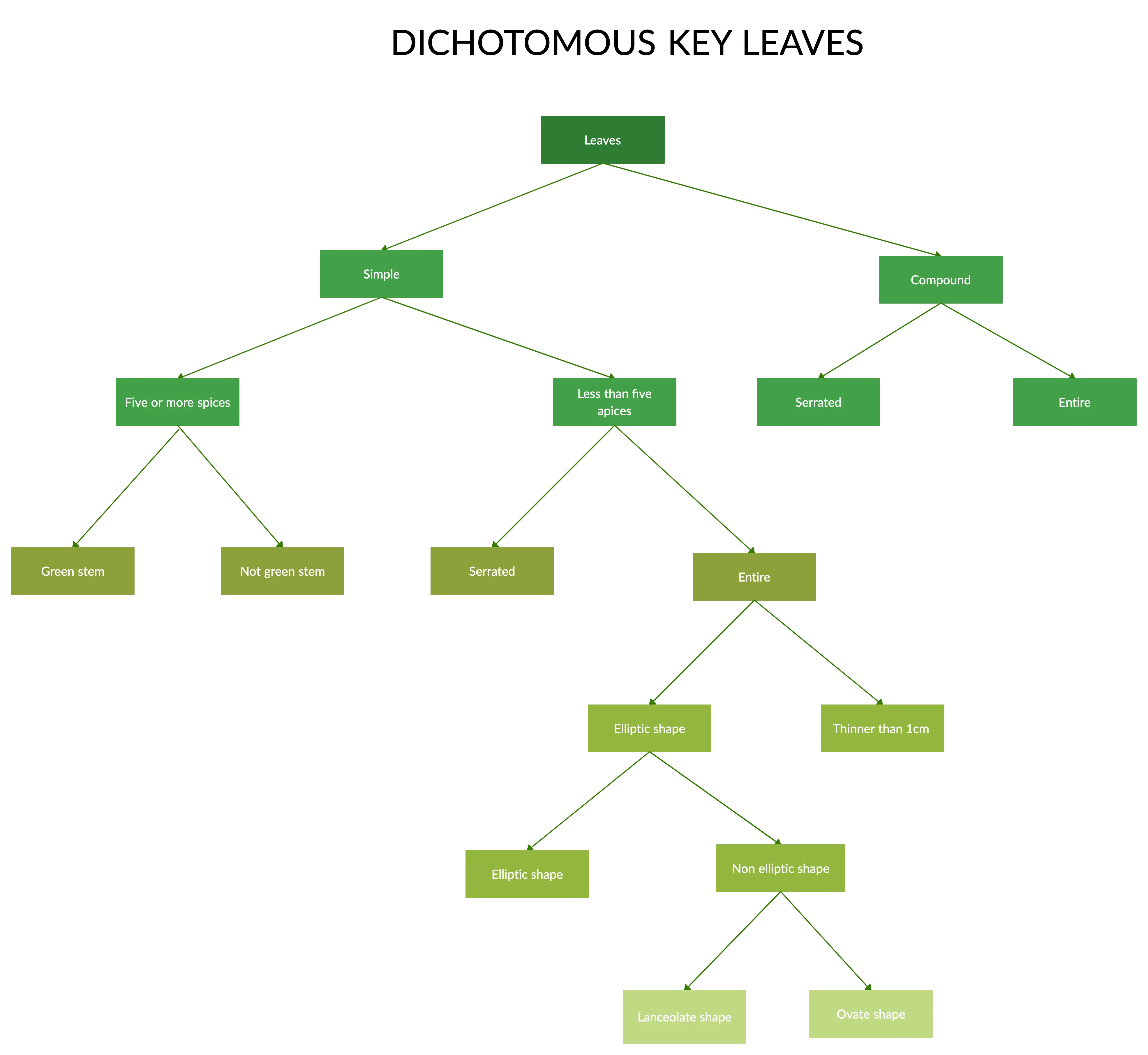
Dichotomous key for leaves
Benefits of Dichotomous Key
Dichotomous keys offer several benefits in various scientific and educational contexts:
Accurate Identification: Dichotomous keys provide a systematic and accurate method for identifying organisms or objects by focusing on their key characteristics. This reduces the likelihood of misidentifications.
Easy to use: The keys are designed to be user-friendly, so they can be used by everyone from students to experts.
Consistency: Dichotomous keys follow a standardized format, using specific terminology and criteria, so that different users can consistently get to the same identification for the same item.
Great for learning: Dichotomous keys help students learn to observe, compare, and understand the characteristics of different organisms, so they can better understand the natural world.
Useful in research: In scientific research, these keys are useful for cataloging and documenting biodiversity, which is important for understanding species relationships and ecological dynamics. S
Helps with field work: Dichotomous keys are portable and can be used in the field, which makes them ideal for on-site surveys, ecological studies, and biodiversity assessments.
Any More Tips on Making a Dichotomous Key?
We hope that this guide will help you familiarize yourself with the dichotomous key method. Make use of the editable templates to get a headstart in class. Invite your friends/ students to edit them online, and make a fun group activity out of it.
Any more useful tips on creating a dichotomous key that our readers can rely on? Do share them in the comments section below.
FAQ About Dichotomous Keys
What are the different types of dichotomous keys?
Dichotomous keys are categorized into different types based on their form.
Nested style – This style of dichotomous keys shows the next identification question nested under its answer. Each question is indented, and as the dichotomous key grows, each question will be indented further from the one after to keep the chart organized.
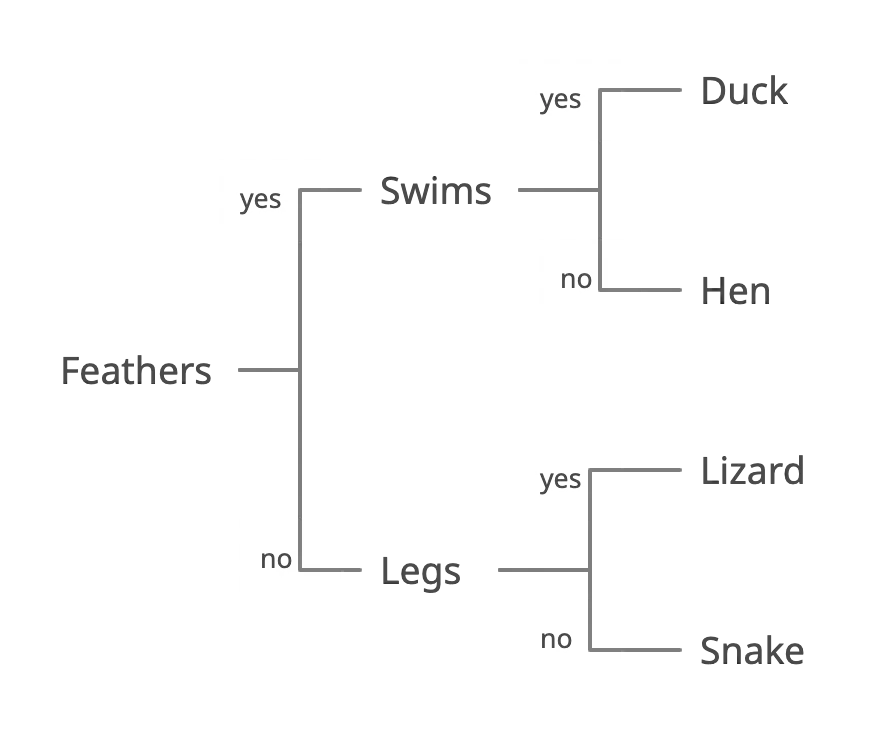
Linked dichotomous key – This type of dichotomous key has questions written in a listed form, one after the other. Each answer on a row will lead to a question in a different line.

Branching tree – This is one of the most common types of dichotomous keys. It takes a tree diagram form where each question or characteristic of the organism forms a new branch of the tree.
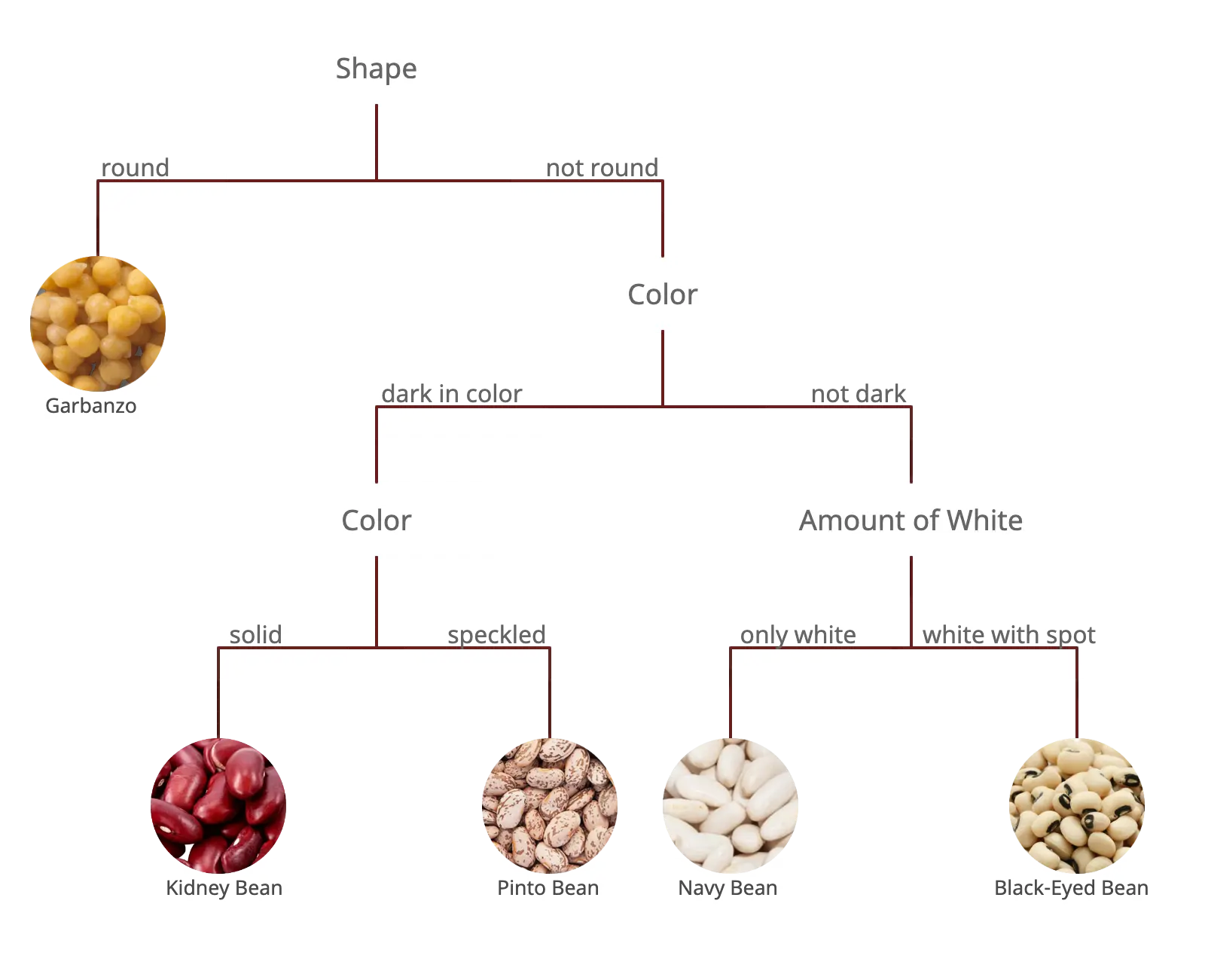
How does a dichotomous key work/ how to use a dichotomous key?
A dichotomous key work by asking questions about an organism to which there is only a yes or no response. Depending on the yes or no answer, the researcher is taken on a certain path through levels of classification until the organism is identified. Before using the dichotomous key, the researcher should have some knowledge about the features of the type of organism being investigated.
What tools do you need to create a dichotomous key?
You can easily create a dichotomous key diagram on paper using a pen for drawing and pictures to paste on it for better classification. You can also use an online tool or software that will allow you to create the dichotomous key diagram online. This kind of tool comes with intuitive diagramming capabilities, features to add images, downloading the diagram in different image formats suitable for embedding and taking printouts, and also collaboration capabilities with which multiple people can work together on the same dichotomous key diagram.