This concept map tutorial is to help you master the technique of using concept maps, whether it is for your education or for your business.
In this concept map guide, you will find insight into,
- What is a Concept Map?
- Origin of Concept Maps
- The Characteristics of a Concept Map
- How to Draw a Concept Map
- How Do You Fine-tune a Concept Map
- Concept Map Templates
- Uses of Concept Maps
- What are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid When Creating a Concept Map
- Concept Map Best Practices
What is a Concept Map?
Concept maps are a graphical tool that is used to visualize meaningful relationships among concepts. It’s used as a knowledge representation tool, meaning they basically represent the knowledge structure that we humans store in our minds about a certain topic.
Both simple and complex concept maps consist of two things: concepts and relationships among them.
Origin of Concept Maps
Concept maps were the outcome of a research done in the 1970s at Cornell University by Joseph Novak – an American Educator and Research Scientist – and his research team.
In order to study how children understand basic science concepts, they studied and interviewed many children. However, they found it difficult to identify the changes in the ways children understood science concepts with the detailed interview transcripts alone.
The need to find a better solution to represent children’s conceptual understanding led to the development of the concept map in 1972.
Since then it has been used extensively not only in the fields of education and research but also in business.
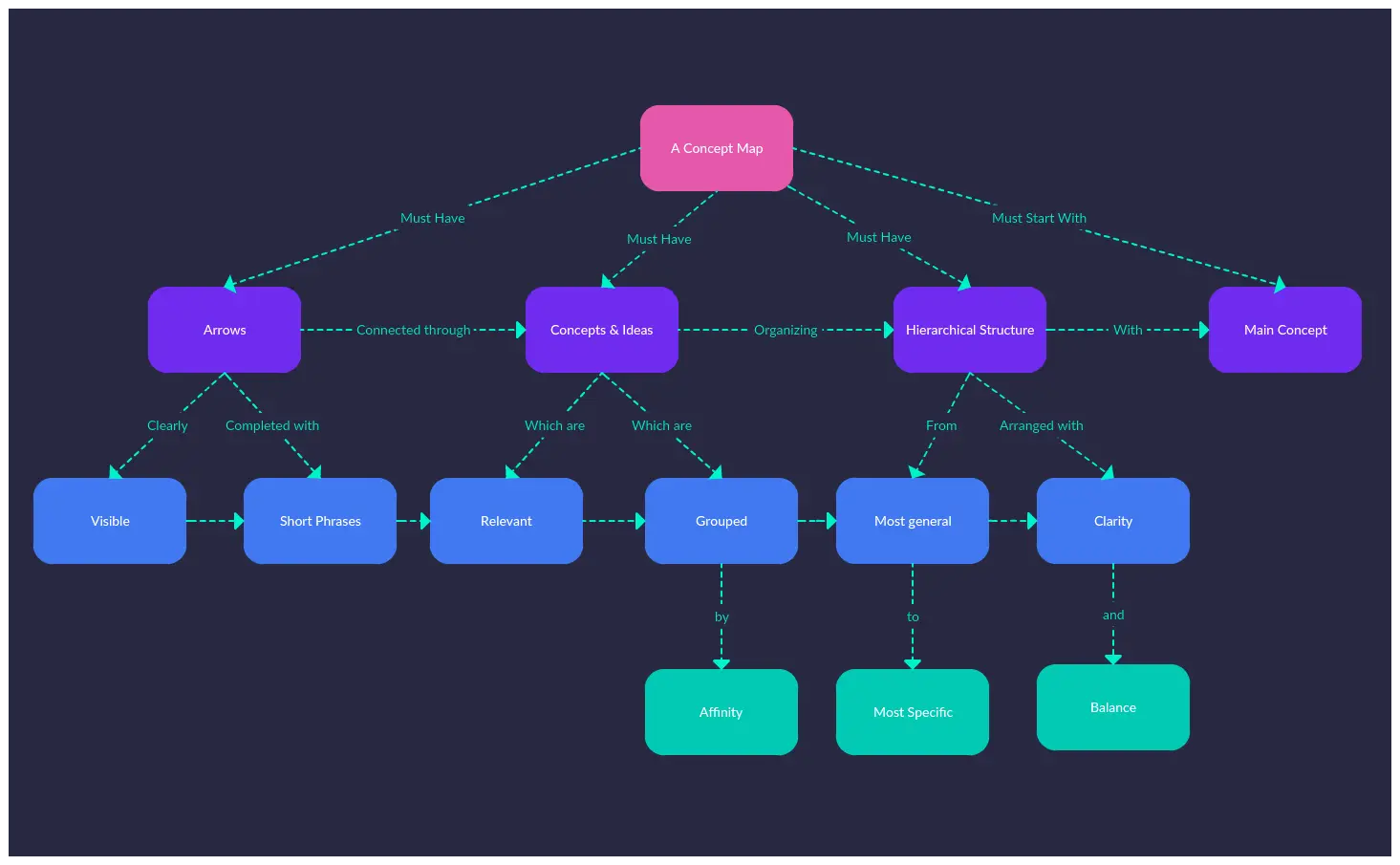
The Key Characteristics of a Concept Map
Not all diagrams that have words/ phrases inside nodes are concept maps. Concept maps have specific characteristics that distinguish themselves from other diagrams that are used to represent knowledge. And they are,
Nodes
Nodes are the circles or the boxes that are used to represent a concept or an idea. These may vary in size, according to their hierarchy on the map; for example, more general nodes at the top of the map may be bigger than the more specific nodes that follow them.
Cross-Links
Concept maps consist of concepts in different domains. And the relationships between these different domains of knowledge are shown with cross-links.
Linking Words
Or linking phrases if it contains more than a word. These describe the type of relationship between the two concepts and appear on the line connecting them.
Hierarchical Structure
Usually, concept maps are organized hierarchically. This means the most general and inclusive concepts are placed at the top of the map. Those that are more specific are positioned below them. Accordingly, hierarchical concept maps are read from top to bottom.
However, the structure of a concept map is not limited to this structure, it could take a free-form approach too – starting from the center and spreading outwards.
Propositional Structure
A concept map illustrates a set of meaningful propositions about a topic.
Every two concepts (in some cases more than two,) along with the linking phrases, form a meaningful sentence, otherwise known as a proposition.
For example, in the following concept map, the concepts “Relationships” and “Connectors and linking words” are connected by the linking phrase “Are represented by”. When connected, this forms the proposition “Relationships are represented by connectors and linking words”. 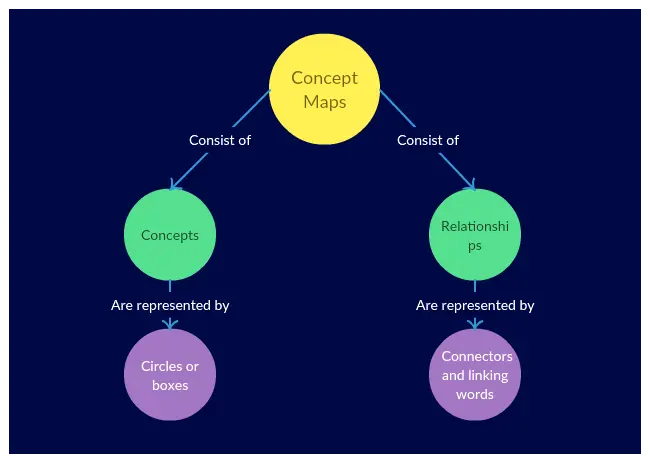
Focus Question
Generally, a concept map should be woven around a focus question, which is the problem or the issue the concept map seeks to resolve. The better the focus question, the richer the concept map will be.
Underlying Theory
Concept maps are based on Ausubel’s Assimilation theory. This is built around the fact that new knowledge can be learned effectively by linking it to what is already known. Concept maps are seen as a methodological tool of this theory.
Generate new ideas and add structure to your thoughts with concept maps. Explore connections between concepts to better understand them with Creately.
How to Draw a Concept Map
You can either draw a concept map on a piece of paper or on a concept mapping software. Either way, stick to the following steps when you are drawing one.
Step 1: Pick a Topic
The first step is to identify a topic you need to study with your concept map. This could be an idea, a question or an issue.
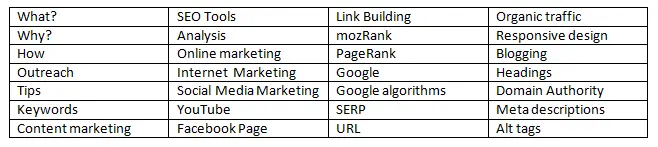
For example, let’s say you are interested in SEO or Search Engine Optimization.
Step 2: Do a Quick Brainstorm
What are the facts, ideas, concepts, themes, queries etc. that come to your mind when you think about this topic? Note these down as you brainstorm around the topic you have selected. Remember to keep these as concise as possible.
Step 3: Start to Draw the Map
It’s recommended to start a concept map from the top and develop it downward, although you can put down your topic at the center and expand it outwards. Either way make sure that the central topic stands out from the rest (use a bigger node, a different color etc.).
Step 4: Connect the Concepts
Now it’s time to connect what you have brainstormed to the central topic and to each other. Remember, the more important the idea, the closer it should be to the top or the center.
As you identify these connections put down the linking words or phrases to indicate the relationship between the two concepts you are linking.
Once the direct connections between concepts have been identified, look for crosslinks that link together concepts from different areas or domains.
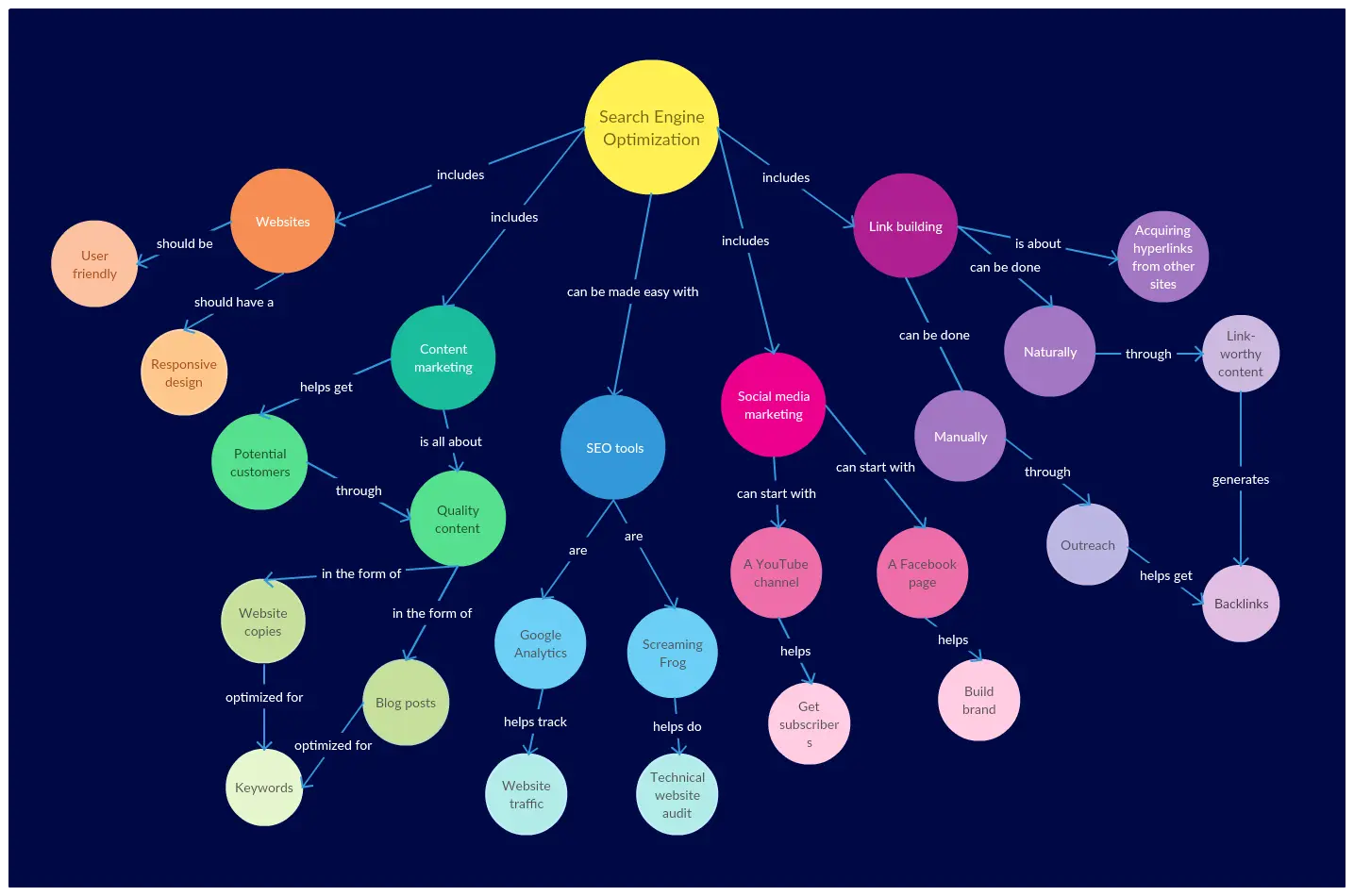
Step 5: Anything Missing?
Scrutinize what you have created to make sure that you haven’t missed anything and that the relationships you have identified make sense.
How Do You Fine-tune a Concept Map?
Fine-tuning the concept map is a crucial step when effectively visualizing complex information. Below are some key pointers to follow.
- Begin by reviewing the entire map to identify areas needing improvement or some adjustments.
- Refine the central idea, if necessary, to ensure that the central idea accurately represents the main topic of the concept map.
- If there are long labels, simplify them using specific or descriptive keywords that represent the concept or idea of the map. This will help to reflect the content of each node accurately.
- Evaluate whether any nodes should be added or removed depending on their relevance and redundancy. Look to see if any additional concepts or ideas should be included.
- Review the connections to ensure they correctly represent the relationships between the concepts. If necessary, add or remove connections or adjust the placement of nodes to reflect the connections better.
- Test the map! Test the map with others for feedback, especially on its accuracy and effectiveness.
Editable Concept Map Examples and Templates
Here are some concept map diagram templates you can edit right away on Creately. Click the image to open it in the editor. Make changes according to your needs and export them as images, PNG, PDF, or JPEG.
Concept Map Example 1
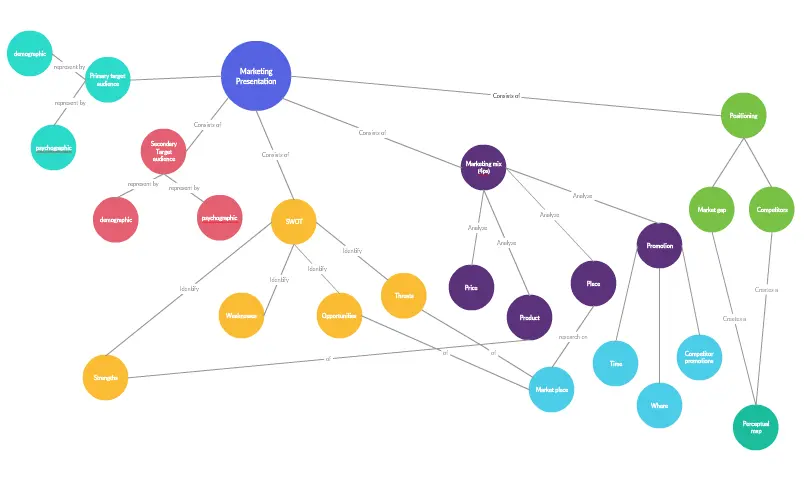
Concept Map Example 2
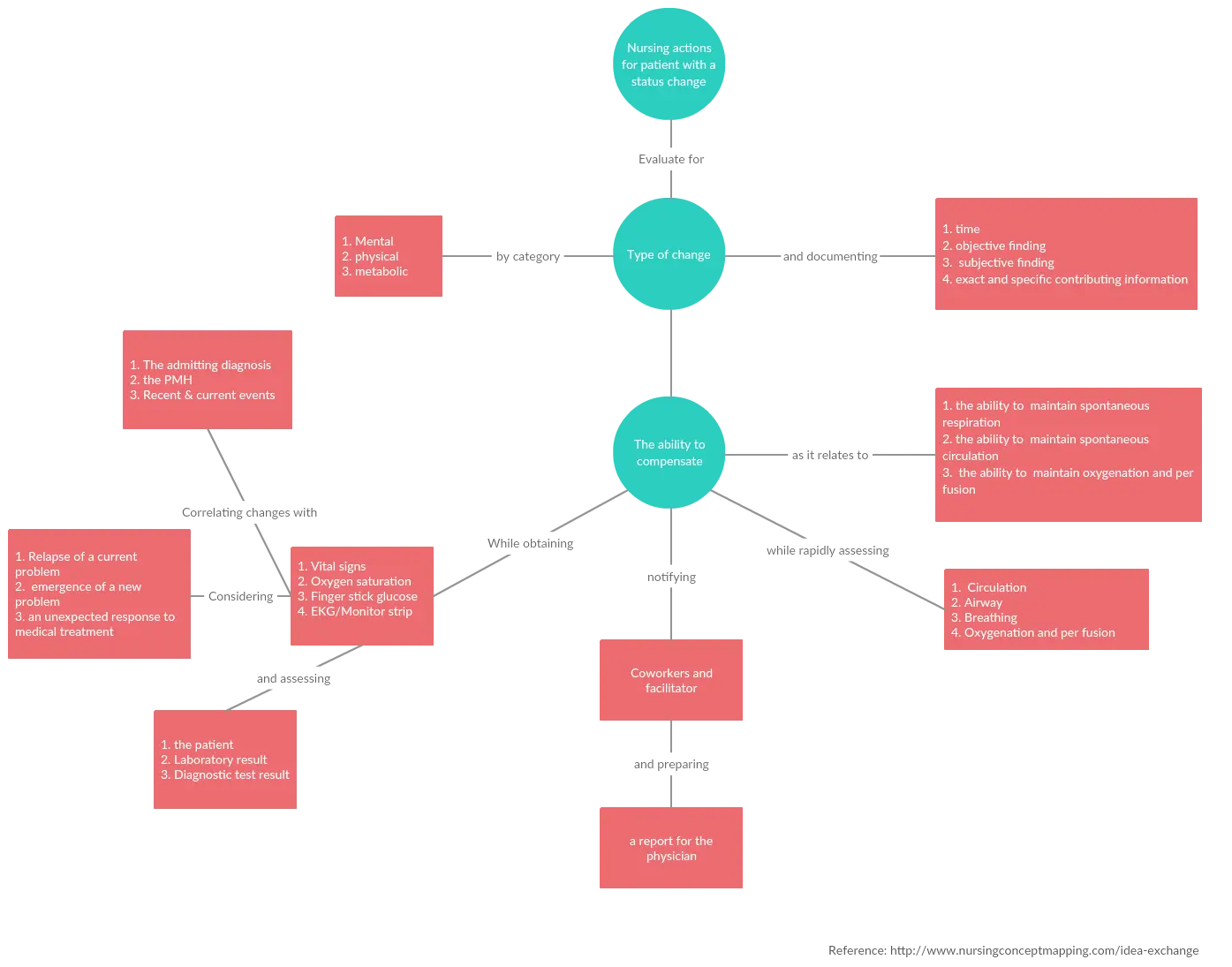
Concept Map Example 3
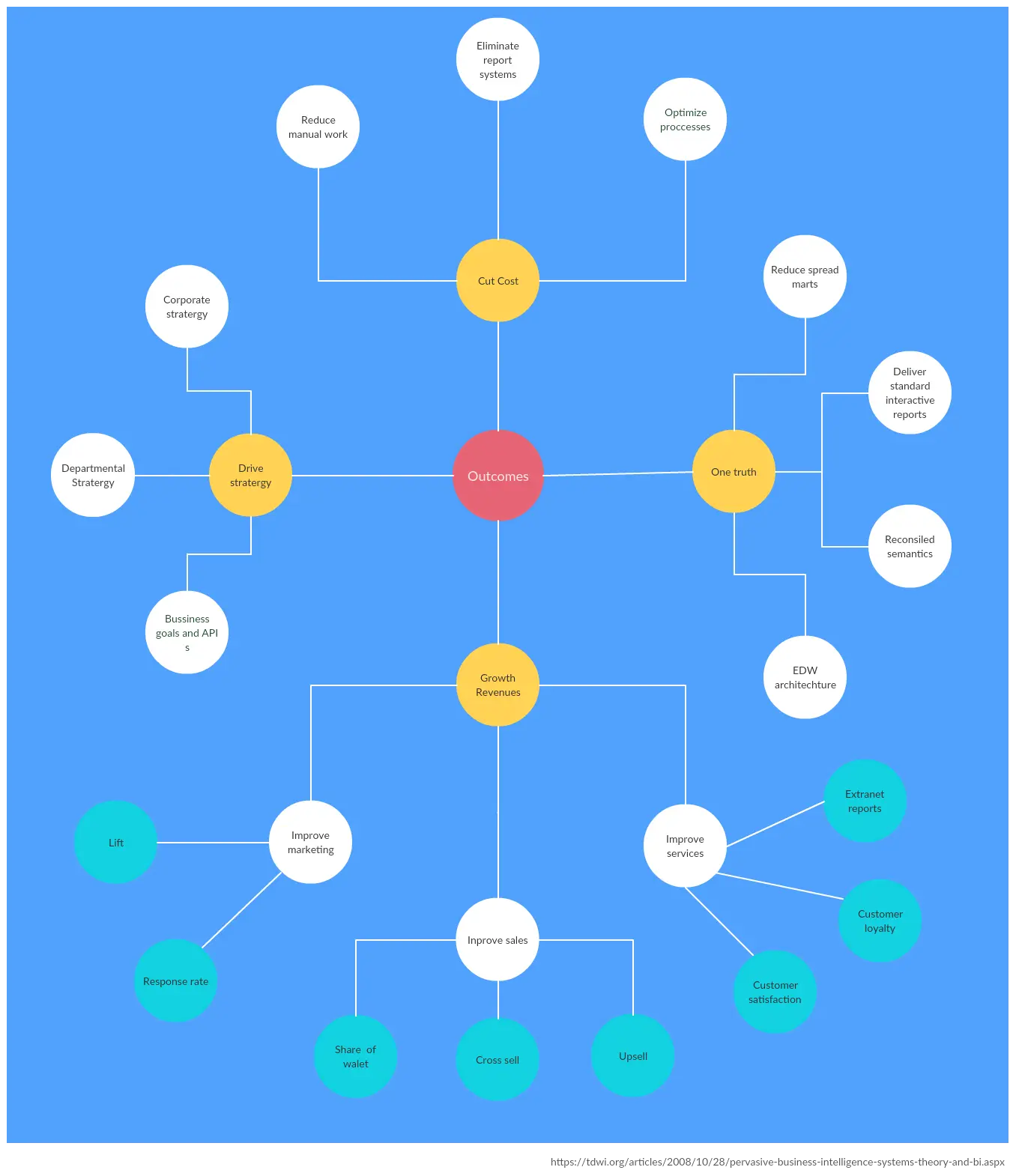
Concept Map Example 4
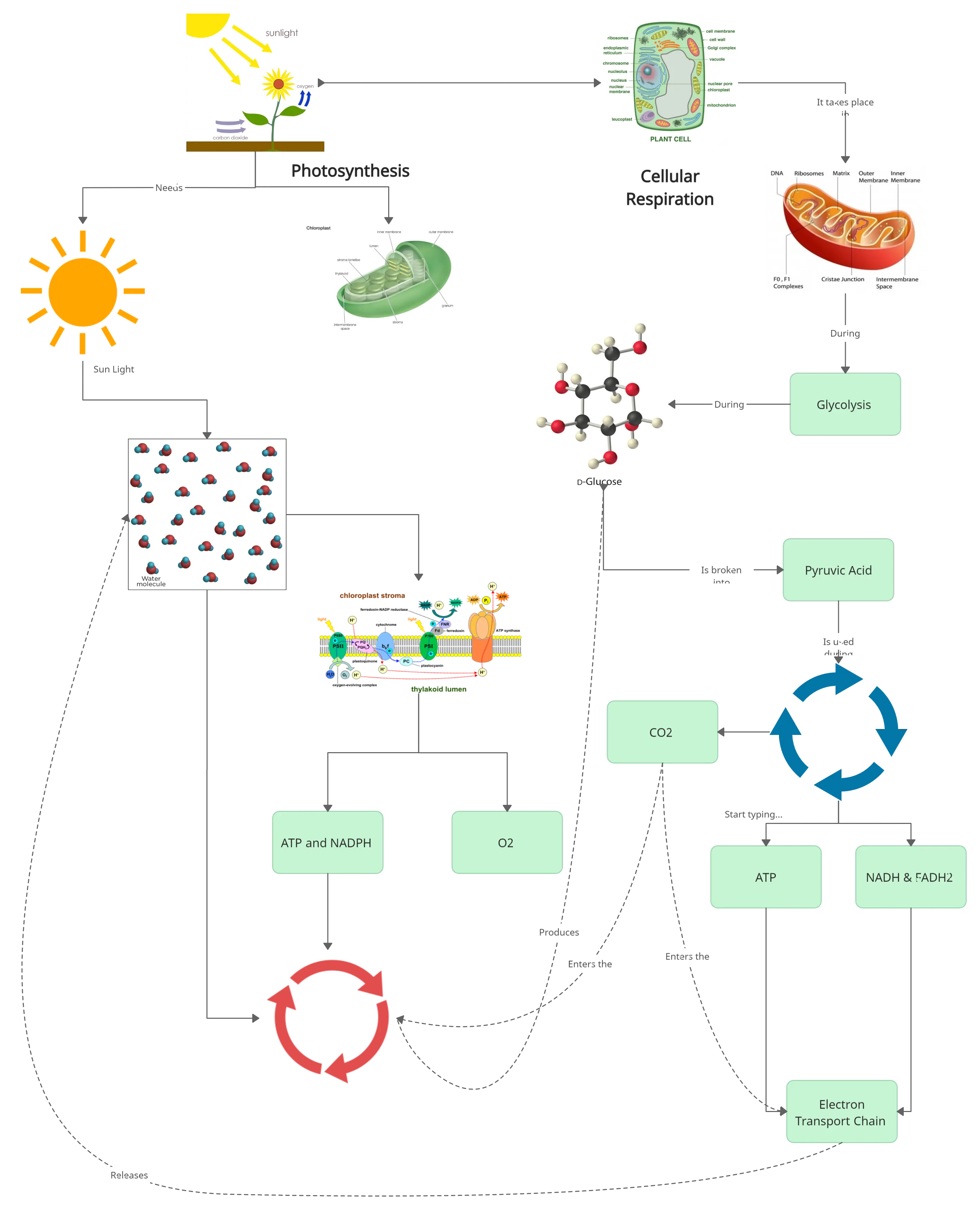
Concept Map Example 5
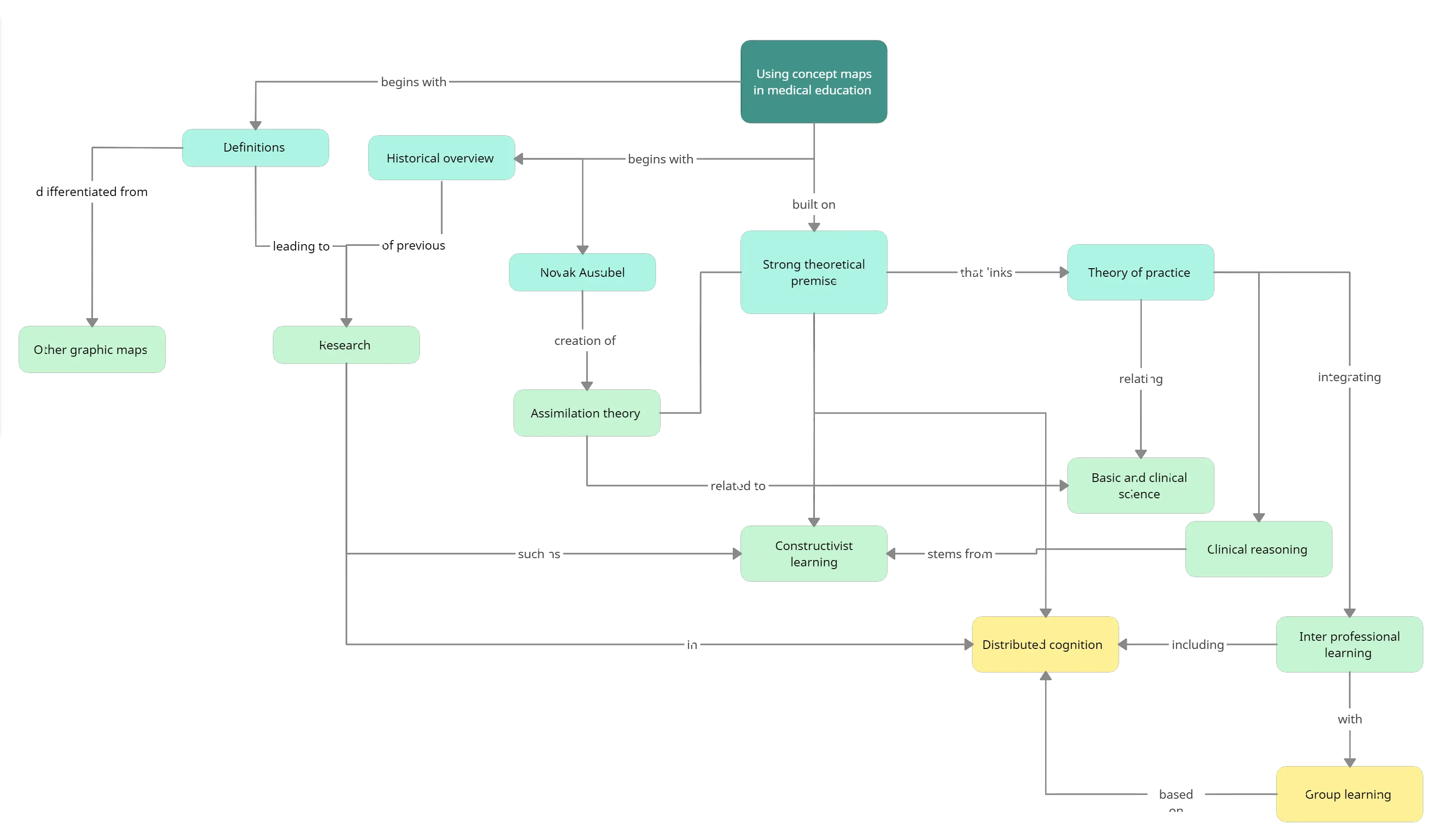
Concept Map Example 6
Concept Map Example 7
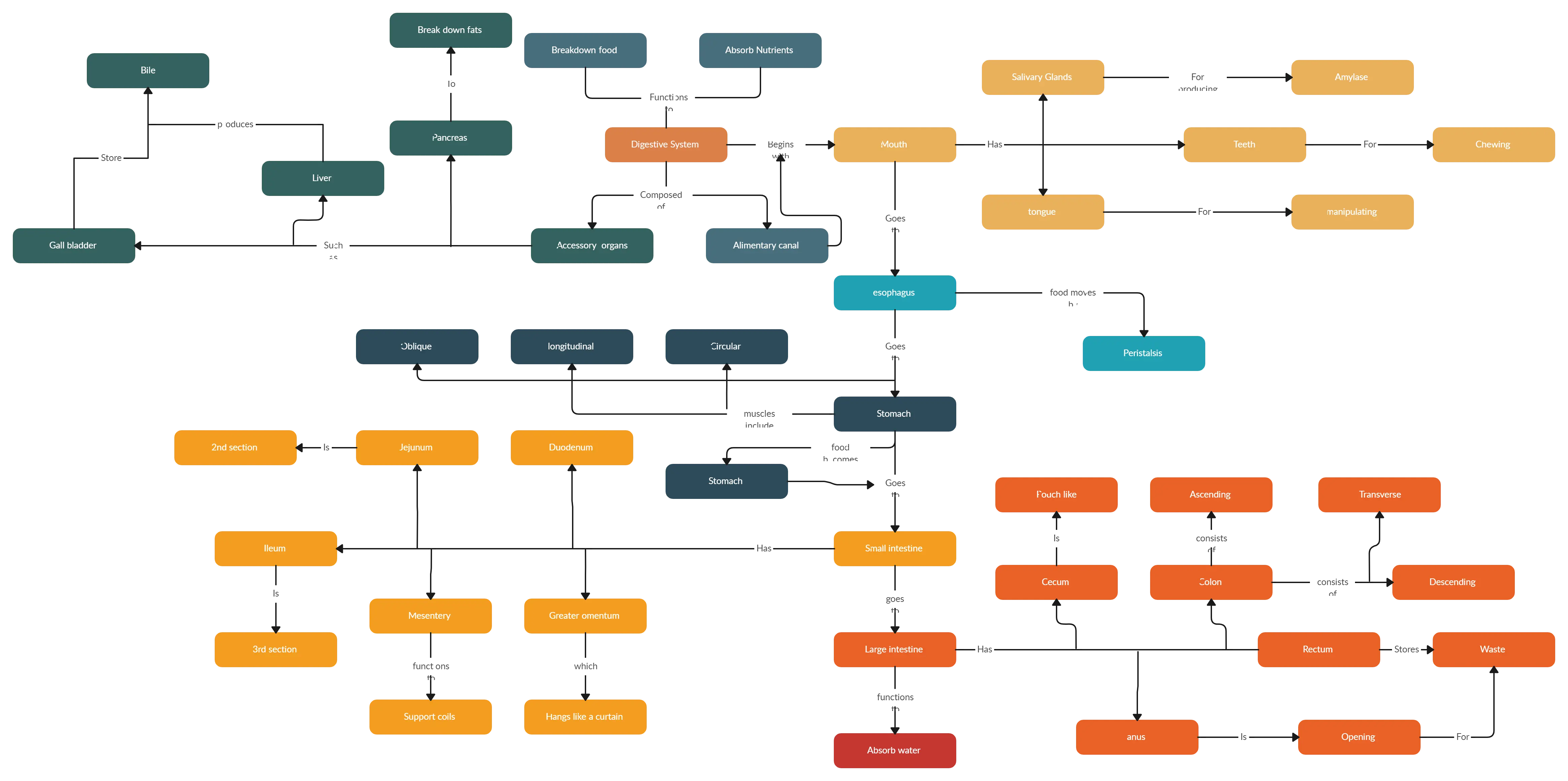
Uses of Concept Maps
Although first introduced to the field of education, concept maps have gained popularity across a number of other fields over the last few decades.
Concept Maps in Education
In the field of education, concept maps are used as both a learning tool and an evaluation tool to assess student learning.
- Foster meaningful learning by helping create connections between what students already know and new knowledge they acquire
- Organize knowledge around a subject for quick analysis
- Assess students’ understanding to see where their knowledge needs improvement
- Conduct effective brainstorming around a topic
- Present complex concepts in an easily digestible way
- Organize instructional material for courses or curricula
- Can be used as a basis for discussion among students
- Help identify valid and invalid ideas held by students
- Help promote creative and critical thinking among students
- Can be used as an alternative to traditional note-taking and writing assignments
Concept Maps in Business
By design, concept maps are apt for business analysis. In the field of business, concept maps are popularly used to preserve, generate and share knowledge.
- To facilitate team brainstorming sessions to come up with new strategies, new business concepts etc.
- Support creative and result-oriented approach towards business development
- Can be used as a systematic way to share expert business ideas, insights etc. with others
- Help with planning and drafting business documents, business presentations etc.
Concept Maps in Qualitative Research
Concept maps in qualitative research are used as a methodical research strategy.
- Can be used to plan a research project
- Can help reduce voluminous text-based data into a manageable form without losing the meaning
- Identify interconnections between concepts in a study and analyze themes
- Analyze the information provided by interviewees in a study; help the researcher maintain the meaning of the interview
- Present findings in an effective way
What are Some Common Mistakes to Avoid when Creating a Concept Map
When creating your concept map, avoid the below common mistakes that will undermine the map’s effectiveness.
- Overcomplicating. This will make the map too complex or difficult to understand.
- Focusing too much on the details. Getting bogged down with too many details will derail you from the main focus with too much irrelevant and unnecessary information.
- Not using a hierarchy. Without a hierarchy, the concept map will be too complicated to follow and disorganized.
- Not using consistent formatting. It will be difficult to read or understand without consistent formatting and symbols throughout the map, leading to confusion and misunderstandings.
- Being too rigid by not making changes as and when necessary to reflect new information or insights.
- Not testing the map for effectiveness to help identify areas that may need further improvement.
Concept Mapping Best Practices
Start with a Clear Central Idea
Begin the concept map with a clear yet concise central idea representing the main topic or theme. The central idea should be easily understood, and it should also be the focal point of the map.
Stick with the Hierarchical Structure
Concept maps organized according to the hierarchical structure are easier to read. As the most general concepts go at the top and the more specific ones coming below them, it can easily be read from top to bottom.
Keep a Single Root Concept
A concept map can have two root concepts, but limiting it to one helps the learner easily identify how concepts are constructed. On the other hand, having two root concepts may make it confusing.
Use Meaningful Keywords
Use meaningful and specific keywords to label the concepts. The labels should be descriptive and accurately represent the content of each node.
Color Code Your Concept Maps
Colors help distinguish concepts in different domains immediately. This does not only make it easier to read the map but when it comes to recalling information, color coding plays a vital role.
Add Visual Cues to the Map
Add visual cues such as symbols and images if necessary to highlight important information and to make the concept map more engaging and visually appealing.
Connect Related Ideas
Add visual cues such as symbols and images to highlight important information and make the concept map more engaging and visually appealing.
Make Sure Linking Phrases Make Sense
Two concepts and a linking phrase should make a meaningful sentence. This could be a word, phrase or sometimes even a symbol such as + or %. In any case, make sure that your concept map reads well.
Be Consistent
Use consistent formatting, symbols, and color codes throughout the concept map to make it easier to read and understand.
Always Base Your Concept Map on a Focus Question
Having one single question to answer will help you better structure your concept map and keep yourself from deviating from your focus.
Keep it Simple
If possible, avoid using complex sentences or too much text. Instead, use simple phrases or keywords to communicate the main ideas and connections.
Link to Further Resources
If you are drawing your concept maps with a concept mapping software, you have the ability to make it more resourceful. When mentioning concepts, you can add active links to your concept maps allowing the reader to study the idea more thoroughly.
Review and Revise
One thing to remember is that concept maps can be changed and updated regularly as needed. This will help to refine your ideas and to identify new connections between concepts.
Feed Back on the Comprehensive Concept Map Tutorial
In this concept map tutorial we have covered, everything – whether you are a stranger to concept mapping or have used it before – you should know when it comes to concept map diagrams. If you are ready to go ahead and draw your concept map, start with the Creately Concept Map Maker.
And don’t forget to leave your feedback!