What is Operations Strategy?
Definition of Operations Strategy
An operations strategy is a comprehensive plan that outlines the actions and decisions needed to manage and optimize the production and delivery of goods and services. It’s a roadmap designed to align day-to-day operations with long-term business goals, ensuring all activities contribute to overall organizational success. This type of strategy is crucial for establishing the methods and frameworks through which an organization achieves its objectives efficiently.
Importance of Operations Strategy
The significance of effective operations strategy cannot be overstated. By aligning operations strategy with broader business aims, companies can enhance their competitive positioning, realize cost efficiencies, and ensure smoother execution of business activities. Without a well-defined operations strategy, it becomes challenging to scale operations, enhance customer satisfaction, or achieve long-term sustainability. Explore business diagrams for strategic planning.
Aligning Operations Strategy with Business Goals: Ensures coherence and unified direction across all departments.
Enhancing Competitive Advantage: Through optimized processes and resource allocation, companies can outperform competitors.
Operational Efficiency: Streamlines processes to reduce waste and manage costs effectively.
For those interested in operational action planning, Learn more about Operational Planning.
Examples of Operations Strategies
An operations strategy is a long-term plan that outlines how an organization will utilize its resources to support business objectives, deliver value to customers, and gain a competitive edge. Here are some examples of operations strategies across different industries:
1. Cost Leadership Strategy
Example: A manufacturing company might focus on reducing production costs through economies of scale, lean manufacturing techniques, and efficient supply chain management. Companies like Walmart and IKEA leverage cost leadership by focusing on high efficiency, large-scale production, and cost-saving measures to offer low prices to consumers.
2. Quality Improvement Strategy
Example: A luxury car manufacturer, such as BMW or Mercedes-Benz, might focus on superior quality as a core element of its operations strategy. This can involve implementing rigorous quality control processes, investing in advanced manufacturing technologies, and sourcing high-quality materials to maintain a premium brand image.
3. Customer Service Strategy
Example: A company like Ritz-Carlton focuses on delivering exceptional customer service as part of its operations strategy. By empowering employees to provide personalized service and resolving issues on the spot, the company creates a loyal customer base and enhances its brand reputation.
4. Sustainability Strategy
Example: A company like Patagonia emphasizes sustainability in its operations strategy. This might include using environmentally friendly materials, reducing waste in manufacturing processes, and encouraging recycling among customers to align with its brand values and attract environmentally conscious consumers.
5. Technology Integration Strategy
Example: A company like Tesla incorporates advanced technology into its operations strategy by investing in automation, AI, and robotics to streamline production processes, enhance product quality, and improve efficiency in its Gigafactories.
These strategies are often tailored to fit the specific goals and challenges of the organization and are designed to align with the overall business strategy.
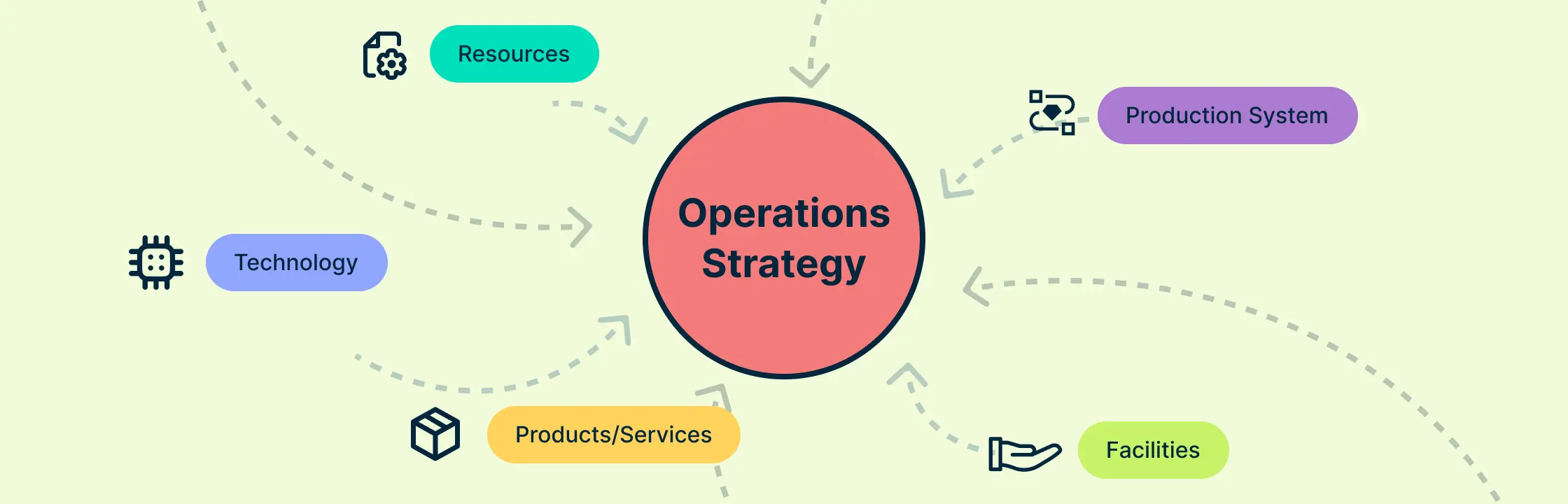
5 Key Elements of an Operations Strategy
A successful operations strategy is comprised of several key components:
Resources: Including human, mechanical, and locational. It’s vital to assess both current capabilities and potential acquisitions.
Technology: Encompassing advanced tools beyond basic software, such as production automation and machine learning.
Products/Services: Analyzing the lifecycle of your offerings and adapting to market trends will optimize efficiency.
Facilities: Ensuring production facilities and inventory management systems meet operational goals and safety standards.
Production System: Essential for effective resource planning and quality control, influencing long-term operational efficiency.
Why is a Successful Operational Strategy Important?
Aligning with Business Goals
An effective operational strategy is pivotal in ensuring that an organization’s daily activities are aligned with its overarching business goals. By synchronizing operational plans with strategic objectives, companies can streamline their processes and improve overall efficiency. This alignment helps in setting clear priorities and ensures that all departments work towards common targets, ultimately leading to cohesive and coordinated business efforts.
Gaining Competitive Advantage
A well-crafted operational strategy enhances a company’s competitive advantage by optimizing resource utilization and improving customer satisfaction. For instance, tailoring production processes to meet unique customer needs not only boosts brand loyalty but also positions the business favorably in the market. Competitive priorities such as speed, quality, and flexibility become achievable, thus providing a significant edge over competitors. Read more on a winning customer experience strategy.
Improving Operational Efficiency
An operational strategy is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency. It allows businesses to identify and eliminate bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and reduce operational costs. Utilizing tools like action plans can further clarify roles and responsibilities, making the execution of operational tasks more structured and effective.
Companies leveraging platforms like Creately, can achieve greater transparency and collaboration, resulting in improved productivity and streamlined operations.
Components of an Effective Operations Strategy
No matter which type of initiative you choose to prioritize in your company, you’ll need to consider several key components for an effective operations strategy:
Capacity Planning:
Accurately assessing your current resources and anticipating future needs is crucial for long-term success. A thorough understanding of your business’s capabilities helps identify what is necessary to sustain or expand operations.
Human Resources Management:
Effective HR planning covers everything from attracting new talent to retaining existing employees. Prioritizing your workforce can reduce turnover, stabilize operations, and preserve valuable institutional knowledge.
Quality Management:
Implementing quality management practices ensures that product development meets desired standards. In a professional service firm, this might involve focusing on client feedback to enhance collaboration and outcomes.
Supply Chain Management:
In manufacturing, supply chain management is vital. Streamlining the flow of goods from suppliers helps reduce costs, support growth, and ensure high levels of customer service.
Technology and Innovation:
Embracing digital transformation and cutting-edge technologies is essential for boosting business efficiency. Regardless of the industry, tools like AI, automation, and cloud computing can greatly enhance operational capabilities and inform better decision-making.
5 Core Types of Operational Strategies
Understanding the different types of operational strategies is crucial for optimizing your business operations. Here, we explore the various approaches and provide operational strategy examples to illustrate their application.
1. Cost-Based Strategy
A cost-based strategy focuses primarily on minimizing expenses to deliver competitive pricing. It involves optimizing the supply chain, automating workflows, and carefully managing resources to maintain low costs without compromising quality. This strategy is particularly beneficial for businesses competing on price.
Focus: Minimizing costs to offer competitive pricing.
Approach: This strategy emphasizes cost efficiency through optimized supply chains, bulk purchasing, automation, and lean production techniques. Companies aim to reduce operational expenses without compromising product quality.
Example: Walmart is known for its cost-based strategy, using its scale and efficient logistics to offer low prices.
2. Quality-Based Strategy
Quality-based strategies prioritize delivering high-quality products or services. This approach aims to enhance customer satisfaction, boost brand reputation, and reduce return rates. Companies implementing this strategy often invest in rigorous quality control processes and continuous improvement initiatives.
Focus: Delivering superior quality products or services.
Approach: Companies that adopt a quality-based strategy prioritize high standards in production and service delivery. They invest in quality control measures, continuous improvement processes, and premium materials to enhance customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Example: Mercedes-Benz focuses on quality-based strategies by producing high-end vehicles with precision engineering and premium materials.
3. Flexibility Strategy
Flexibility strategies are designed to allow businesses to adapt quickly to market changes and customer demands. This strategy involves developing flexible systems and processes that can accommodate varying production volumes or personalized customer requests. Flexibility also fosters innovation and rapid product development.
Focus: Adapting quickly to market changes and customer demands.
Approach: Flexibility strategies involve developing adaptable systems that can respond to varying production volumes, customized orders, or changing market conditions. This strategy often includes diversification, flexible manufacturing systems, and scalable operations.
Example: Amazon’s ability to scale operations during peak times like holidays reflects its flexibility strategy, ensuring timely deliveries and meeting fluctuating demand.
4. Speed-Based Strategy
In today’s fast-paced business environment, speed is often a critical factor in gaining a competitive edge. A speed-based strategy focuses on minimizing the time required to produce and deliver products or services to customers. By implementing techniques such as just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing, lean operations, and process streamlining, companies can significantly reduce lead times and enhance their ability to meet customer expectations swiftly. This strategy is particularly vital in industries where timely delivery is crucial, such as logistics and e-commerce.
Focus: Reducing lead times and accelerating delivery.
Approach: Speed-based strategies focus on reducing the time it takes to produce and deliver products or services. Techniques like just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing, lean operations, and streamlined processes are used to increase efficiency and meet customer expectations for quick service.
Example: Companies like FedEx and UPS utilize speed-based strategies to ensure fast and reliable delivery services.
5. Dependability Strategy
Reliability is the foundation of trust between a company and its customers. A dependability strategy is centered on ensuring that products and services are consistently delivered as promised, maintaining high levels of operational reliability. By focusing on robust supply chain management, consistent production processes, and unwavering service quality, companies can build strong customer loyalty and a solid reputation for dependability. This strategy is essential for businesses where consistency and reliability are key to customer satisfaction and long-term success.
Focus: Ensuring consistent and reliable operations.
Approach: A dependability strategy centers on maintaining high levels of reliability in delivering products or services. This involves robust supply chain management, consistent production processes, and reliable service delivery, which build customer trust and loyalty.
Example: Toyota is known for its dependability strategy, focusing on consistent quality and reliable production processes through its well-established Toyota Production System (TPS).
6. Innovation Strategy
In a rapidly evolving market, innovation is the engine that drives growth and differentiation. An innovation strategy emphasizes the continuous development of new products, services, and business processes to stay ahead of the competition. By investing in research and development (R&D), fostering a culture of creativity, and embracing new technologies, companies can introduce groundbreaking offerings that capture market share and set industry trends. This strategy is crucial for businesses aiming to lead in dynamic sectors where staying innovative is the key to sustained success.
Focus: Driving growth through innovation in products, services, or processes.
Approach: Innovation strategies prioritize the development of new products, services, or ways of doing business. Companies invest in research and development (R&D), encourage creativity, and seek out new technologies to stay ahead of competitors.
Example: Apple’s focus on innovation in product design and technology has kept it at the forefront of the tech industry.
7. Service-Based Strategy
Exceptional customer service can be a powerful differentiator in a competitive market. A service-based strategy focuses on delivering outstanding customer experiences as a core component of the business’s value proposition. Companies adopting this approach invest in comprehensive training, advanced customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and continuous service innovation to exceed customer expectations. This strategy is vital for businesses looking to build strong, lasting relationships with their customers, where service excellence is the hallmark of their brand.
Focus: Providing exceptional customer service to differentiate from competitors.
Approach: Companies adopting a service-based strategy emphasize customer service excellence as a key differentiator. They invest in training, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and service innovation to create a superior customer experience.
Example: Companies like Ritz-Carlton and Zappos are renowned for their exceptional customer service, which is a core part of their operational strategy.
Adopting the right operational strategy can significantly impact your business’s efficiency and competitive stance in the market. By understanding and implementing a suitable strategy, you can better manage costs, maintain high-quality standards, and swiftly adapt to changes, thereby positioning your business for success.
Creating an Operational Plan
Setting Goals and Objectives
Creating a robust operational plan starts with clearly defining your goals and objectives. Understanding what you aim to achieve helps structure your approach and ensures alignment with overarching business strategies. Begin by analyzing your company’s market position, current operational capabilities, and the competitive landscape. Utilizing tools like a SWOT analysis generator aids in pinpointing strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, helping to set realistic and impactful goals.
Budget and Indicators
Once goals are established, the next step is to allocate a corresponding budget. An effective operational plan must include financial planning to fund different activities, whether for marketing, production, or human resources. Incorporating leading indicators is equally crucial, as they provide early signals for potential issues and help in proactively managing operations. Indicators like sales growth, customer satisfaction scores, and production efficiency metrics offer actionable insights for monitoring and adjusting strategies.
Communication and Documentation
A successful operational plan hinges on efficient communication and thorough documentation. It’s essential to communicate the plan’s objectives, strategies, and key performance metrics to team members and stakeholders to ensure everyone is on the same page. Keeping detailed documentation of processes, decisions, and progress aids in maintaining transparency and accountability.
Technology and Tools
Leveraging technology not only enhances the operations planning process but also streamlines execution. Integrated visual collaboration tools like Creately provide an interactive platform that enables users to visualize and manage operational plans effectively. Advanced tools such as Market Research, Competitive Analysis, and cascading OKR Structures can be used to help align day-to-day operations with long-term business goals. These tools facilitate data-driven decision-making, thereby improving overall operational effectiveness.
An operational plan serves as a roadmap to achieving business objectives, ensuring every team member understands their role and how their efforts contribute to the larger mission. By setting clear goals, managing budgets, maintaining open communication, and utilizing the right tools, businesses can vastly improve their operational efficiency and strategic alignment.
Benefits of a Robust Operations Strategy
Cost Savings and Optimization
A well-defined operations strategy helps businesses manage and optimize costs effectively. By streamlining processes and removing inefficiencies, companies can minimize waste and reduce expenses. This strategic approach enables organizations to allocate resources more judiciously, leading to better financial health and a stronger bottom line.
Customer Satisfaction
One of the significant advantages of a robust operations strategy is the ability to deliver high-quality products and services consistently. This reliability boosts customer satisfaction and loyalty. Enhancing customer experience is imperative for long-term success, as satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat buyers and brand advocates.
Operational Efficiency
A meticulously crafted operations strategy ensures that all business activities are optimized for maximum efficiency. By simplifying workflows and leveraging technology, companies can enhance productivity and reduce the time and resources needed to achieve operational objectives.
Market Competitiveness
Companies with strong operations strategies are better positioned to compete in their respective markets. By aligning operational activities with strategic goals, businesses can respond swiftly to market demands, leverage opportunities, and mitigate risks. This proactive approach offers a unique competitive edge, making it easier to thrive in a dynamic market environment.
Leveraging Technology for Operations Strategy
In today’s fast-paced business environment, leveraging technology is critical to maintaining an effective operations strategy. Technology doesn’t just support operational processes; it transforms them. From automating routine tasks to providing real-time data insights, technology enables organizations to streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve productivity and efficiency.
Types of Impactful Technology
Several types of technology can significantly impact your operations strategy:
Production Line Automation: Automation tools can optimize workflows, reduce errors, and increase consistency in production processes.
Machine Learning: Leveraging machine learning algorithms can predict maintenance needs, analyze production data, and improve decision-making processes.
Business Process Automation (BPA) Software: Platforms like Creately’s visual workspace can automate repetitive tasks, ensuring that resources are used efficiently.
Real-Time Data Integration: Tools that provide real-time updates on various KPIs empower businesses to make data-driven decisions quickly and effectively.
Tools like Creately facilitate the creation and execution of an operations strategy with features like Strategy Mapping Software and Real-time Data Integration, making it easier to visualize and align strategic goals effectively within your organization.
Utilizing comprehensive tools like Creately facilitate thorough planning, seamless execution, and continuous improvement, ensuring your operations strategy is always aligned with your overarching business goals.
Integration Benefits
Integrating technology into your operations strategy offers numerous benefits:
Enhanced Efficiency: Automating routine processes frees up valuable time for employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
Improved Decision-Making: Real-time data integration and analysis tools, such as those offered by Creately, provide the insights needed for informed decision-making.
Increased Collaboration: Collaborative tools allow teams to work together seamlessly, regardless of their physical locations.
Reduced Costs: By optimizing processes and reducing manual errors, technology helps to cut down on operational costs, thereby increasing profitability.
Best Practices for Implementing an Operations Strategy
Implementing an operations strategy requires more than just a solid plan. It involves leveraging the right tools, adhering to proven best practices, and constantly measuring and adapting the strategy to suit evolving business needs. Here are some of the key practices, tools, and frameworks that can facilitate the implementation of your operations strategy.
Key Practices
Embedding these key practices into your strategy implementation can ensure better outcomes:
Define Clear Objectives: Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound SMART goals that align with your overarching business strategy.
Engage Stakeholders: Actively involve stakeholders at all levels to foster buy-in and ensure everyone is on the same page.
Document Everything: Maintain comprehensive documentation of all strategic decisions and changes to ensure clarity and accountability.
Communicate Effectively: Foster open communication channels within the organization to ensure smooth execution and alignment with business goals.
Monitor Performance: Use key performance indicators (KPIs) and other metrics to regularly track progress and make necessary adjustments.
Tools and Frameworks
Several tools and frameworks can assist in the successful implementation of your operations strategy:
Visual Strategy Mapping: Utilize visual tools like Creately’s Visual Strategy Mapping Software to create a clear and communicative visual representation of your strategy.
Market Analysis and Competitive Strategy: Regularly conduct market analysis and competitive benchmarking to stay ahead of industry trends and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Real-time Data Integration: Leverage real-time data integration to ensure that all stakeholders have access to the most current information, facilitating informed decision-making.
Analysis Frameworks: Employ various analysis frameworks like SWOT analysis, PESTLE analysis, and Porter’s Five Forces to thoroughly analyze internal and external factors impacting your operations strategy.
Project Management Software: Utilize tools like Creately to manage project timelines, resources, and ongoing tasks efficiently, ensuring a streamlined implementation process.
Measuring and Adapting
Continuous assessment and adaptation are crucial for the long-term success of an operations strategy. Follow these steps for effective measurement and adaptation:
Set Benchmarks: Establish initial benchmarks for various KPIs to gauge the performance against strategic objectives.
Regular Reviews: Conduct regular performance reviews to identify gaps and areas of improvement.
Incorporate Feedback: Actively seek feedback from various stakeholders and incorporate it into your strategic refinements.
Adapt to Changes: Stay agile and be prepared to adjust your strategy based on new data, market trends, and internal performance metrics.
Scale Up Successes: Identify successful elements of your strategy and scale them up across different departments and operations.
By incorporating these best practices, tools, and frameworks into your operations strategy implementation, you can ensure a more effective and dynamic approach to achieving your organizational goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an operations strategy is a vital framework that guides the efficient production and delivery of goods and services within an organization. It aligns daily operational activities with long-term business objectives, ensuring that every action contributes to overall success. The importance of a well-defined operations strategy lies in its ability to enhance competitive advantage, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Key components of an operations strategy include resources, technology, products/services, facilities, and production systems, all of which must be carefully managed and optimized. Different types of operational strategies, such as cost-based, quality-based, and flexibility strategies, can be employed depending on the business’s goals and market conditions.
Effective implementation of an operations strategy involves setting clear objectives, engaging stakeholders, leveraging technology, and continuously measuring and adapting the strategy to meet evolving needs. By following best practices and utilizing tools like visual strategy mapping and real-time data integration, businesses can streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve overall performance, positioning themselves for long-term success in a competitive market.
Helpful Resources
A comprehensive guide featuring 50 business diagrams and visual tools designed to assist in strategic planning and decision-making processes.
This guide explains the steps, strategies, and tools necessary for creating effective operational plans that align with an organization's overall goals.
A detailed overview of operational marketing, focusing on the execution of marketing strategies through well-coordinated and actionable plans.
This guide explores the processes and tools involved in making tactical decisions that bridge the gap between strategic goals and day-to-day operations.