Successful businesses have a knack for developing a clear understanding of the skills and behaviors that drive growth. Many of the best companies use models that offer a structured way to define the key abilities required for employees to thrive in their roles and contribute to broader company objectives. They not only guide recruitment and performance evaluations but also help in career development and team alignment. By establishing a solid competency model, companies can ensure that they are equipped to meet their strategic goals with a capable and well-aligned workforce.
What is a Competency Model?
A competency model is a structured framework that defines the specific skills, behaviors, and knowledge required for employees to succeed in their roles. It serves as a roadmap for aligning employee performance with organizational goals, facilitating effective recruitment, development, and performance management. By clearly outlining these competencies, organizations ensure that all employees are equipped to perform their jobs efficiently and contribute to the company’s strategic objectives.
Competency models come in various forms, each offering unique benefits depending on the organization’s needs:
Integrating these models helps organizations streamline HR functions and optimize workforce capabilities. To explore structured approaches in competency modeling, try our Competency Framework Template
The Importance of Using A Competency Model:
Understanding the significance of competency models is crucial. They foster a cohesive work environment where employees are aligned with the company’s goals, thereby enhancing overall performance and growth. For a visual example, see the Competency Matrix Example, which illustrates how competencies are mapped across various roles.
Competency models offer significant advantages that drive organizational success across multiple areas. Their integration in the human resource management framework can profoundly enhance recruitment, communication, alignment with business strategy, and performance evaluation processes.
Improves Accuracy in Recruitment:
By detailing the specific skills and knowledge required for roles, competency models help streamline the recruitment process. They ensure job descriptions are precise, which attracts candidates who truly fit the role requirements with an effective recruitment process.
Enhances Team Communication:
Competency models clarify roles and responsibilities, leading to more effective communication within teams. This understanding fosters a collaborative environment, making team interactions more productive. Discover strategies for improving communication in the workplace with our guide on Team Communication.
Aligns Business Strategy:
Competencies foster alignment between employee skills and organizational goals, creating a workforce equipped to meet strategic objectives efficiently.
Fair and Consistent Performance Evaluation:
With clear competency criteria, performance evaluations become standardized and objective, reducing biases and ensuring a fair assessment of employee performance.
By utilizing competency models, organizations can establish a robust framework for HR functions, ultimately leading to improved employee performance and a competitive edge in the market.
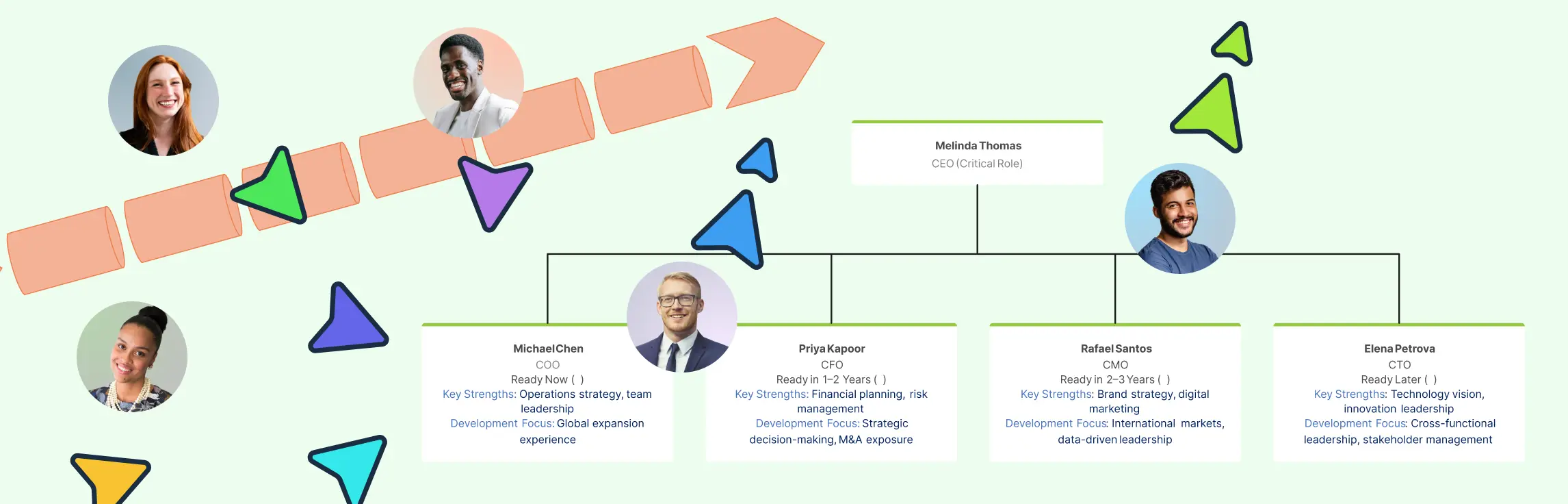
Core Elements of a Competency Model
A competency model is a comprehensive framework that outlines the key skills, behaviors, and knowledge required for employee success. By understanding its core elements, organizations can better align their workforce capabilities with strategic objectives. Here, we explore the essential components that constitute a robust competency model.
Core Competencies
Core competencies are foundational capabilities crucial for all employees, reflecting the company’s values and strategic aims. These competencies ensure that every team member aligns with the organizational goals, fostering a unified culture. Common examples include effective communication, adaptability, and a strong customer focus. By integrating these competencies, companies can optimize HR functions and drive strategic success.
Functional Competencies
Functional competencies are specialized skills and knowledge essential for specific roles or departments. They highlight the technical requirements needed to perform a job effectively, which may vary significantly from one department to another. For instance, competencies in project management or data analysis may be necessary for particular team roles. These competencies allow organizations to bolster productivity by ensuring that team members possess the specialized skills necessary for their roles.
Leadership Competencies
Leadership competencies focus on strategic abilities required for those in management roles. They cover skills such as strategic thinking, decision-making, and team building, which are vital for guiding teams and driving organizational success. Recognizing these competencies helps organizations prepare future leaders who can navigate challenges and inspire their teams.
Companies can leverage with Talent Mapping Template to visually organize and map out these competencies. With features such as skill inventory and talent mapping, organizations can craft effective career development plans and improve HR planning efforts, which are crucial for enhancing team training and onboarding processes.
For detailed use cases in marketing and sales applications, the Creately Marketing & Sales Use Cases offer insights into implementing competency models effectively.
Types of Competency Models and Their Applications (with Templates)
Understanding the different types of competency models is crucial for effectively aligning them with specific organizational needs. Each model serves distinct purposes, facilitating the management of skills and behaviors across various roles and departments. Here, we delve into the four primary types of competency models and their applications:
Job Competency Model
A Job Competency Model focuses on the particular skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success in a specific role. By mapping out these role-specific essentials, organizations can tailor recruitment and training processes to attract and develop individuals who fit these exact needs.
Application: Primary used in recruitment to ensure candidates have the exact skills needed. It’s a foundation for role-specific training and performance evaluations.
Example: For a sales representative role, competencies might include customer relationship management, effective negotiation skills, and deep product knowledge.
Organizational Competency Model
The Organizational Competency Model outlines the key competencies vital for all employees, aligning with the company’s mission, values, and strategic objectives. These are the shared competencies that uphold organizational culture and drive collective goals.
Application: Ideal for fostering a unified corporate culture. It ensures that all employees, regardless of role, contribute to overarching business goals.
Example: Common competencies might include teamwork, effective communication, and commitment to quality, aligning with a company’s broader goals.
Functional Competency Model
A Functional Competency Model focuses on the technical skills and specialized knowledge needed within a particular department or business function. This model ensures employees possess the specific expertise required in their area.
Application: Enhances departmental efficiency by aligning employees’ skills with job duties. Useful for specialized training programs.
Example: In the IT department, required competencies may include software development, cybersecurity proficiency, and system optimization skills.
Leadership Competency Model
The Leadership Competency Model prioritizes competencies necessary for effective team management and strategic decision-making. It concentrates on nurturing skills that facilitate leadership and drive organizational success.
Application: Essential for developing current and emerging leaders. It supports leadership training and succession planning initiatives.
Example: Competencies such as strategic thinking, decision-making ability, and emotional intelligence are commonly included to guide team leaders effectively.
Each of these competency models supports different organizational objectives. For those looking to optimize and manage their workforce effectively, tools like the Skills Matrix Templates can be immensely beneficial. These templates assist in creating comprehensive competency frameworks tailored to organizational needs, ensuring a strategic alignment with business goals.
Developing a competency model is a strategic process that aligns workforce capabilities with organizational goals. To craft an effective model, follow this comprehensive guide divided into distinct phases, ensuring that your model meets the unique needs of your organization.
How To Create a Competency Model
Step 1: Define Purpose and Scope
Defining the purpose and scope of your competency model is the critical first step, as it shapes the foundation for all subsequent actions. Start by clearly articulating the primary goals of the model. Consider whether the focus will be on performance assessments, career development, addressing competency gaps, or a combination of these. Your decision will significantly influence the structure and content of the model.
Next, identify the intended users. Will the model be used by specific departments, leadership teams, or the entire organization? Knowing your audience ensures the model is tailored to their needs and relevant at different organizational levels.
Set clear, concrete objectives. Are you aiming to enhance recruitment accuracy, create career pathways to improve retention, or strengthen team communication by defining key interpersonal skills?
Lastly, decide on the model’s structure. Will it be based on company values, organized around job families, specific roles, or core competencies shared across the organization? You may also opt for a hybrid approach to create a comprehensive framework.
Key Considerations:
Articulate primary goals (performance assessment, career development, addressing skill gaps)
Identify intended users (departments, leadership, entire organization)
Specify concrete objectives (recruitment accuracy, career pathways, team communication)
Align with organizational values and strategic goals
Choose model structure (value-based, job families, roles, core competencies, or hybrid)
Step 2: Select a Relevant System
Selecting the right system for your competency model is critical to shaping how competencies are defined, evaluated, and developed. This step establishes the framework that will guide your competency-based initiatives.
1. Define Competency Types
Start by determining the types of competencies you will include. Will you focus solely on technical skills, or will you also incorporate soft skills and behavioral competencies? Clearly categorizing the types of competencies will ensure that your model is comprehensive and relevant.
2. Determine Proficiency Levels
Consider how many levels of proficiency to define for each competency. You may opt for a simple three-level system (e.g., basic, intermediate, expert) or a more nuanced five or six-level approach, depending on your organization’s needs. The goal is to provide enough detail to differentiate skill levels without making the system overly complex.
3. Distinguish Leadership vs. Individual Contributor Competencies
Decide if you will differentiate between competencies for leadership roles and those for individual contributors. Leadership competencies, such as strategic thinking and team management, are typically distinct from the skills required for non-managerial positions.
4. Set the Number of Competencies per Role
It’s essential to strike a balance between comprehensiveness and practicality. Too many competencies can make the model difficult to implement. As a guideline, aim for a maximum of 12 competencies for individual contributors and 15 for leaders to keep the model focused and manageable.
5. Define Proficiency Levels
Decide how you will represent proficiency levels—whether through a numerical scale, descriptive terms, or a combination of both. Ensure that your system clearly differentiates between levels and offers a pathway for development
Step 3: Define how proficiency levels will be described and measured
Conducting comprehensive research is a critical step in creating a relevant and effective competency model. This phase involves gathering data from various sources to ensure your model is grounded in the realities of your organization and industry.
Begin by reviewing internal documents. Analyze business plans and strategies to understand the direction your organization is heading. Study organizational charts to grasp the current structure and reporting relationships. Examine workforce data, including retention rates and engagement scores, to identify areas where competencies might need development. Review existing job descriptions to understand current role expectations.
Next, look beyond your organization. Analyze industry trends and future predictions relevant to your sector. This forward-looking approach ensures your competency model remains relevant as your industry evolves.
Conduct online research to supplement your internal data. Look at job advertisements from similar companies to see what skills and competencies they prioritize. Review existing competency frameworks from other organizations or industry bodies for inspiration.
Step 4: Compile and Organize Data
After conducting extensive research, the next crucial step is to compile and organize the collected data in a structured, accessible way. This organization is essential for identifying patterns, prioritizing competencies, and building a coherent framework.
1. Create a Digital Folder System
Start by establishing a well-structured digital folder system for all the data you’ve gathered. Use cloud-based tools like Google Drive or SharePoint to ensure easy access and collaboration. Organize folders by type of information, such as:
Business plans
Job descriptions
Survey results
Interview transcripts
2. Develop Summary Documents
Create summary documents that distill key points from each data source. Use bullet points, tables, and charts to make the information more digestible and easy to reference. This prevents the need to constantly revisit raw data and streamlines the process of analyzing key findings.
3. Categorize Data by Themes
Next, categorize the information into broader themes such as:
Technical skills
Soft skills
Behavioral competencies
Industry trends
This thematic categorization will help you see the bigger picture and identify patterns across different data sources.
4. Shortlist Core Competencies
Based on the organized data, shortlist the crucial core competencies. Focus on competencies that are consistently mentioned across various sources and closely align with your organization’s values and strategic goals. Rank these competencies based on their importance and frequency of mention.
5. Create Role-Specific Competency Lists
For role-specific competencies, create separate lists for each department or job family. Use your job descriptions and insights from subject matter experts (SMEs) to map competencies to specific tasks and responsibilities.
6. Define Each Competency Clearly
Once you’ve identified your list of competencies, define each one with clear, measurable descriptions. Avoid vague language. Instead of broad terms like “communication skills,” specify “the ability to convey complex ideas clearly and concisely in both written and verbal forms.”
7. Identify Proficiency Indicators
Finally, for each competency, identify specific behaviors and actions that demonstrate proficiency at different levels. This step is essential for creating a model that supports skill development and career progression
Step 5: Compile Competency Profiles
Compiling competency profiles brings together your research and analysis to create a cohesive, practical framework. This step involves developing detailed profiles for each role or job family in your organization, outlining the competencies required for success.
1. Develop a Standardized Template
Start by creating a standardized template for all competency profiles. This ensures consistency across roles and makes the profiles easier to use and update. Your template should include:
Primary responsibilities
Technical skills
Soft skills
Behavioral competencies
2. Define Primary Responsibilities
For each role, list the primary responsibilities based on job descriptions and input from subject matter experts (SMEs). This section serves as the foundation for identifying the relevant competencies.
3. Identify Core Competencies
Next, list the core competencies that apply across all roles in your organization. These might include universally important skills like “adaptability” or “customer focus.”
4. Add Functional Competencies
For each role or department, identify the functional (role-specific) competencies. These include the technical skills and knowledge areas essential for success in a particular position. For example, a marketing role might require competencies in “digital marketing strategies” or “brand management.”
5. Include Leadership Competencies (If Applicable)
If the role involves leadership, include a section for leadership competencies. These are crucial for managerial and executive positions and may include skills like “strategic thinking” or “team development.”
6. Define and Measure Competencies
For each competency, provide a clear definition and describe the behaviors or actions that demonstrate proficiency at different levels. This helps both employees and managers understand expectations and provides a roadmap for skill development.
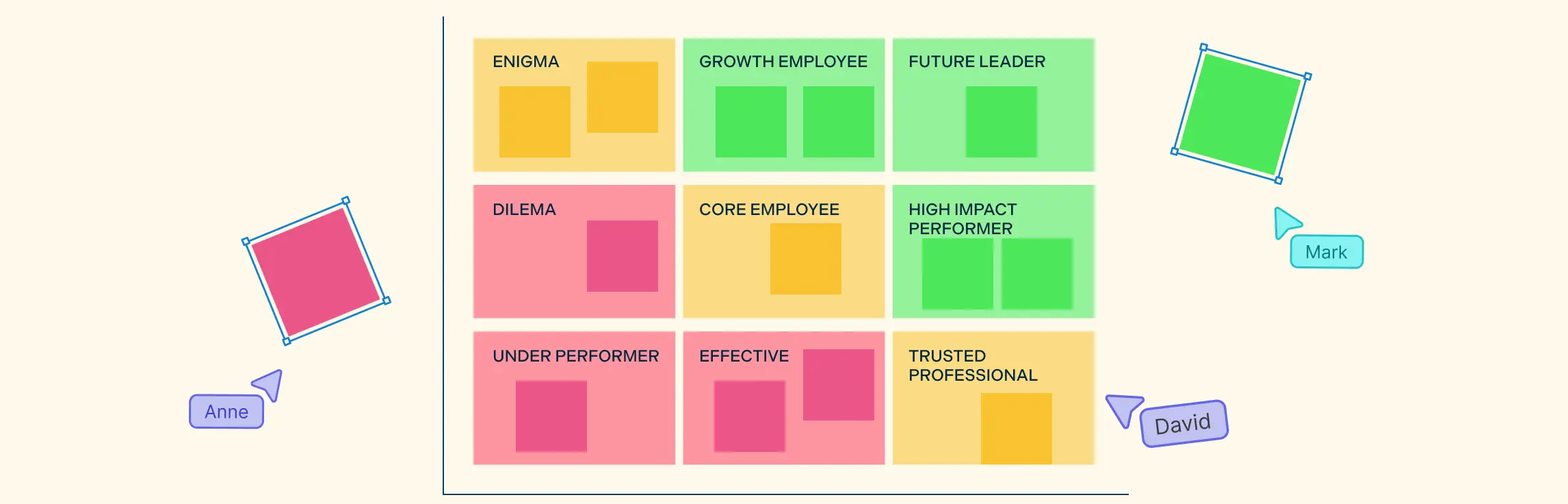
7. Use a Competency Matrix
Finally, use a competency matrix to visually map how competencies apply across different roles and levels within your organization. This is particularly useful for identifying career pathways and planning for succession.
How Creately Helps in Developing Competency Models
Integrating your competency model with the right tools is crucial for mapping, planning, and visualizing organizational strategies. Creately offers a suite of visual tools that can enhance the effectiveness of competency models within an organization.
1. Creately’s Visual Tools for Competency Models
Creately provides multi-level processing and organizational structure frameworks that integrate seamlessly with competency models. Using Creately’s Mind Mapping Software, organizations can easily map competencies across multiple levels and visualize strategic plans that align with organizational goals. This enables a clear pathway for employee growth and development.
2. Simplifying Complex Frameworks
Creately simplifies the visualization of complex competency frameworks, allowing organizations to create detailed maps that link employee skills to specific roles and strategic objectives. These visualizations not only assist HR professionals in managing employee development but also support strategic workforce planning and organizational transformation initiatives.
3. Real-Time Collaboration with Mind Maps
With Creately’s Mind Map Maker, teams can collaborate effectively to refine and enhance competency frameworks in real time. This feature ensures that frameworks remain agile and adaptable to evolving organizational needs. The visual workspaces foster collaboration, making competency management processes more dynamic and effective.
4. Supporting Employee Journey Mapping
Incorporating Creately’s features into your competency model strategy enhances employee journey mapping, providing a clear understanding of career development paths within the organization. This capability helps support organizational objectives, driving performance and engagement across all levels of the company, and ensuring that strategic goals are met cohesively.
In conclusion, a well-designed competency model is a powerful tool that aligns employee skills with organizational goals, driving success at all levels. It not only clarifies the expectations for each role but also facilitates more effective recruitment, performance evaluations, and career development. By focusing on core, functional, and leadership competencies, organizations can cultivate a workforce that is capable, adaptable, and ready to meet strategic challenges. The integration of visual tools like Creately further enhances this process, offering clarity and collaboration in managing competency frameworks. As business environments continue to evolve, a competency model serves as a dynamic framework that supports growth and ensures
that your team is equipped to excel. Building and refining a competency model is an ongoing effort that ultimately leads to a more cohesive, skilled, and engaged workforce, positioning the organization for long-term success.
References:
“How to Create a Comprehensive Competency Model from Scratch (+ Free Templates).” Deel.com, 2024, www.deel.com/blog/create-competency-model/.
Gupta, Disha . “What Is a Competency Model? +Benefits, Examples (2022) | Whatfix.” The Whatfix Blog | Drive Digital Adoption, 30 June 2022, whatfix.com/blog/competency-model/.
FAQs on Competency Model
What are the 5 competency models for HR professionals?
For HR professionals, the following 5 competency areas are often highlighted:
- Business Acumen: Understanding the company’s operations, business strategies, and market dynamics.
- HR Expertise: Knowledge of HR functions like recruitment, talent management, and employee relations.
- Relationship Management: Building and maintaining positive relationships with employees and leadership.
- Consultation: Providing strategic advice to the organization’s leadership and ensuring alignment between HR and business goals. Leadership & Navigation: Guiding the organization through change and influencing its direction effectively.
What is the competence model theory?
Competence model theory is a framework used to define the specific behaviors, skills, and knowledge required to perform a job successfully. It serves as a guide for organizations to ensure employees have the competencies needed to achieve business objectives. The theory emphasizes:
Identifying core competencies for each role or function. Using those competencies to assess performance, guide development, and inform hiring processes. Aligning individual performance with the organization’s goals and values.