Choosing the right network topology can feel confusing, especially when terms like bus and star sound technical but affect how your entire network behaves. This guide breaks down how bus and star topologies work, what makes them different, where they overlap, and when each one makes sense. By the end, you’ll know exactly which topology fits your setup, and how to diagram it clearly using ready-made templates.
What Is Bus Topology?
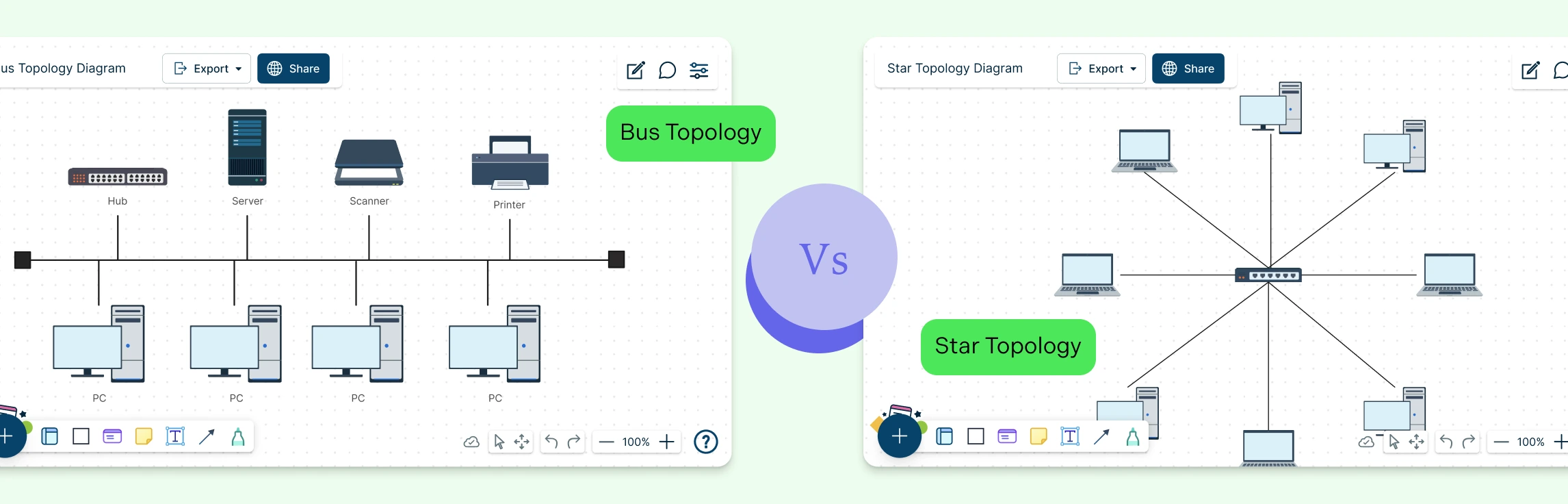
A bus topology is a simple network setup where all devices share a single central cable to send and receive data. It’s easy to set up and works well for small networks with light traffic, which is why it was common in early LANs. However, since every device uses the same line, performance can slow down as more devices connect. If that main cable fails, the entire network goes offline.
What Is Star Topology?
A star topology is a network setup where every device connects to a central hub or switch, creating a clear, organized structure. Instead of sharing one line, each device has its own connection, so data moves faster and problems are easier to isolate. If one device disconnects, the rest of the network keeps running, making star topology a reliable, scalable choice for modern offices, schools, and business networks.
Key Differences Between Bus and Star Topology
Here’s a quick, side-by-side look at bus and star topology to help you clearly understand how their structure, performance, and reliability compare.
| Aspect | Bus Network Topology | Star Network Topology |
| Fundamental element | Single shared backbone cable | Central hub or switch |
| Data transmission method | Data is broadcast along the shared cable to all devices | Data passes through the central hub or switch |
| Signal transmission direction | Unidirectional | Not unidirectional |
| Speed of data transfer | Slower due to shared bandwidth and collisions | Faster due to dedicated links |
| Cable dependency | Entire network depends on a single backbone cable | Each device has its own dedicated cable |
| Cabling requirement | Requires less cabling | Requires more cabling |
| Cost | Low cost due to minimal cabling and hardware | Higher cost because of additional cabling and active devices |
| Hardware requirement | Minimal hardware, no active devices required | Requires active hardware such as hubs or switches |
| Security | Lower security since all devices can see transmitted data | Better control and isolation through the hub or switch |
| Fault detection & troubleshooting | Difficult to isolate faults on the backbone | Easy to detect and isolate faulty devices or links |
| Maintenance impact | Any maintenance on the backbone disrupts all devices | Individual devices can be maintained without network downtime |
| Network extension / scalability | Devices can be added, but performance degrades quickly | Scales easily by adding ports or additional switches |
| Network failure impact | Severe when the common cable fails | Severe when the hub or switch fails |
| Monitoring & control | Limited ability to monitor or manage traffic | Easy to monitor and manage using modern switches |
| Network orientation | Linear | Non-linear |
| Network upgrades | Difficult to upgrade without disrupting the network | Easy to upgrade or replace the central device |
| Technology relevance | Mostly legacy and educational use today | Standard topology for modern Ethernet networks |
| Diagram representation | Single straight backbone with devices branching off | Central hub with devices radiating outward |
Similarities Between Bus Topology and Star Topology Diagrams
Before comparing which topology works best for your network, it’s useful to understand what bus and star topology diagrams have in common. Both are based on the same foundational networking concepts and are often used to explain how devices connect within a local network. In practice:
Both represent LAN (Local Area Network) topologies designed for communication within a limited physical area.
Both illustrate how multiple devices communicate over a shared network infrastructure.
Both rely on physical cabling to transmit data between devices.
Both require proper network configuration and management to prevent performance or connectivity issues.
Both are widely used as foundational examples in networking education and documentation.
For more on LANs, read the local area network diagram guide.
When to Use Bus Vs Star Topology
Use Bus Network Topology when:
You’re working with a very small network and minimal data traffic.
Keeping setup costs low is a priority.
The network is temporary or for basic testing and learning.
You want a simple structure with minimal hardware.
Use Star Network Topology when:
You need reliable, consistent network performance.
The network must scale as more devices are added.
Quick troubleshooting and easy management matter.
Downtime needs to be minimized in offices, schools, or business environments.
Ready to map your network with clarity and confidence? Create clean, professional bus and star topology diagrams in minutes with Creately’s network diagram software. Start with ready-made templates, drag and drop standard network symbols, and collaborate with your team in real time, so your network design is easy to understand, share, and scale.
Free Bus and Star Topology Templates to Get Started
Helpful Resources for Building Network Diagrams
Discover the different types of network topology and their use cases.
Learn about the Bus Network Topology, its key elements, and limitations.
Learn about the Star Network Topology, its key components, types, and its applications.
Learn about the Ring Topology, its components, how it works, and its applications.
Learn about the Tree Topology, its characteristics, how it works, and its applications.
FAQs about Bus Topology and Star Topology
Which topology is more reliable?
Which topology is easier to troubleshoot?
Is bus topology still used today?
How is bus topology different from other topologies?
Resources
Mamat, H., et al. “Network Topology Comparison for Internet Communication and IoT Connectivity.” IEEE Xplore, 1 Nov. 2019, https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8975702/
Mehmet-Ali, M.K., et al. “Traffic Analysis of a Local Area Network with a Star Topology.” IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 36, no. 6, June 1988, pp. 703–712, https://doi.org/10.1109/26.2790.