In an increasingly complex world, managing risks and ensuring safety are critical for businesses across all industries. Event Tree Analysis (ETA) is a systematic and powerful method for evaluating the outcomes of initiating events and understanding potential risks by visually mapping possible scenarios and their probabilities. For professionals responsible for risk assessment, safety management, or compliance, mastering Event Tree Analysis is a valuable skill. This guide not only explains the fundamentals of ETA but also shows how tools like Creately make the process efficient and collaborative, ensuring that teams can focus on delivering better safety outcomes.
What Is Event Tree Analysis?
Event Tree Analysis (ETA) is a systematic, logical approach used to evaluate the potential outcomes of an initiating event. This analytical method helps organizations assess various scenarios that could result from a single occurrence, highlighting the probabilities of success or failure at each step. By mapping out possible sequences of events, event tree analysis provides a clear visualization of risks and opportunities, making it an invaluable tool for decision-making processes.
The primary purpose of event tree analysis is to identify potential risks and mitigate their impact by understanding how an event can evolve. By analyzing each branch of an event tree, decision-makers can uncover hidden vulnerabilities, enhance system reliability, and prioritize safety improvements. This structured methodology ensures that even the most complex scenarios are broken down into manageable components, fostering better risk management and operational efficiency.
The significance of event tree analysis is recognized across various industries such as aerospace, nuclear power, chemical manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, and more. These sectors leverage event tree analysis for its ability to model cause-and-effect relationships in complex environments, ultimately improving safety measures and fortifying system reliability. By analyzing event sequences early in the design phase, organizations can proactively mitigate risks, effectively guide decision-making, and adhere to stringent regulatory compliances.
How to Perform an Event Tree Analysis
Event tree analysis offers a structured approach to assess risks by charting all potential outcomes from an initial event. Here’s a simple guide to performing event tree analysis effectively:
Step 1: System Definition
The first step in any Event Tree Analysis is to clearly define the system or process that is being analyzed. This includes understanding the boundaries of the system, the components involved, and how different elements interact. By thoroughly understanding the system, you ensure that all potential risks are identified and the analysis remains focused and accurate. Without a clear definition, the analysis could overlook critical variables that impact the event outcomes.
Step 2: Identify Initiating Events
Initiating events are the starting points for the analysis. These are the occurrences or conditions that trigger a chain of events. Identifying initiating events is key to setting the scope for the analysis. They could be equipment failures, human errors, environmental factors, or any other situation that could lead to further risk scenarios. Once you pinpoint these initiating events, you lay the foundation for the subsequent analysis and mapping.
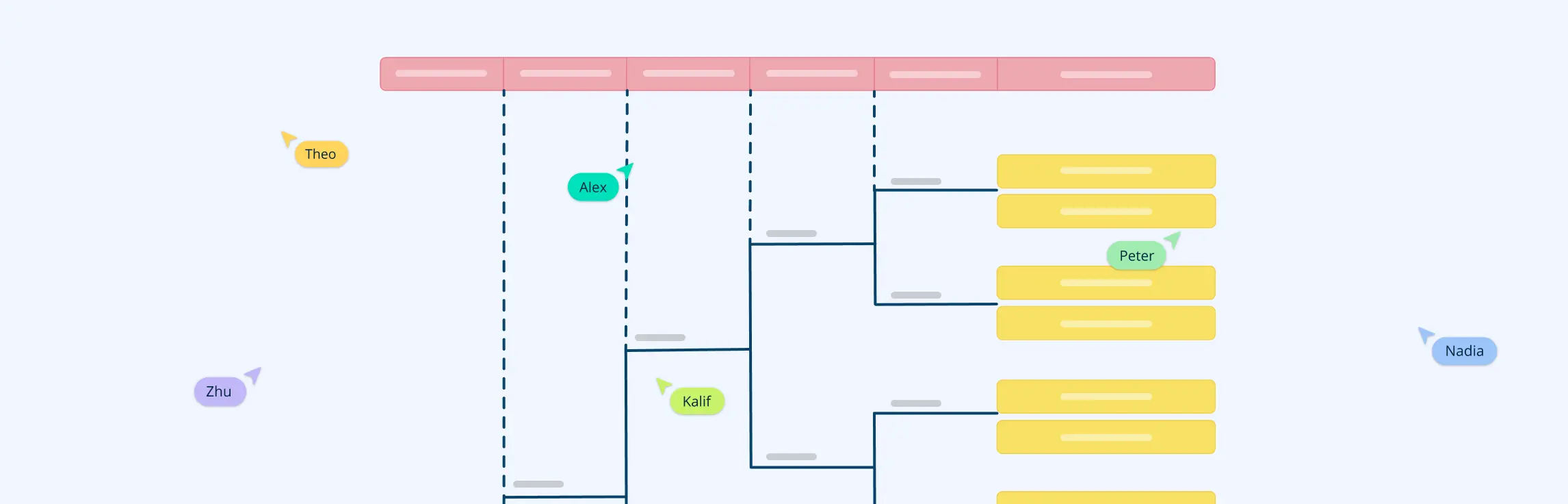
Step 3: Develop the Event Tree
Once the initiating events are identified, the next step is to develop the event tree. An event tree is a branching diagram that illustrates all possible outcomes from each initiating event. The branches represent different pathways, showing the progression of each event through a series of sequential occurrences. Each branch leads to either a success or failure outcome. This helps visualize how different conditions influence the potential results and how different events can influence each other.
Step 4: Assign Probabilities
After the event tree is created, the next important step is to assign probabilities to each event path. This involves estimating the likelihood of each branch happening based on available data, past experiences, and expert judgment. Accurate probability assignment is crucial to understanding the likelihood of various outcomes and calculating overall risk. Historical data, reliability statistics, and expert opinions help provide a reliable basis for these probabilities.
Step 5: Analyze and Evaluate Outcomes
With the event tree in place and probabilities assigned, the next step is to evaluate the potential outcomes. This involves assessing the consequences of each path, considering both the probability and the severity of each outcome. By combining these factors, you can evaluate the risk posed by each possible scenario. This helps prioritize which risks need to be addressed immediately and which ones require less attention.
Step 6: Document and Review
Finally, it’s important to document the findings of the Event Tree Analysis in a comprehensive report. The report should include details of the initiating events, the event tree diagram, probability assessments, and the evaluated outcomes. Regular reviews are necessary to ensure the analysis remains relevant over time, especially when systems or conditions change. Revisiting and updating the event tree as new data becomes available or as system conditions evolve ensures that the risk analysis remains current and effective.
By following these steps, Event Tree Analysis provides a structured approach to unraveling complex risk scenarios, helping organizations proactively manage risks, improve system reliability, and implement safety measures that mitigate potential failures.
Event Tree Analysis Example
Let’s consider a real-world scenario where ETA can be applied: a manufacturing company operating a production line with automated machinery. One of the key risks identified is the potential failure of a machine’s temperature control system, which could lead to overheating.
Applying Event Tree Analysis to the Scenario
- Identify the Initiating Event: The initiating event in this case is the failure of the temperature control system.
- Define the Possible Outcomes: The next step is to map out the potential outcomes of this failure:
- Outcome 1: The system’s automatic shutdown mechanism activates, preventing overheating.
- Outcome 2: The temperature monitoring alert notifies the operator, who intervenes manually.
- Outcome 3: Neither the shutdown nor the alert functions correctly, leading to equipment overheating and possible fire hazards.
- Assign Probabilities: Probabilities are assigned to each branch based on historical data, system reliability metrics, and expert judgment:
- Automatic shutdown: 70%
- Operator intervention: 20%
- System failure leading to fire: 10%
- Evaluate Outcomes: Event tree analysis provides insights into the likelihood of each scenario and its potential impact. This helps the company prioritize safety measures, such as improving the reliability of the alert system or implementing redundant safety mechanisms.
Who Uses Event Tree Analysis
Event tree analysis plays a crucial role in safety assessments by helping organizations anticipate and mitigate potential risks. This proactive approach ensures that safety protocols are well-prepared to handle unforeseen situations, preventing accidents and minimizing risks.
One of the key strengths of ETA in safety is its ability to identify vulnerabilities within systems. For example, in high-risk industries, such as nuclear power and aerospace, ETA helps predict how specific events, like system malfunctions or human errors, might evolve. By mapping out these potential outcomes, safety teams can develop strategies to either prevent or effectively respond to undesirable situations.
Event tree analysis examples are widely used across various industries to enhance safety and operational reliability. Let’s explore how different sectors leverage this method:
Healthcare
Hospitals and medical facilities use event tree analysis to assess risks associated with patient care, such as equipment malfunctions, medication errors, or emergency response delays. By understanding potential outcomes, healthcare providers can refine procedures and improve patient safety.
Oil and Gas Industry
The oil and gas industry uses event tree analysis to evaluate risks in exploration, drilling, and transportation processes. For example, it can analyze the consequences of equipment failures, gas leaks, or pipeline ruptures, enabling companies to develop robust emergency response plans.
Environmental Auditing
Event Tree Analysis plays a pivotal role in environmental auditing by evaluating potential risks associated with pollution, resource depletion, or hazardous waste management. For example, ETA can assess the consequences of a spill in a water body, exploring outcomes such as containment success, cleanup delays, or long-term ecological damage. This structured approach helps organizations identify vulnerabilities, implement effective mitigation strategies, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations, promoting sustainable and responsible operations.
Transportation
Railways, shipping, and road transport sectors leverage event tree analysis to evaluate risks related to collisions, infrastructure failures, or weather-related disruptions. By predicting outcomes, operators can enhance safety protocols and reduce accidents.
Chemical Industry
Event tree analysis is critical for assessing the risks of chemical reactions, storage failures, or equipment malfunctions. It aids in the development of containment strategies and emergency plans to mitigate hazardous incidents.
Energy Production
Renewable energy sectors, such as wind and solar, also use event tree analysis to model risks associated with equipment failures, grid disruptions, or extreme weather events. These insights help ensure continuous energy supply and system reliability.
Aerospace
In aerospace, event tree analysis is vital for assessing risks associated with aircraft operations. By simulating accident scenarios, engineers can design customized preventive measures, ensuring passenger and crew safety while maintaining regulatory compliance.
Nuclear Power
The nuclear power sector relies on event tree analysis to model potential failure pathways that could lead to critical incidents, such as reactor malfunctions or radiation leaks. These insights guide the development of safety protocols to prevent catastrophic outcomes, protecting both the environment and human lives.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, event tree analysis helps identify potential equipment failures or process bottlenecks. By analyzing these scenarios, companies can implement strategic maintenance schedules, reduce unplanned downtime, and improve overall productivity.
These ETA examples demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of the technique in addressing complex safety challenges. Each industry tailors event tree analysis to its unique requirements, enabling informed decision-making and fostering a culture of safety and reliability.
Benefits of Event Tree Analysis
Event tree analysis offers numerous benefits, making it an essential tool for risk management and safety planning across industries. Here are some key advantages:
1. Proactive Risk Identification
Event tree analysis helps organizations identify potential risks and their outcomes before they occur, allowing for proactive measures to mitigate threats.
2. Improved Decision-Making
By visualizing the potential outcomes of an initiating event, event tree analysis provides a clear framework for decision-makers to evaluate risks and prioritize safety measures effectively.
3. Enhanced Safety and Compliance
Event tree analysis ensures that safety protocols are robust by identifying vulnerabilities in existing systems, helping organizations comply with industry safety standards and regulations.
4. Cost-Effective Risk Management
By predicting and addressing potential failures, event tree analysis reduces the likelihood of costly incidents, saving resources on reactive solutions.
5. Supports Continuous Improvement
The insights gained from event tree analysis can be integrated into organizational processes to drive ongoing safety improvements and operational efficiency.
With its ability to systematically evaluate risks and outcomes, event tree analysis empowers businesses to safeguard their operations while optimizing safety strategies. Tools like Creately make the process even more efficient by simplifying the creation and visualization of complex event tree analysis diagrams, enabling teams to collaborate effectively and make data-driven decisions.
How to Create Event Tree Analysis Diagrams with Creately
Creately is a powerful visual collaboration platform designed to simplify the process of creating and managing Event Tree Analysis diagrams. Its intuitive interface, ready-to-use templates, and real-time collaboration features make it the go-to tool for teams looking to streamline their risk analysis efforts.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to using Creately for creating Event Tree Analysis diagrams:
1. Start with a Template
Creately offers pre-designed event tree analysis templates to help you get started quickly.
- Navigate to the template library and search for “Event Tree Analysis.”
- Choose a template that fits your scenario and load it into the workspace.
- These templates are fully customizable, so you can tailor them to suit your specific needs.
2. Customize Your Diagram
- Use the drag-and-drop interface to add, edit, or rearrange branches of your event tree.
- Label each branch with initiating events, intermediate steps, outcomes, and probabilities.
- Incorporate visual elements like color-coding to distinguish different paths or outcomes, making the diagram easier to interpret.
3. Link Data to Your Diagram
- You can directly add data from external sources to your diagram as notes or links.
- Use this feature to include failure probabilities, risk factors, or historical data, keeping your analysis precise and well-informed.
4. Collaborate with Your Team
- Invite team members to collaborate on the diagram in real time.
- Use Creately’s in-app comments and video conferencing features to discuss updates or refine details.
- Assign specific tasks to team members using integrated project management features, ensuring accountability and progress tracking.
5. Export and Share Your Diagram
- Once your diagram is complete, export it in your preferred format, such as PNG, PDF, or SVG.
- Share it with stakeholders or embed it directly into presentations, reports, or documentation for a professional touch.
Helpful Resources
Uncover potential system failures, analyze their causes, and develop preventive measures.
Explore the methodology, tools, and applications of FTA to transform failure scenarios into manageable solutions.
Discover how to identify potential threats, visualize risks, prioritize actions, and allocate resources efficiently.
Gather information about potential risks and vulnerabilities within an organization to systematically evaluate various risks.
Event Tree Analysis (ETA) and Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
Event Tree Analysis (ETA) and Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) are both powerful risk analysis tools, but they approach risk assessment from different perspectives. The table below highlights the key differences and similarities between ETA and FTA:
Aspect | Event Tree Analysis (ETA) | Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) |
| Purpose | Evaluates the outcomes of an initiating event and its possible consequences. | Identifies the causes or faults leading to a specific undesirable event. |
| Approach | Forward-looking (top-down): Starts with an initiating event and traces the possible outcomes. | Backward-looking (bottom-up): Starts with a specific undesirable event and works backward to find its causes. |
| Focus | Focuses on the consequences of events and the probability of their occurrence. | Focuses on identifying the root causes or failures that lead to a system's malfunction. |
| Diagram Type | Event tree diagram (branching diagram) showing different possible outcomes. | Fault tree diagram (inverted tree) showing logical relationships between failures. |
| Application | Used to analyze systems where multiple possible outcomes exist from a starting point, such as in safety or emergency scenarios. | Used to identify system vulnerabilities by pinpointing potential failures that lead to a critical incident or failure. |
| Probability Assignment | Each branch in the event tree has a probability assigned to its outcome based on available data. | The fault tree uses probabilities of failure for each component in the tree and the logical relationships to evaluate the likelihood of system failure. |
| Use Cases | Risk analysis in safety-critical industries such as aerospace, nuclear, chemical, and manufacturing. | Used for identifying and analyzing causes of system failure, common in engineering, nuclear, and safety-critical systems. |
| Strength | Excellent for assessing the impact of unexpected events and how different paths can lead to success or failure. | Excellent for determining what could go wrong in a system and identifying preventative measures at the component level. |
| Time Perspective | Focuses on potential future scenarios. | Focuses on analyzing past failures to prevent future occurrences. |
| Common Users | Safety engineers, risk managers, and operational planners. | Engineers, system reliability experts, and safety analysts. |
While both ETA and FTA are essential for risk assessment and safety planning, they serve different purposes. ETA is ideal for evaluating the potential consequences of an initiating event, while FTA focuses on identifying the causes of failures in a system. Both methods can be complementary when used together, providing a holistic view of risks and vulnerabilities in complex systems.
Wrapping Up: Elevate Your Risk Management with ETA
Event tree analysis is an indispensable tool for identifying and mitigating risks in any organization. By breaking down potential scenarios and assessing their outcomes, ETA empowers businesses to make informed decisions, enhance safety measures, and improve operational resilience. Industries ranging from aerospace to environmental auditing rely on ETA to navigate complexities and uphold safety standards.
Creately simplifies the process of creating event tree analysis diagrams with its intuitive templates, customization options, and real-time collaboration features. Whether you’re a seasoned safety professional or new to risk assessment, Creately’s tools ensure you can focus on analyzing risks without the hassle of designing complex diagrams from scratch.
FAQs about Event Tree Analysis
What is the purpose of Event Tree Analysis (ETA)?
What industries commonly use Event Tree Analysis?
How is Event Tree Analysis different from Fault Tree Analysis?
How does Creately simplify the creation of Event Tree Analysis diagrams?
Resources:
Andrews, J.D. and Dunnett, S.J. (2000). Event-tree analysis using binary decision diagrams. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 49(2), pp.230–238. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/24.877343.
Ferdous, R., Khan, F., Sadiq, R., Amyotte, P. and Veitch, B. (2009). Handling data uncertainties in event tree analysis. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 87(5), pp.283–292. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2009.07.003.