In a world where every misstep can cost valuable time and resources, businesses are constantly searching for ways to cut through inefficiencies and improve customer satisfaction. Lean Six Sigma emerges as a powerful solution, offering more than just process improvements – it’s a comprehensive approach to eliminating waste and reducing variation. But what sets it apart from other management philosophies? How can it drive not only operational efficiency but also transform organizational culture? In this article, we’ll break down the core principles of Lean Six Sigma and explore how it can steer your business toward lasting excellence and customer satisfaction.
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma principles merge the Lean methodology with Six Sigma principles to optimize processes and improve efficiency. Originating from Toyota’s Lean manufacturing and Motorola’s Six Sigma, this approach focuses on eliminating waste and reducing variation.
With roots deeply embedded in manufacturing excellence, Lean Six Sigma utilizes a customer-centric approach to deliver value consistently. It employs a methodical framework designed to ensure continuous improvement and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Focus on the Customer: Prioritize customer needs to enhance value.
Map the Value Stream: Identify steps that add value and eliminate those that don’t.
Remove Waste to Create Flow: Streamline workflows by eliminating wasted steps.
Communicate with Your Team: Foster a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement.
Create a Culture of Change and Flexibility: Adapt with data-driven insights and flexible strategies.
By leveraging the combined strengths of its dual methodologies, Lean Six Sigma offers a holistic approach to reducing defects and improving process efficiency. To better understand these principles, consider exploring our Six Sigma Tools and Templates
Why Lean Six Sigma Matters
In the fast-paced world of modern business, achieving operational excellence is paramount. This is where Lean Six Sigma comes into play. By combining Lean’s focus on waste elimination and Six Sigma’s emphasis on defect reduction, businesses can streamline operations, reduce costs, and significantly enhance customer satisfaction. Here are some key reasons why Lean Six Sigma is crucial in today’s business environment:
Streamlines Operations and Maximizes Efficiency: Lean Six Sigma methodologies help identify and eliminate waste in processes, leading to streamlined operations and maximized efficiency. The focus on continuous process improvement ensures that businesses can adapt and evolve in a highly competitive market.
Reduces Costs by Eliminating Waste and Defects: By targeting inefficiencies and defects, Lean Six Sigma contributes to substantial cost savings. Businesses can allocate saved resources to other critical areas, such as innovation or customer service.
Enhances Customer Satisfaction: Consistent quality improvement is a cornerstone of Lean Six Sigma. By meeting or exceeding customer expectations, businesses can foster loyalty and improve their market position. Want more tips?
Promotes a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Implementing Lean Six Sigma promotes a mindset of ongoing enhancement and adaptability. Employees are encouraged to identify problems and implement solutions proactively, leading to a dynamic and productive work environment.
Moreover, Lean Six Sigma aids in visualizing and optimizing business processes, which is essential for maintaining an edge in business process management. For more insights on effective business process management, try our solution on Business Process Management
Understanding the Lean Six Sigma Principles

1. Focus on the Customer
At the heart of Lean Six Sigma is an unwavering focus on the customer. This principle goes beyond simply meeting stated needs; it involves a deep, ongoing commitment to understanding and anticipating customer expectations.
Customer Needs Analysis: Organizations must implement robust systems for regularly gathering and analyzing customer feedback. This can include surveys, interviews, focus groups, and data analytics. The goal is to create a comprehensive picture of current customer needs and to identify emerging trends that could shape future expectations.
Voice of the Customer (VOC): Implementing a structured VOC program ensures that customer insights are systematically captured and integrated into decision-making processes. This involves not just collecting feedback, but also translating customer needs into specific, actionable requirements for products and services.
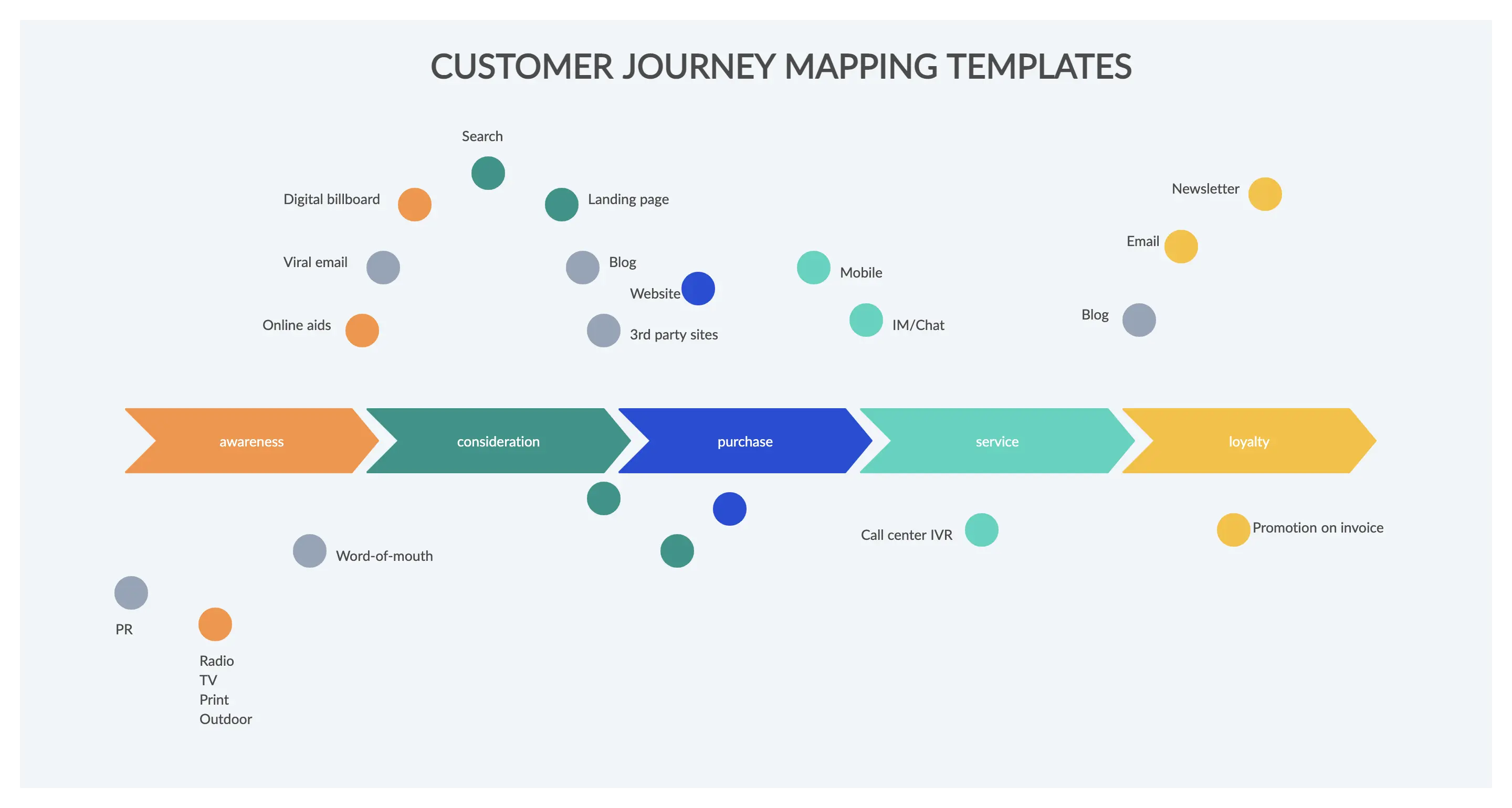
Customer Journey Mapping: By meticulously mapping out each step of the customer’s interaction with the organization, companies can identify pain points, moments of delight, and opportunities for improvement. This holistic view allows for targeted enhancements that can significantly improve the overall customer experience.
Metrics and Continuous Improvement: It’s crucial to align key performance indicators (KPIs) with customer satisfaction and value creation. This ensures that improvement efforts are directly contributing to enhanced customer experiences. Moreover, establishing a continuous feedback loop allows organizations to stay agile, constantly refining their offerings based on evolving customer needs and preferences.
2. Map the Value Stream
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is a powerful tool for visualizing and optimizing the flow of materials and information required to deliver a product or service to the customer. This principle is about gaining a comprehensive understanding of your processes to drive meaningful improvements.
End-to-End Visualization: Creating a value stream map involves documenting every step from the initial customer request to final delivery. This includes not just the obvious production steps, but also information flows, decision points, and support processes. The goal is to create a complete picture of how value is created and delivered to the customer.
Identifying Value and Waste: A key aspect of VSM is distinguishing between value-adding activities (those the customer is willing to pay for) and non-value-adding activities (waste). This clear delineation helps organizations focus their improvement efforts where they’ll have the most impact.
Time Analysis and Bottleneck Identification: VSM involves measuring lead times, cycle times, and wait times throughout the process. This detailed time analysis helps identify bottlenecks and areas of inefficiency. By pinpointing where work accumulates or slows down, organizations can prioritize their improvement initiatives for maximum effect. Other useful techniques include Fishbone diagram tool and Process Mapping.
Future State Mapping: Beyond documenting the current state, VSM also involves envisioning and mapping an ideal future state. This forward-looking aspect guides improvement efforts and helps align the team around a common vision for process excellence.
3. Remove Waste to Create a Flow
The principle of removing waste to create flow is fundamental to Lean thinking. It’s about streamlining processes to ensure smooth, efficient operations that deliver maximum value to the customer.
Understanding the 8 Wastes: Lean Six Sigma identifies eight types of waste, often remembered by the acronym DOWNTIME: Defects, Overproduction, Waiting, Non-utilized talent, Transportation, Inventory, Motion, and Extra-processing. Each of these represents an opportunity for improvement.
Systematic Waste Elimination: Removing waste is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. It involves regularly scrutinizing operations to identify and eliminate activities that don’t add value. This could mean redesigning workflows, implementing new technologies, or changing organizational structures.
Creating Flow: The ultimate goal of waste removal is to create a smooth, uninterrupted flow of work. This means minimizing delays, reducing batch sizes, and ensuring that work moves seamlessly from one step to the next. Achieving flow often requires breaking down silos between departments and fostering cross-functional collaboration.
Empowering Employees: Effective waste removal relies heavily on empowering frontline employees. They are often best positioned to identify inefficiencies and suggest improvements. Creating a culture where all employees feel responsible for and capable of contributing to continuous improvement is crucial for sustained success.
4. Communicate with Your Team
Effective communication is the glue that holds Lean Six Sigma initiatives together. It ensures that all team members understand the goals, their roles, and the progress being made.
Transparent and Consistent Messaging: Communication in Lean Six Sigma should be open, clear, and consistent. This means regular updates on project status, sharing of key metrics, and transparency about challenges and successes. Leaders should strive to create an environment where information flows freely both up and down the organizational hierarchy.
Collaborative Tools and Platforms: Leveraging modern collaboration tools can significantly enhance communication. Platforms like Creately’s visual workspace provide a shared environment for documentation, real-time updates, and collaborative problem-solving. These tools help ensure that everyone has access to the latest information and can contribute effectively to improvement efforts.
Feedback and Continuous Learning: Communication should be a two-way street. Regular feedback sessions allow team members to share insights, concerns, and ideas. This not only improves processes but also fosters a sense of ownership and engagement among employees.
5. Create a Culture of Change
The final principle focuses on fostering an organizational culture that embraces continuous improvement and adaptability.
Embedding Continuous Improvement: Creating a culture of change means making continuous improvement a part of everyday work. This involves encouraging employees at all levels to constantly look for ways to enhance processes, reduce waste, and increase value for customers.
Data-Driven Decision Making: A key aspect of this culture is relying on data to guide decisions. By consistently gathering and analyzing relevant data, organizations can make informed choices about where to focus improvement efforts and how to measure success.
Leadership and Change Management: Leaders play a crucial role in creating and sustaining a culture of change. This involves not just championing improvement initiatives but also modeling the behaviors and mindset required for continuous improvement. Effective change management strategies are essential to overcome resistance and ensure that new practices are adopted and sustained.
Adaptability and Innovation: A true culture of change prepares an organization to swiftly adapt to new challenges and opportunities. It encourages innovation and experimentation, viewing failures as learning opportunities rather than setbacks. This adaptability is crucial in today’s fast-paced business environment.
By thoroughly understanding and implementing these five Lean Six Sigma principles, organizations can drive significant improvements in efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. While each principle is powerful on its own, their true strength lies in how they work together to create a comprehensive approach to operational excellence.
Practical Tips to Implement Lean Six Sigma Principles in Your Organization
1. Secure Leadership Commitment and Create a Vision
Implementing Lean Six Sigma principles requires unwavering support from top management. Leaders must not only endorse the initiative but actively champion it throughout the organization. Start by educating executives on the benefits of Lean Six Sigma, emphasizing how it aligns with strategic goals and can drive competitive advantage. Develop a clear vision for what Lean Six Sigma implementation will achieve, and communicate this vision consistently across all levels of the organization.
Key actions:
Conduct executive workshops on Lean Six Sigma principles and benefits
Develop a compelling business case showcasing potential ROI
Create a roadmap for implementation with clear milestones and objectives
2. Build a Strong Foundation with Training and Certification
A successful Lean Six Sigma initiative relies on having a skilled workforce capable of applying its principles and tools effectively. Invest in comprehensive training programs tailored to different roles within the organization. Begin by training a core group of employees to lead projects and mentor others. As the initiative grows, expand training to cover a broader base of employees.
Training structure:
White Belt: Basic awareness for all employees
Yellow Belt: For team members supporting projects
Green Belt: For project leaders and key process owners
Black Belt: For full-time Lean Six Sigma experts
Master Black Belt: For strategic oversight and program management
3. Start with Pilot Projects to Demonstrate Value
Rather than attempting a company-wide rollout immediately, begin with carefully selected pilot projects. Choose projects that are likely to yield significant, measurable results within a reasonable timeframe. These early successes will help build momentum, generate enthusiasm, and provide valuable learning experiences for your teams.
Criteria for selecting pilot projects:
Clear alignment with strategic objectives
High potential for measurable impact
Manageable scope and timeline
Strong support from relevant stakeholders
4. Implement a Robust Project Selection and Management Process
As your Lean Six Sigma program matures, establish a systematic approach to identifying, prioritizing, and managing improvement projects. This ensures that resources are allocated to initiatives that will deliver the greatest value to the organization and its customers.
Key components:
Project selection criteria aligned with strategic goals
Regular project review meetings to track progress and address challenges
Standardized project documentation and reporting templates
A centralized project tracking system or dashboard
5. Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Lean Six Sigma is not just a set of tools; it’s a mindset that should permeate the entire organization. Cultivate an environment where all employees feel empowered to identify and address inefficiencies in their daily work. Encourage experimentation and learning from both successes and failures.
Strategies to promote a continuous improvement culture:
Implement a suggestion system for improvement ideas
Recognize and reward employees who contribute to process improvements
Share success stories and lessons learned across the organization
Integrate continuous improvement goals into performance evaluations
6. Leverage Data and Technology
At its core, Lean Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology. Invest in tools and systems that enable efficient data collection, analysis, and visualization. This not only supports better decision-making but also helps quantify the impact of improvement initiatives.
Key technological enablers:
Statistical analysis software
Process mapping and simulation tools
Real-time data dashboards
Collaboration platforms for project teams
7. Sustain and Scale the Initiative
Maintaining the momentum of your Lean Six Sigma program over the long term requires ongoing effort and attention. As initial enthusiasm wanes, it’s crucial to have mechanisms in place to sustain improvements and continue driving the initiative forward.
Sustainability measures:
Regularly review and refresh training programs
Conduct periodic audits of improved processes to prevent backsliding
Integrate Lean Six Sigma principles into standard operating procedures
Develop a succession plan for key Lean Six Sigma roles
Continuously evolve the program based on lessons learned and changing organizational needs
By following these seven key steps, organizations can create a strong foundation for their Lean Six Sigma implementation, driving sustainable improvements in efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. Remember that successful implementation is a journey that requires patience, persistence, and a commitment to continuous learning and adaptation.
Key Tools and Techniques in Lean Six Sigma
Successful implementation of Lean Six Sigma principles relies on a robust set of tools and techniques designed to eliminate waste, improve process flow, and reduce defects. Below are some of the essential tools and techniques in Lean Six Sigma:
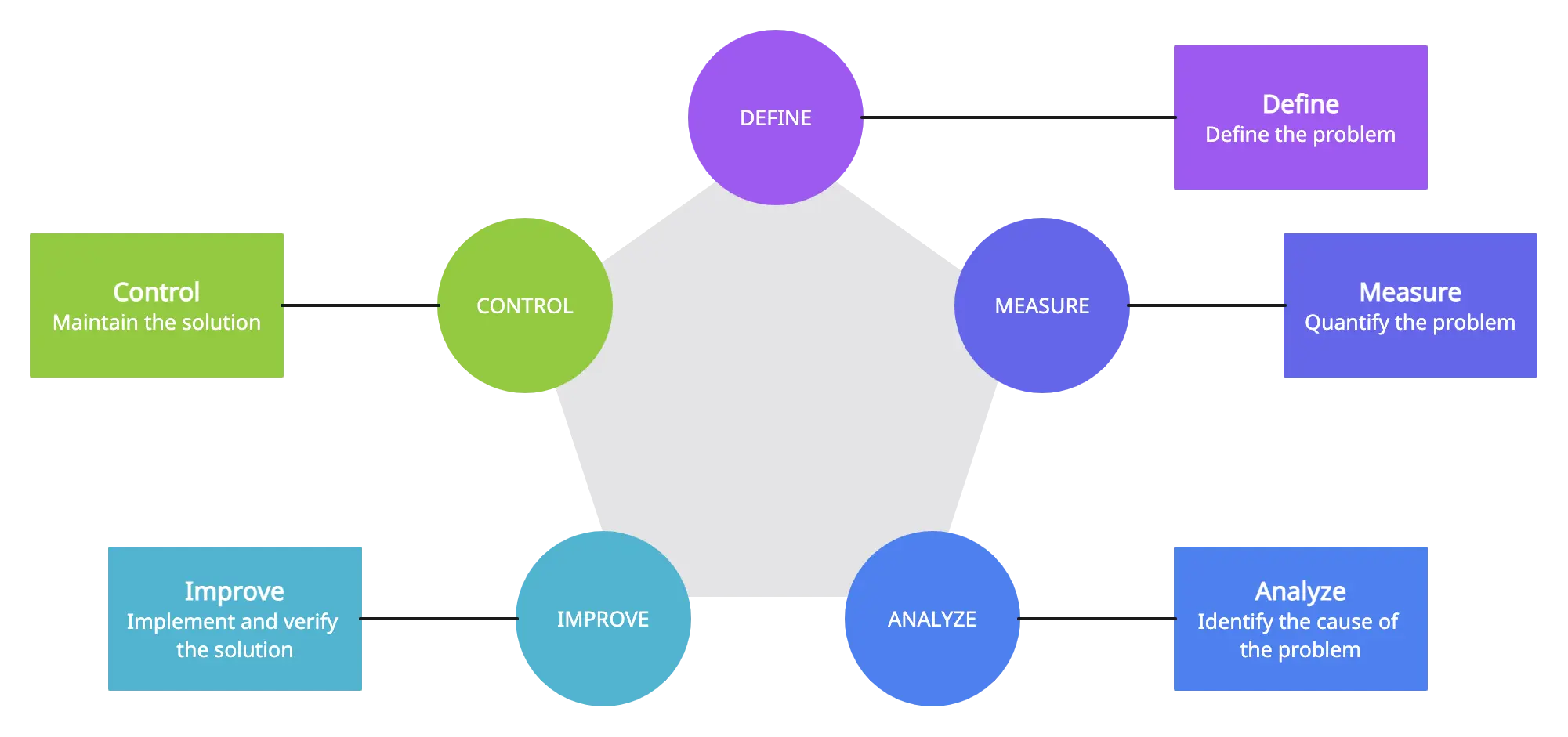
1. DMAIC
DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It is a structured, customer-focused methodology used for process improvement in Lean Six Sigma. Each phase of DMAIC helps in identifying issues, quantifying problems, and implementing solutions that result in improved efficiency and reduced variations.
2. Kanban
Kanban is a visual workflow management tool that helps in optimizing the flow of tasks and managing work in progress. By visualizing the workflow on a Kanban board, teams can identify bottlenecks, prioritize work, and ensure tasks move smoothly through each stage of completion.
3. 5S
The 5S technique focuses on workplace organization and standardization. The five S’s stand for Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain. Implementing 5S helps in maintaining a clean, organized workspace, which eventually leads to improved productivity and reduced waste.
4. Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is a lean-management method used to document, analyze, and improve the flow of materials and information. It helps in identifying areas of waste and opportunities for process enhancement. You can leverage Value Stream Mapping Software to create and analyze your value stream maps efficiently.
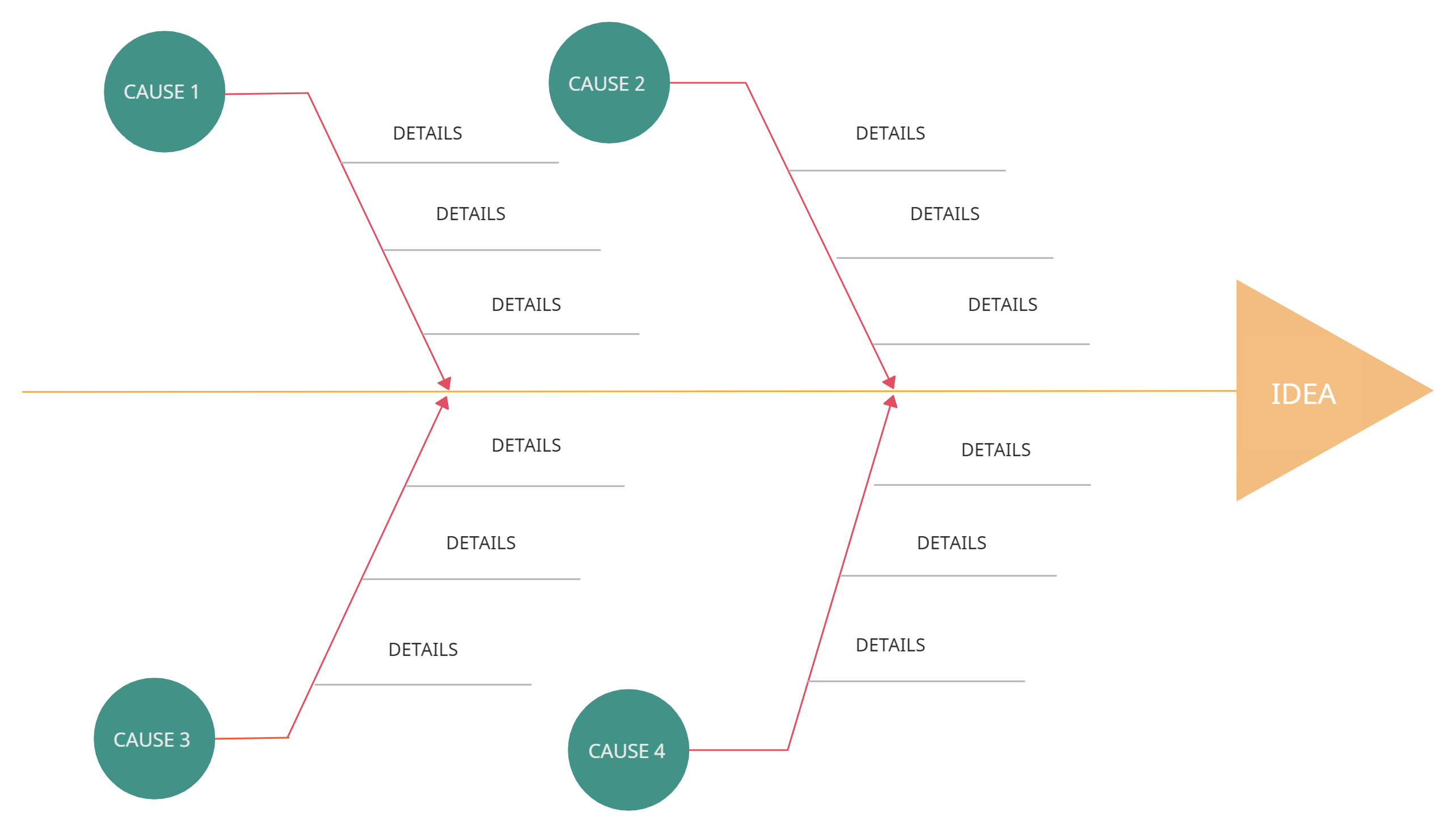
5. Fishbone Diagram
Also known as Ishikawa or Cause-and-Effect Diagram, this tool is used to identify the root causes of problems within a process. By laying out various potential causes and their effects, teams can systematically tackle issues and implement effective solutions.
6. SIPOC Analysis
SIPOC stands for Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers. It is a tool used to understand all the elements involved in a process. By mapping out these elements, teams can visualize the entire process, identify critical areas for improvement, and ensure consistency and quality in outputs.
Utilizing these tools and techniques, along with a robust platform like Creately, can greatly enhance your Lean Six Sigma implementation. Creately supports process mapping and visualization, enabling real-time data integration, collaborative planning, and improved documentation. For instance, you can use a Value Stream Map Template to streamline your processes and identify waste effectively.
How Lean Six Sigma Principles Can be Applied Across Industries
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, Lean Six Sigma has drastically improved production efficiencies and decreased defect rates. For example, a well-known automobile company utilized these principles to refine its production processes. By employing value stream mapping and the DMAIC framework, they identified bottlenecks and waste. The result was a 30% increase in production efficiency and a significant drop in defect rates. This case underscores the importance of Lean Six Sigma in optimizing complex manufacturing processes to achieve both speed and quality.
Healthcare
Lean Six Sigma methodologies have been transformative in the healthcare sector. Hospitals have used these principles to enhance patient care and streamline operations. One notable case involved a hospital that implemented Lean Six Sigma to address long patient wait times and inefficient emergency room procedures. Through process mapping and root cause analysis, they were able to reduce average patient wait times by 50%, significantly improving patient satisfaction and overall care quality. This indicates the enormous potential for Lean Six Sigma to drive improvements in healthcare delivery.
Financial Services
In financial services, Lean Six Sigma has been employed to streamline processes and reduce errors. A major bank implemented Lean Six Sigma techniques to refine its loan approval process. By conducting a thorough SIPOC analysis and eliminating non-value-added steps, they managed to cut the time required for loan approvals from weeks to mere days. This not only increased customer satisfaction but also boosted the bank’s operational efficiency, proving how Lean Six Sigma can enhance service delivery in the financial sector.
Government
Government agencies have also benefited from Lean Six Sigma by increasing transparency and service efficiency. A local government body utilized these principles to improve its permit approval process. By involving and equipping employees with Lean Six Sigma tools and undergoing continuous process improvements, the agency reduced approval times by 40% and improved public satisfaction. This demonstrates how even public sector organizations can leverage Lean Six Sigma for operational excellence and enhanced citizen services.
For more information on improving your processes and understanding Lean Six Sigma, you may find the following resources helpful:
Lean Six Sigma is more than a methodology; it’s a catalyst for organizational transformation. As businesses navigate increasingly complex challenges, these principles offer a roadmap to excellence. While implementation may be challenging, the rewards in efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction are substantial.
The future of Lean Six Sigma lies in its integration with emerging technologies, promising new frontiers in process optimization. However, its true power resides in its ability to cultivate a culture of continuous improvement and data-driven decision-making.
By empowering employees to become agents of change, Lean Six Sigma doesn’t just transform processes—it revolutionizes mindsets. Organizations that successfully embed these principles will be well-equipped to thrive in an ever-evolving business landscape, turning challenges into opportunities for growth and innovation.