A product manager plays a crucial role in bringing great ideas to life. They are the bridge between customers, business goals, and development teams, ensuring that products are valuable, feasible, and marketable. But what exactly does a Product Manager do?
This guide will break down product manager roles and responsibilities in a clear and practical way. Whether you’re considering a career in product management or just want to understand how this role impacts businesses, you’ll find everything you need to know right here.
What Is a Product Manager?
A product manager (PM) is the person responsible for making sure a product solves the right problems for the right people. They connect business goals, customer needs, and technical development to create products that people love and businesses thrive on.
Think of a product manager as the captain of a ship—they don’t build the ship themselves, but they decide where it’s going, why it’s going there, and how to get there efficiently. They work with designers, engineers, marketers, and executives to define what should be built, ensure it meets user needs, and guide it from an idea to a real product.
A great PM listens to customers, studies the market, prioritizes the most important features, and makes trade-offs when needed. They don’t just focus on what’s possible today—they think ahead, plan strategically, and ensure that their product keeps evolving to stay relevant and competitive.
At its core, product management is about solving problems. A product manager’s job is to figure out what problems exist, which ones are worth solving, and how to create the best possible solution.
10 Core Responsibilities of the Product Manager
A product manager wears many hats, but at the heart of the role is one simple goal: build the right product for the right people. To do that, they take on a variety of responsibilities that shape the success of a product. Let’s take a look at the project manager responsibilities and project manager duties.
1. Understanding and representing user needs
A great product solves real problems. A PM listens to customers, gathers feedback, and ensures that what’s being built actually helps users. This means talking to customers, analyzing customer pain points, and making decisions based on what will bring them the most value.
2. Gather market research and competitive analysis
It’s not enough to know what customers want—you also need to understand the bigger picture. A PM conducts industry analysis and competitive analysis, and looks for gaps in the market. This helps the team build products that stand out and stay ahead of the competition.
3. Defining product vision and strategy
Where is the product headed, and why? A PM sets the long-term vision for a product and builds a product strategy to bring it to life. This means answering big-picture questions like: What problem are we solving? Who are we solving it for? How does this fit into the company’s goals?
4. Building and managing the product roadmap
A product roadmap is a plan that outlines what features or improvements will be built and when. A PM prioritizes what’s most important and ensures that the team is focused on delivering the right things at the right time.
5. Gathering and prioritizing product requirements
A product can’t have everything at once, so a PM decides and plans which features are a must-have, which are nice-to-have, and which can wait. This requires balancing user needs, business goals, and technical feasibility.
6. Overseeing product development and lifecycle management
From the first idea to launch and beyond, a PM keeps the product moving forward. They work closely with engineers, designers, and other teams to ensure that what gets built matches the vision and meets quality standards.
7. Collaborating with cross-functional teams
Product management isn’t a solo job. A PM works with engineering, design, marketing, sales, customer support, and leadership to bring a product to life. Good communication and teamwork are key to making everything run smoothly.
8. Setting product pricing and positioning strategies
How much should a product cost? Who is the ideal customer? How should it be marketed? A PM works with business and marketing teams to figure out the best way to position and price the product in a way that drives sales and keeps it competitive.
9. Managing product launches and marketing initiatives
A great product needs a great launch. A PM helps coordinate the release strategy, making sure that marketing, sales, and support teams are ready. They ensure that customers know about the product, understand its value, and are excited to use it.
10. Monitoring product performance and iterating based on feedback
The work doesn’t stop after launch. A PM keeps an eye on how the product is performing, looks at customer feedback and data, and decides what needs to be improved. This cycle of launch, learning and improving keeps the product relevant and successful over time.
7 Key Skills and Competencies Required of a Product Manager
A product manager needs a mix of skills to succeed. It’s not just about coming up with great ideas—it’s about making them happen. Here are the key product manager skills that set top PMs apart:
1. Analytical and problem-solving skills
One of the key product manager qualifications is to identify problems and find the best solutions. This means digging into data, understanding user pain points, and making smart, informed decisions. Whether it’s figuring out why users are dropping off or deciding which feature to build next, strong analytical thinking is essential.
2. Strong communication and interpersonal abilities
Product managers work with many different teams—engineering, design, marketing, sales, and executives. Clear workplace communication ensures that everyone is aligned and moving in the same direction. Whether it’s explaining the product vision, writing clear requirements, or handling tough conversations, a PM needs to get their message across effectively.
3. Leadership and team management
Even though a PM doesn’t usually have direct authority over teams, they still need to lead and inspire. A great PM motivates teams, removes roadblocks, and creates an environment where people can do their best work. It’s about influence, not control—getting people excited and focused on a shared goal.
4. Business acumen and strategic thinking
A product isn’t just about cool features—it needs to drive business success. One of the key product manager skills is to understand market trends, customer needs, and how the product fits into the bigger picture. They make decisions that balance customer value, business growth, and technical feasibility.
5. Technical proficiency and understanding
While a PM doesn’t need to code, they do need to understand how technology works. This helps them communicate effectively with developers, assess technical trade-offs, and make informed decisions about what’s possible and realistic.
6. Customer-centric mindset
The best PMs are obsessed with the customer. They listen to feedback, study user behavior, and make sure every product decision improves the customer experience. It’s not just about what the company wants—it’s about what truly benefits the user.
7. Adaptability and resilience
Things don’t always go as planned. Priorities shift, roadmaps change, and unexpected challenges come up. A great PM stays flexible, adapts quickly, and doesn’t get discouraged by setbacks. Instead, they find new ways forward and keep the momentum going.
Product Manager Qualifications
There’s no single path to becoming a product manager, but most successful PMs have a mix of education, experience, and skills that prepare them for the role. Here’s what typically matters as product manager qualifications:
1. Educational background
While there’s no strict degree requirement, most Product Managers come from backgrounds like:
- Business (MBA, marketing, management, or economics) – Helps with strategy, market positioning, and business growth.
- Computer science, engineering, or IT – Useful for working with technical teams and understanding product feasibility.
- Design or psychology – Helps in building user-friendly products with a customer-first mindset.
That said, many great PMs come from diverse fields, including journalism, healthcare, and finance, proving that experience matters more than a specific degree.
2. Work experience
Most PMs don’t start as Product Managers right away. Many transition from roles like:
- Business Analyst (understanding market needs and trends)
- Software Engineer (building and improving tech products)
- Marketing or Sales (understanding customer behavior and positioning)
- UX/UI Designer (creating user-centered experiences)
- Project Manager (managing timelines and execution)
The key is having experience in problem-solving, working with teams, and making data-driven decisions.
3. Certifications and training
While not mandatory, product management certifications can help build relevant skills, especially for career changers. Popular options include:
- Certified Scrum Product Owner (CSPO) – Focuses on Agile and Scrum methodologies.
- Pragmatic Institute Certifications – Covers strategy, market research, and go-to-market execution.
- Google/Amazon Product Management Courses – Offer industry insights from leading tech companies.
4. Industry knowledge
Understanding the market, customer needs, and competition is critical. Whether it’s tech, healthcare, finance, or retail, knowing the industry’s challenges and opportunities makes a big difference.
Product Manager Key Deliverables
As a product manager, the goal is to create products that truly meet user needs and business goals. To achieve this, a PM must deliver key items that guide the product development process and ensure the product’s success. Here are the key deliverables a PM is responsible for:
1. Product vision and strategy
A PM defines where the product is headed and why it matters. The product vision provides a clear picture of what the product will be in the future, while the strategy outlines how the PM plans to get there. These documents align the entire team around a shared goal.
2. Product roadmap
A product roadmap is like a blueprint for the product’s journey. It outlines what features and improvements will be worked on and when they’re expected to be completed. The roadmap helps everyone—from developers to marketers—understand the product’s direction and priorities.
3. Product requirements document (PRD)
The PRD is a detailed guide that explains what the product should do and how it should work. It includes things like user stories, feature descriptions, design specifications, and success metrics. This document is key for the development team to build the product correctly.
4. Go-to-market plan
A go-to-market (GTM) strategy is essential for launching a product successfully. This plan outlines how the product will be introduced to customers, what messaging will be used, and the marketing efforts required. It ensures that everyone, from sales to customer support, is aligned on how to promote and support the product.
5. Product backlog
The product backlog is a prioritized list of features, improvements, and bug fixes that need to be done. It’s a living document that is constantly updated, ensuring the team is always focused on the most valuable tasks next.
6. Metrics and performance reports
Once a product is live, the PM needs to track its performance. This includes defining key performance indicators (KPIs) like user engagement, revenue, or customer satisfaction, and regularly reporting on how well the product is doing. The goal is to measure success and identify areas for improvement.
7. Post-launch evaluation
After a product is launched, the PM evaluates how it performed against expectations. They gather customer feedback, analyze usage data, and work with teams to iterate on improvements. This ensures the product continues to evolve and meet user needs.
8 Types of Product Managers
Product management is a dynamic field with various roles tailored to different aspects of product development and business needs. Here are some common types of product managers:
1. Generalist product manager
A generalist product manager oversees a product’s entire lifecycle, from ideation to launch and beyond. They handle a broad range of tasks, including market research, user feedback analysis, and cross-functional team coordination. This role requires versatility and a comprehensive understanding of the product and its market.
2. Technical product manager
Technical product managers focus on products with significant technical components, such as software platforms or complex systems. They often have a background in engineering or computer science, enabling them to collaborate effectively with development teams and understand technical constraints.
3. Data product manager
Data product managers specialize in products that handle large volumes of data, like analytics platforms or data-driven applications. They work closely with data scientists and engineers to ensure data quality, define data collection requirements, and develop features that leverage data insights.
4. Growth product manager
Growth product managers concentrate on strategies to expand the user base and increase engagement. They analyze user behavior, run experiments, and implement features designed to drive user acquisition and retention.
5. Product marketing manager
Product marketing managers focus on positioning and promoting products to the market. They conduct market research, develop messaging strategies, and collaborate with sales teams to ensure the product meets customer needs and stands out in the market.
6. UX product manager
UX product managers prioritize user experience, ensuring that products are intuitive and user-friendly. They conduct user research, create wireframes, and work closely with design teams to enhance the overall user experience.
7. AI product manager
AI product managers oversee products that incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies. They collaborate with data scientists and engineers to develop intelligent solutions that automate processes and personalize user experiences.
8. Product operations manager
Product operations managers focus on streamlining processes within the product lifecycle. They manage data infrastructure, optimize workflows, and ensure efficient cross-functional collaboration to enhance product development and delivery.
Product Manager vs. Product Owner
Over time, the roles of Product Manager (PM) and Product Owner (PO) have evolved as organizations grow and adapt to changing market needs. While the core responsibilities of each role remain somewhat distinct, the lines between them can blur, especially in smaller teams. In some organizations, the Product Manager is more strategic, overseeing the entire product lifecycle, while the Product Owner is more focused on tactical tasks, working directly with the development team.
However, in many companies, these roles have become more collaborative, with Product Managers and Product Owners working closely to ensure a product’s success. In larger organizations, the roles tend to be split more clearly, with the Product Manager focusing on the “big picture” and the Product Owner handling the day-to-day details of development.
| Aspect | Product Manager | Product Owner |
| Role Focus | Strategic, focused on product vision and business goals. | Tactical, focused on executing the product vision in development. |
| Key Responsibilities | Defines product strategy, vision, and roadmap. Ensures alignment with business goals. | Manages the product backlog, ensures the development team understands product requirements. |
| Interaction with Teams | Works with marketing, sales, executives, and customers. | Primarily works with the development team. |
| Customer Involvement | Gathers customer insights and feedback to shape the product. | Ensures the product is built to meet customer needs, but is less involved in gathering insights. |
| Decision-Making | Makes high-level strategic decisions. | Makes decisions on product features and backlog priorities. |
| Time Horizon | Long-term focus (1 year or more). | Short-term focus (sprints or weeks). |
| Product Roadmap | Defines the overall product roadmap. | Ensures that the roadmap items are implemented and delivered. |
| Role in Execution | Oversees product launch, positioning, and market strategy. | Ensures that the development team executes on the features and functionality. |
Read more: Product Manager vs Product Owner: Key Differences
Best Practices and Tips for Becoming a Great Product Manager
Being a great Product Manager goes beyond just managing tasks; it’s about creating products that meet user needs, drive business goals, and evolve with changing markets. Here are some key best practices and tips to help you excel in your role:
1. Continuous user engagement and feedback loops
Engaging with users regularly helps you understand their pain points and needs. This allows you to create better products and improve existing ones.
How to do it:
- Set up channels for continuous user feedback, such as surveys, user interviews, or in-app feedback tools.
- Regularly interact with users through customer support, online forums, or user testing to stay updated on their experience.
- Act on feedback quickly and iteratively to show users that their input matters.
2. Data-driven decision-making
Making decisions based on data rather than assumptions reduces risk and ensures you’re creating the right features.
How to do it:
- Use analytics tools to track user behavior, performance metrics, and product usage patterns.
- Regularly review key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of your product.
- A/B test new features to validate ideas before making big changes.
3. Agile and iterative development methodologies
Agile helps you adapt to changes and deliver product updates more frequently, keeping the product aligned with market demands.
How to do it:
- Break the product development process into smaller, manageable tasks (sprints) that can be completed quickly.
- Focus on delivering a minimum viable product (MVP) and then iterate based on user feedback.
- Hold regular sprint reviews and retrospectives with your team to discuss progress and adjust goals.
4. Clear documentation and communication channels
Clear communication ensures all team members are on the same page and reduces misunderstandings.
How to do it:
- Create detailed product roadmaps and backlogs that everyone can access and refer to.
- Document requirements, user stories, and decisions so that nothing gets lost in translation.
- Set up communication tools and regular meetings to facilitate collaboration between product, development, marketing, and sales teams.
5. Ongoing market and competitive analysis
Understanding the market and competitors helps you stay ahead, identify opportunities, and avoid potential pitfalls.
How to do it:
- Monitor competitors regularly to identify gaps in the market and emerging trends.
- Analyze customer feedback and market research to ensure your product meets current demands.
- Adjust your product strategy as needed based on new market data or competitive shifts.
Helpful Resources
Learn the essentials of agile product management, a flexible approach that prioritizes adaptability, customer feedback, and continuous improvement.
Discover the 7-step product management process to effectively develop, launch, and refine products that meet customer needs and drive business growth.
Understand the key differences between product management and project management. Learn their unique roles, responsibilities, and how they work together to drive business success.
Discover the key responsibilities of a director of product, their role in product strategy, team leadership, and business growth.
Explore different product team structures, their benefits, and how to choose the right one for your organization.
Understand the differences between a product manager and a product owner, their unique roles, responsibilities, and how they collaborate to drive product success.
Using Creately to Simplify Product Manager Roles and Responsibilities
As a product manager, you need to handle a variety of tasks, from defining the product vision to making sure it gets to the market. Creately is a powerful tool that helps you manage and streamline many of these tasks. Here’s how Creately can help you become a more effective product manager.
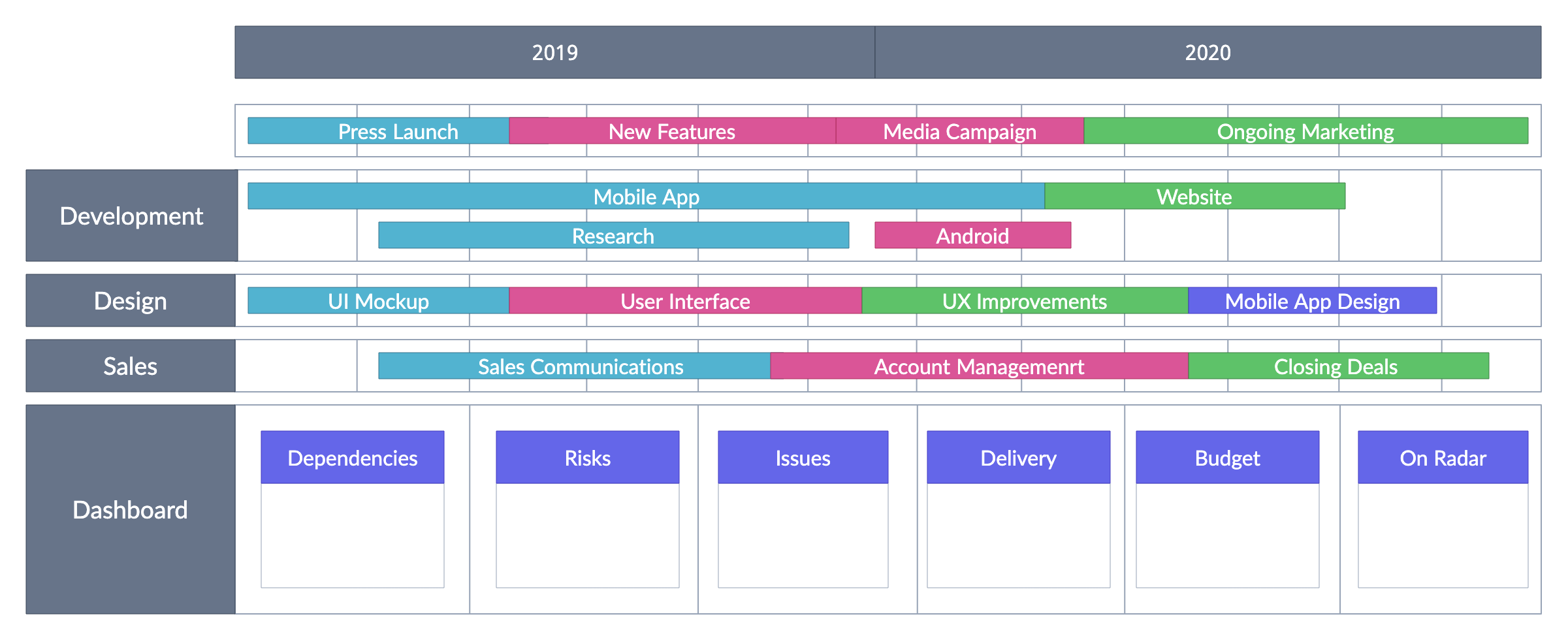
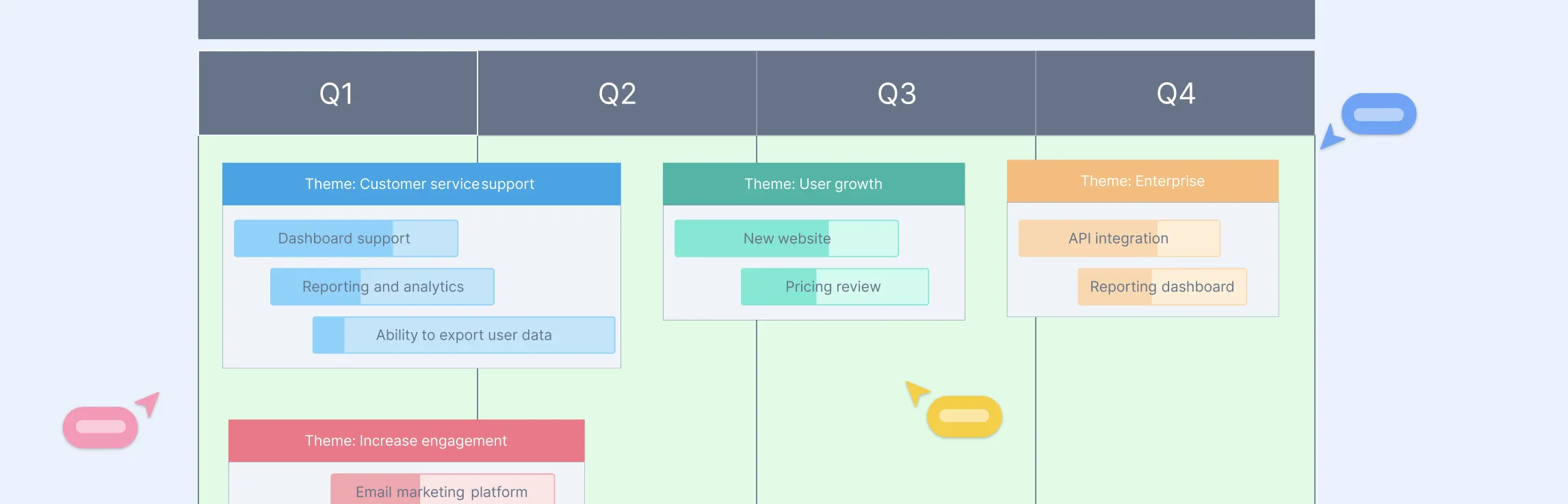
Create and manage roadmaps
A product roadmap keeps your team aligned and focused on the product’s goals. Creately offers easy-to-use product roadmap templates for creating roadmaps, so you can plan out your product’s journey. You can make real-time updates to your roadmap, making it clear for everyone involved and helping you track key milestones and deadlines.
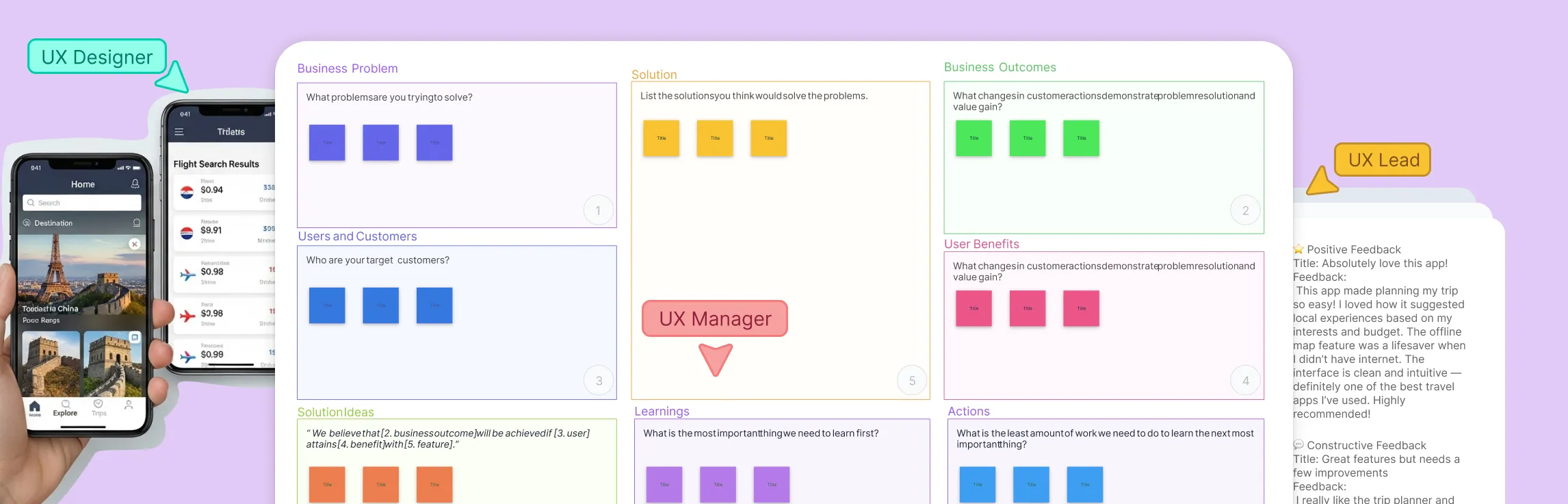
Map out user journeys
Understanding your customers is key to making a great product. With Creately, you can visually map out user journeys to see exactly how your customers interact with your product with customer journey maps. This allows you to identify pain points and make decisions that improve the user experience, making sure your product truly meets customer needs.
Collaborate with your team
Being a product manager means working with different teams—design, engineering, marketing, and more. Creately’s collaboration tools let you work together in real-time. Whether you’re making updates, sharing ideas, or asking for feedback, Creately makes communication easy with real-time editing and contextual comments and comment threads. You can also use Creately’s presentation mode to create dynamic presentations out of any element on the canvas to showcase ideas and get your team on the same page quickly.
Use brainstorming and voting tools
Creately comes with brainstorming tools like sticky notes, mind maps and notes to help you gather ideas. You can create an open-ended brainstorming board and let your team share their thoughts. After collecting ideas, use the voting tools to prioritize them, so you can focus on the most important features or tasks.
Combine templates to build a strategy
Creately lets you use multiple templates to build out your product strategy. For example, start with a brainstorming template, then move to a Business Model Canvas or Product Positioning Canvas to a Kanban board for task management. This lets you structure your thinking and ensure your product strategy is clear and well-organized.
Prioritize with visual tools
Prioritizing tasks or features can be tough, but Creately makes it easier with templates for prioritization matrices like RICE, Impact-Effort Matrix, and MoSCoW. These tools help you visually organize and prioritize what matters most, making it easier to decide where to focus your efforts.
Manage tasks with Kanban boards
Keeping track of tasks and progress is key to any project. Creately’s Kanban boards let you easily organize tasks, assign team members, and track deadlines. Whether it’s for product features, sprint tasks, or general to-dos, the Kanban board helps you stay on top of everything.
Integrate with GitHub and Jira
Creately integrates with tools like GitHub and Jira, which are commonly used in product development. You can sync data between Creately and GitHub, so any changes you make in one tool are reflected in the other. Creately gives you the ability to view your GitHub or Jira tasks from different perspectives, helping you manage your product in a visual way. Whether you’re tracking progress, prioritizing tasks, or analyzing dependencies, Creately’s visual approach makes it easier to see where things stand and what needs attention.
Use AI to streamline workflows with Creately VIZ
Creately VIZ, the AI-powered assistant, helps product managers work faster by automating tasks like creating Business Model Canvases, mind maps, and user journey maps. It can generate structured templates based on simple inputs, suggest relevant ideas, and organize complex information visually. This makes brainstorming, strategy planning, and workflow management much easier and more efficient.
Conclusion: Product Manager Roles and Responsibilities
Understanding product manager roles and responsibilities is key to driving product success. Being a great Product Manager isn’t just about managing tasks – it’s about building a product that truly meets the needs of users and helps the business grow. By focusing on user feedback, making decisions based on data, adopting agile methods, and keeping clear communication, you’ll ensure your product delivers real value.
The world of product management is always changing, and the best Product Managers are those who stay curious, adaptable, and proactive. Keep learning, collaborating with your team, and staying open to new ideas. This will help you create products that solve real problems and make a difference for your customers and the business.
By embracing the product manager roles and responsibilities, you’ll be well on your way to mastering the role and driving success for both your product and your company.
References
Maglyas, A., Nikula, U. and Smolander, K. (2013). What are the roles of software product managers? An empirical investigation. Journal of Systems and Software, 86(12), pp.3071–3090. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2013.07.045.
Majka, M. (2024). The Role of a Product Manager. [online] Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/381847111_The_Role_of_a_Product_Manager.