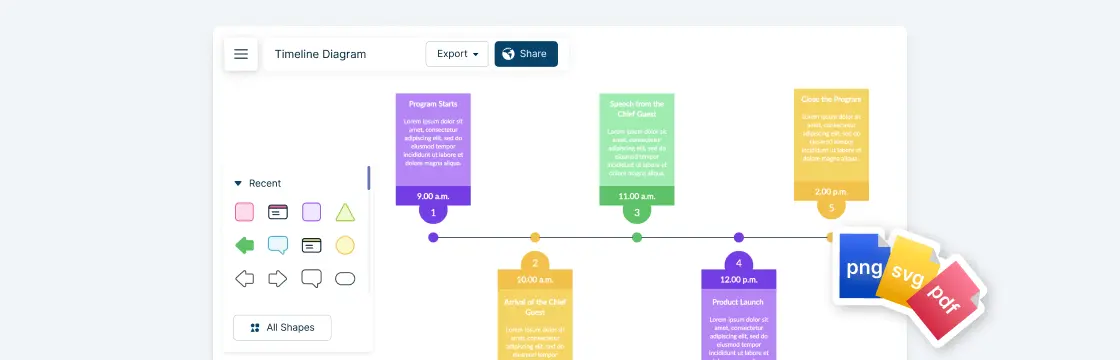
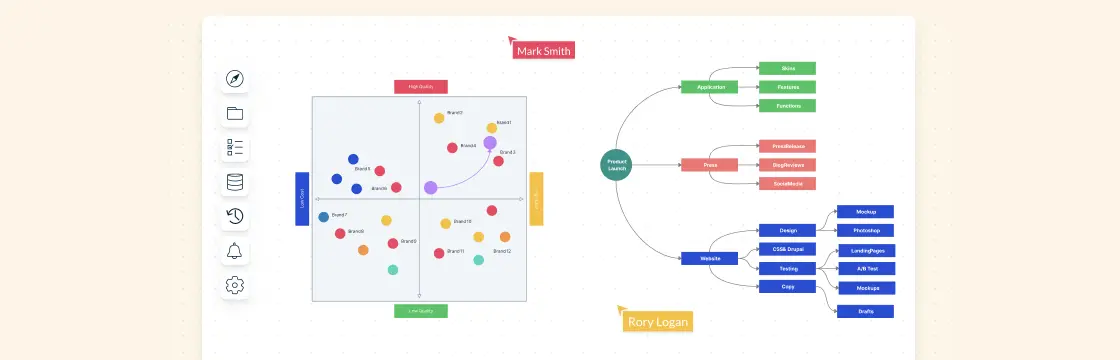
From what originated as a guide map for cyclers of New York City in the 1890s, later being adopted by Motorola in the 1980s to align their product and technology development, roadmaps have come a long way in assisting businesses to stay relevant and competitive in a setting where customer needs change frequently in pace with technological advancements.
Today, product roadmaps have come to play a major role in orchestrating the product development process. They help ensure that the daily tasks carried out by the team are in alignment with your high-level business strategy.
In this post, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about roadmaps – product roadmaps in particular – along with the steps you need to follow to create one successfully. We’ve also provided templates that you can edit and customize online or share with your team to collaborate on in real-time.
- What is a Roadmap?
- What is a Product Roadmap?
- What is the Importance of a Product Roadmap?
- What is the Role of a Product Roadmap in Product Management?
- How to Create a Product Roadmap Successfully
- Who Requires a Product Roadmap?
- How to Effectively Collaborate During the Creation of a Product Roadmap?
- Why is it Important to Iterate and Update Product Roadmaps?
What is a Roadmap?
A roadmap is a visual representation of a strategic plan, highlighting the key steps or milestones required to accomplish the defined goal or a desired outcome. It gives a quick overview of what is to be done, the progress made and who is involved.
Its purpose is to quickly communicate your plan to your stakeholders, executives, and the team while ensuring that they are in alignment with your high-level business strategy, allowing them to perform their best.
A roadmap can take the form of a single-page document or of several pages. Every roadmap is different and what it looks like depends on what you want to communicate and to whom.
A roadmap can highlight,
- How the initiatives line up with the high-level (business or product) goals or strategy
- How the team will achieve these goals and the resources they will need
- When the key deliverables are due
- Which teams and team members are involved
A roadmap is:
- Not a list of features. It, in fact, is a high-level plan portraying the strategic objectives and the key steps outlined to achieve them
- Not a backlog containing a list of tasks to complete an initiative. Rather, the high-level strategic components of a roadmap are built out of the backlog tasks.
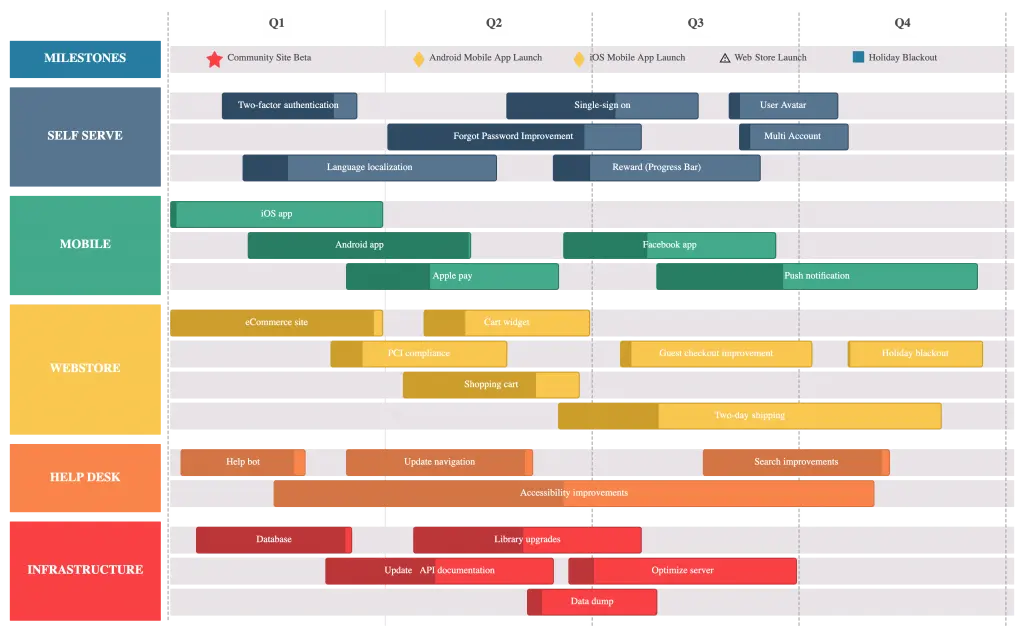
What is a Product Roadmap?
A product roadmap outlines how you plan to achieve your product vision. It communicates the value you expect to deliver to your customer and to your organization in order to win the support of your stakeholders and coordinate support among them.
It should provide an overview of your product’s current state as well as how it will evolve in the future.
What is the Importance of a Product Roadmap?
The importance of a product roadmap can be summarized via the following points.
- A product roadmap establishes a shared vision and aligns stakeholders around the product’s direction and strategy.
- The roadmap enables strategic planning by helping prioritize features, set timelines, and allocate resources effectively.
- A well-defined roadmap enhances communication and transparency, allowing teams to share plans, gather feedback, and foster collaboration.
- The roadmap assists in prioritizing features, managing dependencies, and optimizing resource allocation for efficient product development.
- The roadmap ensures a customer-centric approach by incorporating customer feedback and addressing their needs and pain points.
- The roadmap allows for flexibility and adaptability to respond to market changes, emerging opportunities, or challenges.
- The roadmap engages stakeholders, encourages their involvement, and invites their feedback in shaping the product’s roadmap.
What is the Role of a Product Roadmap in Product Management?
A product roadmap plays an essential role in product management. It is multifaceted and serves as a central guiding document that supports product managers in effectively managing and delivering successful products. Here are the key roles a product roadmap plays in product management.
Strategy Alignment
A product roadmap ensures that the product’s strategy aligns with the organization’s goals, vision, and mission. It communicates how the product contributes to the company’s overall success and guides decision-making.
Vision Communication
The roadmap serves as a communication tool to convey the product manager’s vision, goals, and planned features to stakeholders. It ensures that all parties have a shared understanding of the product’s direction and purpose.
Prioritization and Planning
The roadmap helps product managers prioritize features, enhancements, and initiatives based on customer needs, market trends, and business value. It facilitates informed decision-making, resource allocation, and timeline setting for effective product development.
Stakeholder Management
The roadmap provides visibility into the product’s development plans, enabling product managers to engage with stakeholders, gather feedback, and manage expectations. It fosters stronger relationships, gains stakeholder support, and allows for proactive concern addressing.
Release Management
The roadmap guides product managers in planning and coordinating product releases, including milestones, feature launches, and updates. It facilitates managing dependencies, coordinating cross-functional teams, and ensuring timely delivery.
Iterative and Agile Development
The roadmap supports iterative and agile development practices by breaking down the product’s development into manageable increments. It enables continuous feedback loops, aligns product iterations with the overall vision, and guides sequencing of features.
Customer Focus
The roadmap maintains a customer-centric approach by incorporating customer research, user feedback, and market insights. It ensures that the product addresses customer needs and preferences, delivering a solution that meets or exceeds their expectations.
Adaptability and Flexibility
A flexible roadmap allows product managers to adapt to changing priorities, market conditions, and customer feedback. It enables responding to emerging opportunities, addressing challenges, and adjusting the product’s direction as necessary. The roadmap serves as a living document that can be updated to reflect new information and circumstances.
How to Create a Product Roadmap Successfully
Creating the perfect product roadmap is crucial for product managers to guide successful product development. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, following key steps or best practices would help in creating a successful product roadmap.
- Understanding the Big Picture
- Define Your Product Strategy
- Gather Inputs
- Align Everyone Around Common Priorities
- Identify Roadmap Themes
- Set Broad Timeframes
- Customize Your Roadmap to Your Stakeholders
- Revisit and Update Your Product Roadmap
Understand the Big Picture
Before you plan out what your team should be working on, step back for a moment to understand the product vision – why are you developing this product in the first place? What will the success of the product bring to the customer, to the organization, and to the market if not the world?
Without a sense of the big picture, the individual decisions of the different teams involved in the process won’t be united by a common vision, hence leading to uncoordinated efforts.
The easiest way to define your product vision is to link it to your organization’s vision or its purpose for being. Everything that is on your product roadmap should support that vision.
Suppose you’re developing a project management software. Understanding the big picture might involve recognizing the increasing demand for remote work collaboration tools and the need for seamless integration with other productivity tools.
“Your product roadmap should slot right in between your company vision and your more detailed development, release, and operational plans.” – Product Roadmaps Relaunched: How to Set Direction While Embracing Uncertainty by C. Todd Lombardo, Bruce McCarthy, Evan Ryan, Michael Connors)
Tip: Involve stakeholders early in the roadmap planning process. Pay attention to their concerns and objections on what needs to be prioritized and what should be not. Their contribution is crucial to making an effective roadmap that everyone’s in line with.
Define Your Product Strategy
Your product strategy outlines how you will achieve your product vision. It links your product vision and product roadmap by translating the vision into actions that will be highlighted in the roadmap.
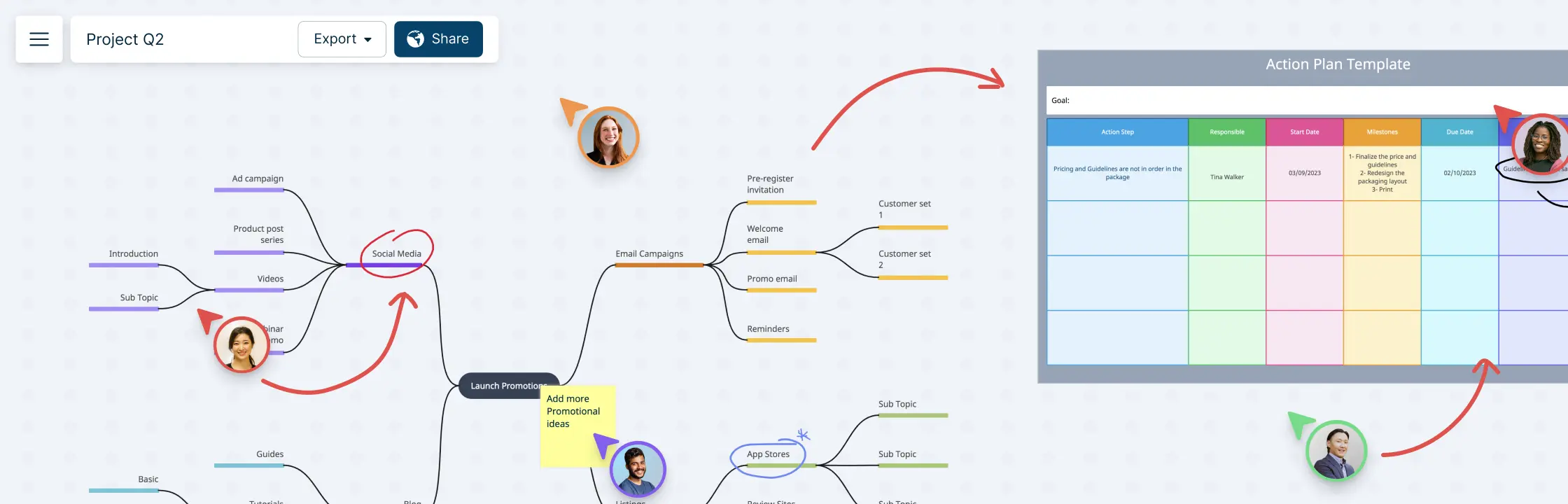
 Product Strategy and Roadmap in Context
Product Strategy and Roadmap in Context
Your product strategy helps you develop your future product and hence lay the foundation you need to build your roadmap. Your product strategy should include information on;
- what kind of a product it will be
- who it will benefit (who its customers are)
- how it will fit into the market
- how it will create value for your customers
- how it will help you achieve your goals
For example, your product strategy for the project management software should provide a user-friendly interface, advanced task management capabilities, and integrations with popular project management methodologies.
Tip: Use frameworks like the Lean Canvas or the Value Proposition Canvas to define your product strategy effectively.

Gather Inputs
This is where you collect all the information that you need to form your roadmap. There are several different sources you can gather these requirements from to develop the ideal solution or features to implement.
- Internal stakeholders such as your sales, marketing, and support teams as well as external stakeholders such as key investors.
- Users of your product who can provide you valuable insight into the usage of your products and what features to add.
For example, to gather inputs, your customer support team might identify recurring customer complaints about a missing feature in your project management software that helps visualize task dependencies.
Tip: Conduct regular feedback sessions, surveys, and user testing to gather insights directly from your target audience.
Align Everyone Around Common Priorities
There might be too many good ideas that will sometimes compel you to work on all of them at once. In reality though, you can’t implement everything at once, so you have to make a choice in order to execute better.
Equally important is to align all teams – not only the development and product teams but also the marketing and sales – around the same priorities and goals. Involve them in making the decisions that will affect them, early on and accept their input in the development of the roadmap. Precise prioritization of their commitments will also enable them to make the most effective use of their time.
After gathering inputs, for example, you might want to align with stakeholders that improving task dependency visualization is a priority, as it addresses customer needs and enhances the overall user experience.
Tip: Conduct workshops, meetings, and presentations to share your roadmap and gather feedback from stakeholders.

Identify Roadmap Themes
Your roadmap should highlight how you intend to deliver value to your customers and stakeholders as you get closer to accomplishing your vision. These values are known as themes and they help group similar features, initiatives, or epics together.
They describe a customer need, problem, or what your customers will receive (the job that your product/ service will help them complete). For example, under the theme improving customer support experience you can group initiatives that support it.
You can derive your product roadmap themes from your company’s long-term strategic initiatives. You can also identify themes for your product roadmap from your Product backlog by grouping the individual backlog feature ideas according to their related areas.
Under the themes, you can add objectives to help evaluate the progress made toward solving the customer problem or epics (you can also add features under each epic as additional detail depending on your requirement).
Themes for your project management software might include “Task Management Enhancements,” “Collaboration and Communication,” and “Integrations with Third-Party Tools.”
Tip: You can add diagrams, mockups, demos or other exhibits to better elaborate your theme. Use color coding or labels to visually represent different themes on your roadmap.
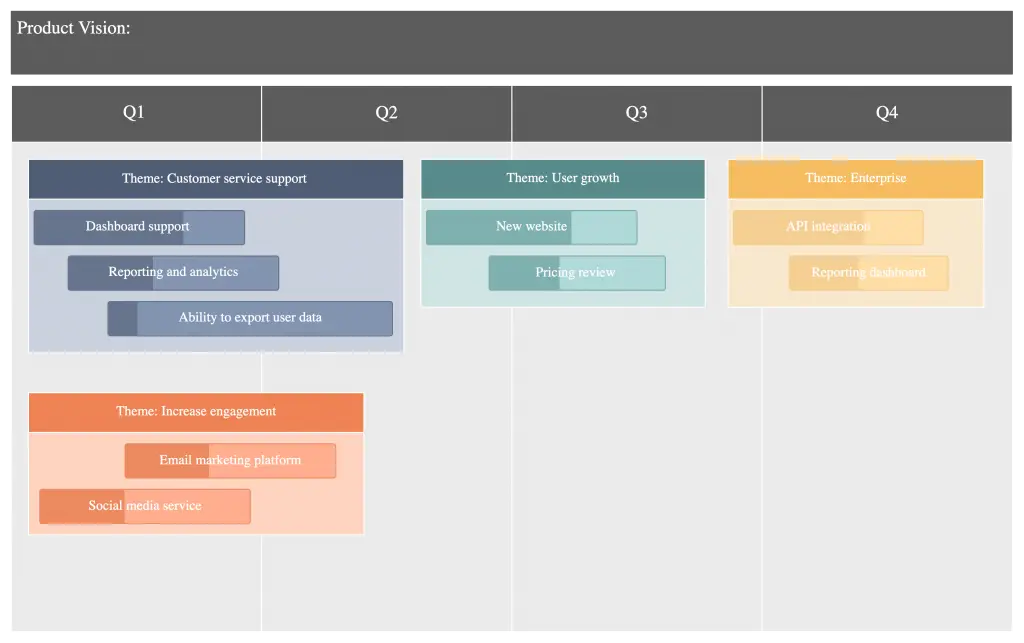
Set Broad Timeframes
A roadmap is a strategic document that is purposed for offering your team guidance on what to focus on. Therefore it shouldn’t revolve around estimating design and development efforts or specific release dates. A project plan or a release plan is more suited for these time estimations.
By constraining your roadmap with specific ship dates for roadmap themes and solutions, you will be distracting your team with unnecessary pressure to focus on time and thus hinder the process of innovation.
The roadmap should highlight what needs to be prioritized instead of due dates, therefore set broad timeframes such as calendar quarters or Now, Next, Later to make it seem more flexible and to avoid overcommitment. Your roadmap might outline a quarterly release cadence, with each quarter focusing on different themes or major feature updates
Tip: Use timeframes to indicate the sequence of major releases or key milestones rather than specific dates.
Customize Your Roadmap to Your Stakeholders
The process of developing and delivering a product involves different teams and consists of initiatives exclusive to each of them. While your development team may want to see the product’s development aspect of the product roadmap (i.e. what technology they’ll be expected to use, timeframe for them to get the work done, etc.), your investors may expect an overview of how you plan to increase market share over the next few quarters.
Therefore tailoring your product roadmap to highlight the particular information they are interested in is important.
Executives and top management: the product roadmap you create for them may need to include the elements that you have highlighted in your product strategy, and data pertaining to market size
Development team: requirements, individual tasks, deadlines, sprints
Marketing team: you may need to illustrate aspects such as product features, how your product positions itself against that of your competitors, and its potential to generate sales
Sales team: here you may need to customize the product roadmap to show how the product will benefit your customers, as well as important timelines for the customers
When presenting the roadmap to executives, emphasize the alignment of the project management software with the company’s overall goals, market trends, and competitive advantage. Provide a strategic overview and highlight the business impact.
Tip: Use visual aids like charts, graphs, and progress bars to convey information more effectively.
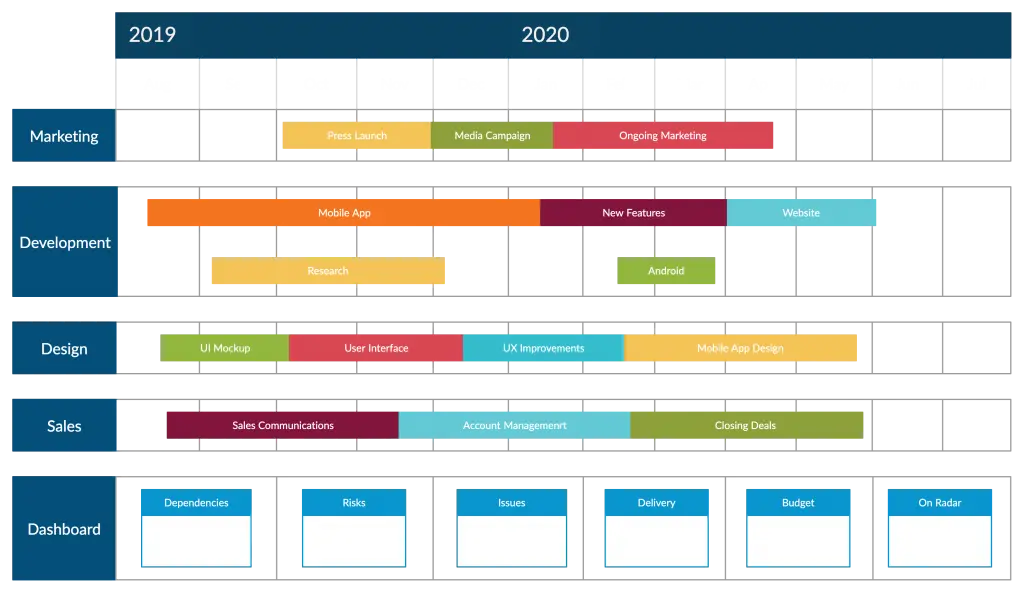
Revisit and Update Your Product Roadmap
The details in your roadmap are not set in stone. As the priorities of your company change, and as the customer needs and market trends evolve, updates to your product roadmap along the way will be inevitable.
For example, a software company adjusts its product roadmap after discovering a growing demand for mobile compatibility in the market. They revise their priorities and allocate resources to develop a mobile app, aligning with the changing customer needs and gaining a competitive edge.
Tip: Embrace agility and be open to change when revisiting and updating your product roadmap. Adapt quickly and iterate based on new information and insights to ensure its effectiveness.
Who Requires a Product Roadmap?
A product roadmap is a great tool for the various stakeholders involved in the product development and management process. Here are the key individuals or groups who benefit from having a product roadmap:
- Product Managers: Product managers are responsible for a product’s overall strategy, development, and success. They rely on the roadmap to define and communicate the product’s vision, set priorities, and guide development efforts.
- Development Teams: Engineering teams, designers, and other development stakeholders use the product roadmap to understand the product’s long-term vision, prioritize features, and plan their work for efficient execution.
- Executives and Stakeholders: Executives and stakeholders gain visibility into the product’s direction, progress, and expected outcomes, enabling informed decision-making and resource allocation.
- Sales and Marketing Teams: Sales and marketing teams align their efforts, develop strategies, and communicate the product’s value proposition based on the roadmap’s upcoming features and releases.
- Customer Support and Success Teams: Support teams anticipate changes, manage customer expectations, and align their efforts based on the roadmap’s insights into upcoming improvements. This knowledge enables them to provide proactive assistance, manage customer expectations, and align their support efforts.
- Customers and Users: Customers benefit indirectly by understanding the product’s commitment to improvement, managing expectations, and gaining insight into future features that address their needs.
How to Effectively Collaborate During the Creation of a Product Roadmap?
- Identify and involve stakeholders interested in the product’s success, such as executives, development teams, sales and marketing teams, customer support teams, and key customers, to gather diverse perspectives.
- Foster open and transparent communication channels with stakeholders, clearly communicating the purpose, goals, and progress of the roadmap creation process to keep stakeholders informed and engaged.
- Conduct workshops and interviews to gather input and insights from stakeholders, understanding their needs, pain points, and expectations for the product to incorporate their perspectives into the roadmap.
- Establish feedback mechanisms, like surveys or suggestion boxes, to encourage stakeholders to provide ongoing input and ideas and communicate how their feedback is considered and incorporated.
- Organize collaborative sessions where stakeholders can contribute ideas and suggestions in a safe and inclusive environment, using visual tools to effectively capture and organize their input.
- Involve stakeholders in prioritization exercises using voting or weighted scoring techniques to identify high-impact items and foster discussions on rationale and trade-offs.
- Share drafts of the roadmap with stakeholders for feedback, iterate based on their input, and seek clarification on requirements or conflicts to ensure alignment with their needs.
- Schedule regular check-ins with stakeholders to keep them informed about the roadmap’s progress, gather feedback, and address any concerns or additional input they may have.
- Utilize collaboration tools and platforms to facilitate remote stakeholder engagement, allowing stakeholders to provide input and collaborate effectively regardless of location.
- Ensure the roadmap reflects stakeholder perspectives, aligns with their needs, and communicates how it contributes to the organization’s objectives, fostering a sense of ownership and buy-in.
Why is it Important to Iterate and Update Product Roadmaps?
Iterating and updating product roadmaps based on feedback, market changes, and insights is crucial for maintaining a product’s relevance, competitiveness, and success.
- Responding to Customer Needs: By iterating and updating the product roadmap based on customer feedback, you can address their evolving needs and enhance their user experience.
- Adapting to Market Changes: Iterating and updating the roadmap helps you stay ahead of the competition and align your product with market trends, ensuring its continued relevance and success.
- Embracing New Insights and Learnings: Updating the roadmap based on new insights and learnings allows you to make informed decisions, refine the product strategy, and improve its chances of success.
- Managing Resource Allocation: Iterating and updating the roadmap enables efficient resource allocation, prioritizing the right features and initiatives.
- Enhancing Stakeholder Alignment and Support: Incorporating feedback and insights into the roadmap enhances stakeholder alignment, trust, and support for the product.
- Facilitating Agile and Iterative Development: Iterating and updating the roadmap aligns with agile methodologies, promoting continuous improvement and faster time-to-market.
- Managing Expectations and Communication: Iterating and updating the roadmap helps manage expectations and facilitates clear communication with internal teams, stakeholders, and customers.
- Seizing New Opportunities: Iterating and updating the roadmap allows you to seize new opportunities during product development.
Got More Tips on How to Create a Product Roadmap?
A proper product roadmap outlines your vision for your product and how your product will help accomplish your organizational strategic goals.
We hope this post will be a good starting point for you when building your own product roadmap. Got more tips on how to create a product roadmap? Let us know in the comments below.
FAQs About Product Roadmaps
- Overview or Summary: A concise description of the product, its purpose, and strategic goals, providing a high-level understanding of the product’s direction.
- Themes or Goals: Strategic areas of focus that outline key objectives or problem areas the product aims to address, guiding the development efforts.
- Features or Initiatives: Specific items to be developed and delivered, aligned with the product strategy, and providing detailed descriptions of the planned functionalities or enhancements.
- Timelines or Releases: Clearly indicate when features or initiatives are planned for delivery, showcasing the sequence and timing of different milestones.
- Dependencies: Identification of relationships or dependencies between features or initiatives, helping to coordinate efforts and manage potential bottlenecks.
- Success Metrics or KPIs: Measurable goals or indicators that determine the product’s success, allowing progress tracking and assessing the roadmap’s impact.
- Risks and Mitigation Strategies: Identify potential risks or challenges that could affect the roadmap’s execution and strategies to mitigate those risks and ensure smooth progress.
- Communication and Collaboration: Focus on stakeholder engagement, communication plans, and collaboration methods to effectively share the roadmap, gather feedback, and foster collaboration among relevant parties.
Strategies for dealing with changes or unexpected events include
- maintaining flexibility in the roadmap,
- conducting regular reviews and assessments,
- engaging in ongoing communication with stakeholders,
- prioritizing features or initiatives based on impact and value, and
- allocating additional resources or adjusting timelines when necessary.