Many organizations fall into a costly trap when implementing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems – they assume that new technology alone will streamline their operations, without first examining and understanding their actual business processes. This fundamental misconception often leads to expensive corrections, implementation delays, and sometimes outright project failures.
Successful ERP implementations are driven not by software capabilities, but by a deep understanding and optimization of business processes. Before any technology decisions can be made, organizations must invest time in documenting, analyzing, and improving their operational workflows. This is where business process mapping becomes an indispensable tool throughout the ERP journey.
What is Process Mapping?
Process mapping is a systematic method of visually documenting and analyzing the sequence of steps, decisions, inputs, and outputs that make up a business process. It creates a detailed visual representation of how work flows through an organization, showing:
Who performs each task
What actions are taken
When activities occur
Where information or materials flow
How decisions are made
Why certain steps are necessary
By visually documenting and analyzing workflows, companies gain a comprehensive view of their operations, which is essential for aligning the ERP system with organizational goals. Process mapping not only highlights inefficiencies and opportunities but also fosters collaboration, ensuring every department is on the same page from the start. This approach minimizes disruptions, sets realistic expectations, and provides a roadmap for achieving sustainable change. Whether starting fresh or upgrading an existing system, process mapping lays the groundwork for a successful ERP implementation, creating a blueprint for continuous growth and improvement thorough erp business process mapping.
What is ERP Business Process Mapping?
ERP Business Process Mapping has become a fundamental practice that visually represents an organization’s business processes. It plays a crucial role in demonstrating how these processes function, the resources involved, and the outcomes they deliver. This method not only identifies current operational roadblocks but also aligns future strategies with technology capabilities.
When implemented effectively, ERP Business Process Mapping becomes an integral part of aligning business objectives with the technological aspects of ERP systems. It maps out the current state of business operations (“As-Is”) and the desired future state (“To-Be”), providing a clear pathway for transformation and optimization. For instance, mapping your sales to invoice process ensures every stage from purchase requisition to payment is documented and analyzed. Such mapping aids in aligning workflows directly with business needs, helping in selecting an ERP system that cuts inefficiencies and enhances performance.
Moreover, business process mapping enhances decision-making capabilities leading to better ERP system selection. Accurate process maps eliminate assumptions and uncover non-negotiable functions even before ERP implementation. They also pave the way for process improvements, allowing enhancements beyond replicating existing systems. This foresight ultimately drives higher efficiency and productivity across the enterprise thorugh ERP Business Process Mapping.
The relationship between business process mapping and ERP flows in multiple stages:
Pre-Implementation Mapping:
Organizations map their current business processes to understand exactly how work flows through the organization. This critical first step helps identify:
Core business functions and their interconnections
Existing inefficiencies and bottlenecks
Areas requiring automation or improvement
Essential requirements for the ERP system
During Implementation:
Process maps guide the configuration and customization of the ERP system, ensuring it aligns with:
Required workflows and business rules
Data flow requirements
Integration points with other systems
User roles and permissions
Post-Implementation Documentation:
After ERP deployment, process maps evolve to document:
How business processes operate within the ERP system
Integration points between the ERP and other organizational systems
Updated workflows and procedures
System dependencies and relationships
Helpful Resources
Comprehensive software solutions for visually documenting and analyzing business processes. Allows you to create detailed process maps, flowcharts, and workflows.
Robust tools for designing, automating, and optimizing business processes
Intuitive diagramming software for creating high-quality flowcharts, process diagrams, and other visual representations of workflows and procedures.
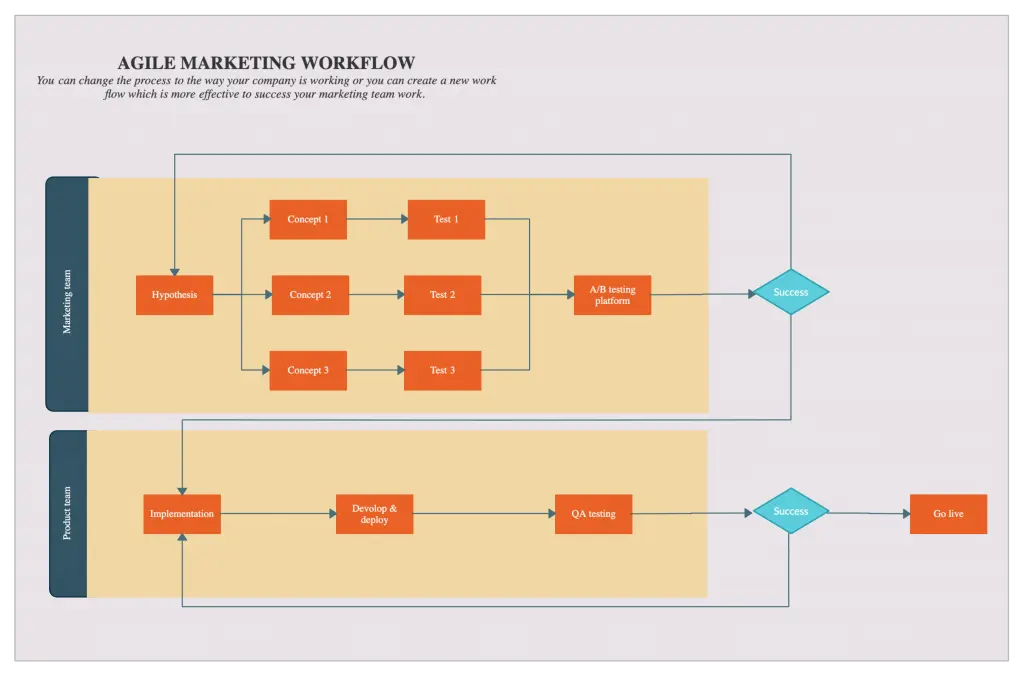
How Process Mapping Drives ERP Success
In the intricate landscape of enterprise resource planning, understanding the role and impact of process mapping in the ERP implementation process can significantly improve organizational outcomes. It serves as a vital blueprint that guides businesses from selecting the right ERP system to ensuring successful deployment and operation.
Identifying Gaps and Inefficiencies
Process mapping is critical in identifying gaps and inefficiencies within underlying business workflows. By visualizing current state processes, organizations gain insights into bottlenecks and repetitive tasks that demand optimization. This proactive approach reduces the risk of overlooking process inadequacies during ERP integration, thereby promoting efficiency in operations.Selecting the Right ERP Software
One major advantage process mapping brings to the table is aiding in the selection of ERP software that aligns with organizational needs. It ensures that key functionalities vital to business operations are identified early, reducing the likelihood of costly post-implementation modifications. With a clear-mapped strategy, businesses can narrow down ERP solutions that not only match current needs but are also scalable for future growth.Supporting Data Migration and User Training
In addition to aiding software selection, process mapping plays a pivotal role in facilitating smooth data migration from legacy systems to new ERP configurations. It provides a structured framework that guides stakeholders through the complexities of data transfers, ensuring that all relevant information is accurately integrated into the new system. Additionally, having a mapped-out process aids in planning targeted user training programs, enabling employees to better understand and navigate the new ERP system.
| Aspect | Benefits of Process Mapping |
| Gap Identification | Unveils inefficiencies and bottlenecks for improvement. |
| ERP Selection | Ensures alignment with business needs, reducing unnecessary customizations. |
| Data Migration | Facilitates structured and accurate data integration. |
| User Training | Optimizes training programs by clearly outlining new processes. |
Overall, process mapping promotes clarity and alignment during the ERP implementation process, minimizing transition risks and paving the way for smoother operations. By embedding these foundations to ERP initiatives, companies position themselves for a higher likelihood of success and improved return on investment. This makes the process of ERP Business Process Mapping all the more vital.
Why You Need a Well-Mapped Process For ERP
Implementing an ERP system can transform organizational efficiency, but only when the underlying business processes are clearly understood and mapped. Here’s how ERP business process mapping delivers substantial advantages during ERP implementation:
Promotes Transparency: By providing a visual representation of business workflows, process mapping fosters a shared understanding among stakeholders. It enhances communication and aligns strategic goals with operational execution.
Facilitates Stakeholder Engagement: Process mapping encourages collaboration across departments, ensuring diverse viewpoints contribute to the workflow design. This engagement is crucial for garnering support for the ERP implementation process.
Comprehensive Documentation of Workflows: A robust ERP process map documents each step, decision point, and required resource across business processes. This detailed record assists in analyzing existing practices and designing future improvements.
Identification of Key Non-negotiable Functionalities: One of the key benefits of ERP business process mapping lies in identifying critical functions that the ERP system must support. It prevents the overlook of essential features and aids in selecting the suitable system with appropriate capabilities.
Ensures Efficient Knowledge Transfer: As personnel changes occur, having a well-defined process map ensures continuity. New employees can quickly understand organizational workflows, which streamlines onboarding and training processes.
Moreover, business process mapping is also essential post-implementation. It provides the tools to monitor ERP performance and offers a framework for continuous process improvement. In fact, when organizations reflect on pre- and post-ERP implementation scenarios, they often uncover opportunities for optimization and innovations. The importance has led to rise of a new field called ERP Business Process Mapping.
Additionally, tools like Creately’s visual workspace allow teams to construct comprehensive maps effortlessly. With features for Business Process Management and Visual Process Optimization, users can not only document processes but actively model, analyze, and refine them in collaboration with stakeholders. This approach assures that the benefits of ERP business process mapping stretch beyond initial implementation to drive long-term business success.
Finally, ensuring efficient knowledge transfer means that process understanding and skills are retained within the organization, reducing dependency on single individuals. By embracing the process mapping methodology, companies effectively lay a solid groundwork to maximize the return on their ERP investments.
How to Use Process Mapping For ERP Implementation
A detailed, step-by-step process map not only facilitates a smooth ERP transition but also ensures that every stage of the implementation aligns with organizational goals. Here’s a breakdown of how to use process mapping effectively for ERP implementation:
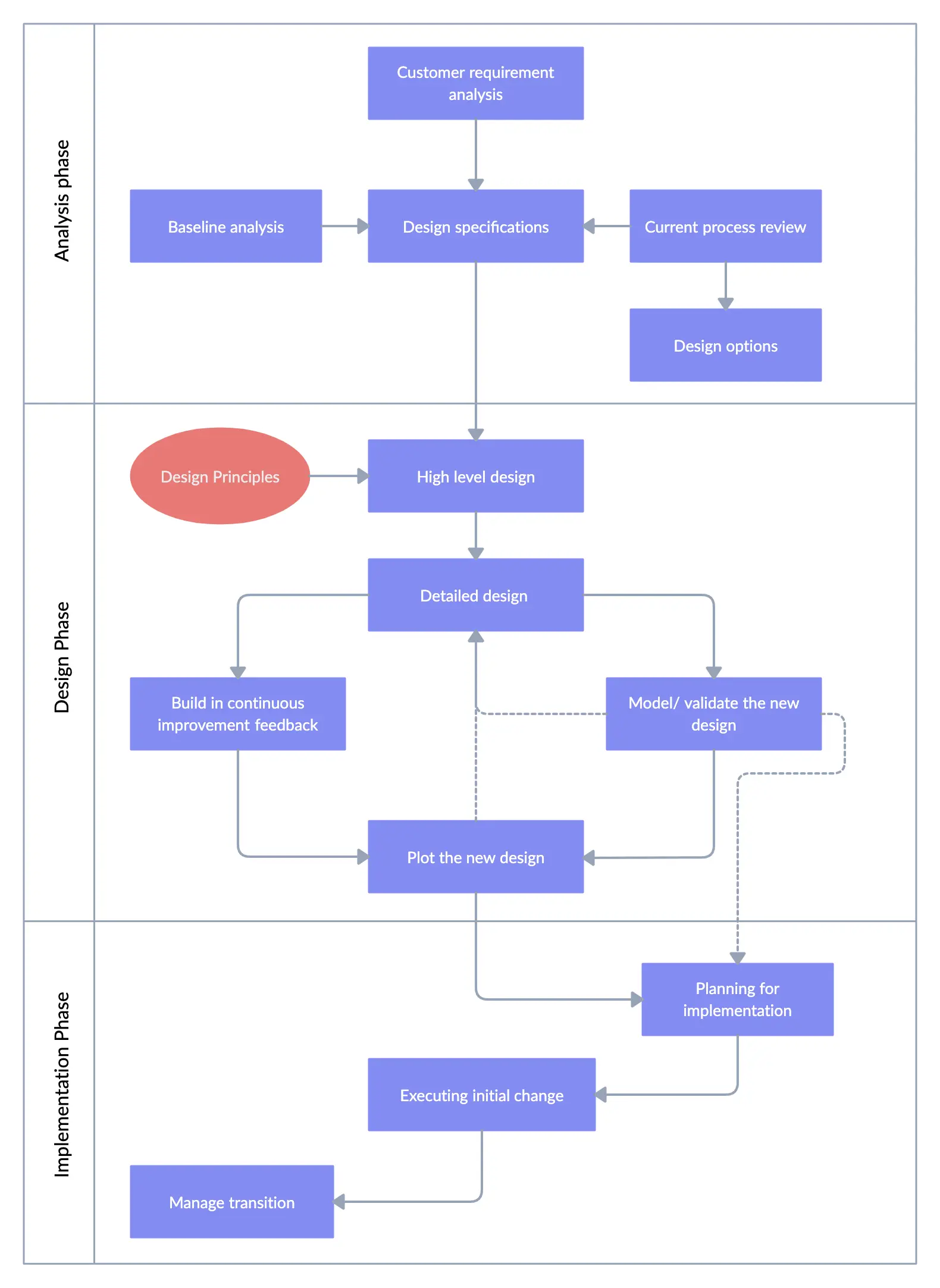
1. Define and Document Current State Processes:
The first and foremost step in process mapping is assessing where your business currently stands, often known as documenting the “As-Is” state. This process involves:
- Identifying Current Workflows: Outline existing workflows across departments, detailing each step involved. This creates a baseline that reflects day-to-day operations.
- Defining Roles and Responsibilities: Documenting the individuals or teams responsible for each process element provides insight into current task ownership and resource allocation.
Highlighting Inefficiencies: Identifying operational gaps, bottlenecks, and redundancies lays the groundwork for improvement. By understanding these pain points, organizations can prioritize areas needing streamlining.
Creating a Visual Representation: Tools like flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, or process maps can represent complex workflows, making it easier for stakeholders to analyze and discuss processes collectively.
This comprehensive “As-Is” documentation serves as both a reference and a benchmark against which future improvements can be measured.
2. Evaluate and Design Future State Processes:
Once the current state has been mapped, the next step is to create a vision of the desired “To-Be” processes, focusing on operational excellence rather than specific technologies. This step involves:
- Reengineering Workflows: Reevaluate each process to identify ways to eliminate bottlenecks and optimize efficiency. This may include consolidating steps, automating manual tasks, or improving communication flows between departments and reengineering workflows.
Aligning Processes with Strategic Goals: Ensure each redesigned workflow supports broader business objectives. By aligning workflows with strategic priorities, organizations ensure that future state processes are purpose-driven.
Maintaining a Technology-Agnostic Approach: Designing workflows without focusing on specific ERP systems keeps the emphasis on functional requirements. This approach provides flexibility when selecting ERP solutions, ensuring the technology supports, rather than constrains, process improvement.
Engaging Stakeholders for Input: Involving department heads, team leaders, and end-users in the future state design process ensures that workflows meet practical needs and are realistic for daily execution.
3. Compile Technology Requirements Based on Process Findings
After defining the future state, organizations can identify the specific technological requirements to support the mapped-out processes. This step is crucial to ensure the ERP system aligns with both current and future needs:
Identifying Essential Functionalities: Based on the future state processes, outline the necessary ERP features to support each function. For example, automated invoice processing, real-time data tracking, or integration with other business systems may be required.
Setting Growth and Scalability Expectations: Consider long-term organizational goals and determine if the ERP system can scale to accommodate future requirements. This can save significant customization costs post-implementation.
Minimizing Customizations: Analyzing technology requirements in the context of process findings reduces the need for excessive customizations, ensuring the ERP aligns closely with the business without unnecessary, costly modifications.
Mapping these requirements enables a more targeted and efficient ERP selection process, reducing the risk of selecting systems that require significant changes later.
4. Facilitate Stakeholder Alignment and Collaboration Using Process Mapping Tools:
Visual tools, such as Creately, are instrumental in fostering collaboration throughout the mapping journey. By providing a visual workspace, Creately enables organizations to:
Collaboratively Document and Refine Processes: Teams can map out processes together in real time, ensuring that all inputs and departmental insights are captured.
Simplify Communication: A visual representation of processes helps stakeholders from various departments understand and engage in discussions, making collaboration more effective.
Enable Continual Adaptability: By centralizing and updating process maps within Creately, organizations can keep process documentation current, promoting a responsive, adaptable approach post-implementation.
Following this structured approach to process mapping not only provides clarity and alignment but also optimizes ERP implementation by harmonizing operational objectives with technological capabilities. This approach ensures a seamless ERP integration that’s efficient, resilient, and adaptable to future needs and is one of the core purposes of ERP Business Process Mapping.
Tips to Optimize Your Process Mapping Strategy
ERP business process mapping is an essential step in ensuring that your implementation is successful. To maximize its effectiveness, consider the following best practices:
Engage Cross-Functional Teams: Involving team members from various functional areas ensures comprehensive input into the process maps. This engagement leads to a more holistic view of how processes impact different departments and encourages better alignment and buy-in.
Keep Maps Technology-Agnostic: Focus on outlining what needs to be accomplished rather than how specific technologies will be used. This approach allows for clear process documentation that highlights requirements without being constrained by existing technical capabilities.
Regularly Update Documentation: ERP processes and business landscapes evolve, and your process maps should reflect these changes. Post-implementation, regularly update your process maps to ensure they continue to support business objectives effectively.
Incorporating these practices into your ERP business process mapping endeavors not only promotes alignment and efficiency during implementation but also facilitates continuous improvement. For organizations seeking an effective tool to undertake these strategies, products like Creately offer a visual workspace that supports collaborative mapping, making it easy to engage multiple stakeholders and keep process documents up-to-date seamlessly.
ERP process mapping can present several challenges that, if overlooked, may jeopardize the success of an ERP implementation. One of the most common pitfalls is misalignment between business processes and ERP functionality. Failing to correctly map out and integrate these processes can lead to inefficient operations and unmet objectives. To prevent this, organizations should ensure thorough process documentation and engage stakeholders at every stage.
Another challenge is the risk of inefficiency due to outdated or redundant processes being carried over into the new system. To mitigate this, a critical evaluation of current workflows should be conducted to identify opportunities for process improvement and optimization.
Organizations often struggle with ensuring complete stakeholder communication. Lack of communication can result in incomplete process maps and overlooked functionalities, which could necessitate costly adjustments later. Overcoming this requires establishing open lines of communication and regular updates with all stakeholders involved.
| Challenge | Solution |
| Misalignment with ERP functionality | Thoroughly document and integrate processes; maintain stakeholder engagement. |
| Risk of inefficiency | Critically evaluate and streamline processes before mapping. |
| Incomplete stakeholder communication | Establish clear communication lines; ensure ongoing stakeholder updates. |
Acknowledging and addressing these challenges not only helps in creating an accurate ERP process map but also ensures a smoother ERP implementation pathway. Using tools like business process mapping can elevate both communication and process alignment, aiding significantly in the success of the ERP implementation process.
Some Critical Processes to Map for ERP
When embarking on an ERP implementation, it is crucial to identify the most critical business processes that must be thoroughly mapped. These processes typically have the greatest impact on overall organizational efficiency and productivity. Here are some of the key processes that are usually prioritized for ERP business process mapping:
- Order-to-Cash Process:
The order-to-cash process encompasses the entire customer journey, from initial order placement to final payment collection. Mapping this process ensures seamless integration between sales, inventory management, invoicing, and accounts receivable modules within the ERP system.
- Procure-to-Pay Process:
The procure-to-pay process covers purchasing, from requisition to vendor payment. Mapping this process helps align procurement, inventory, accounts payable, and general ledger functionalities in the ERP system.
- Inventory Management
Effective inventory tracking and optimization are critical to business success. Mapping inventory management processes, including stock replenishment, warehouse operations, and inventory reporting, allows the ERP system to be configured to support these core functions.
Financial Reporting and Accounting:
The financial reporting and accounting processes ensure accurate financial statements and regulatory compliance. Mapping these processes guarantees the ERP system can generate the necessary reports and maintain proper accounting controls.Human Resources and Payroll:
HR and payroll processes, such as employee onboarding, time-off tracking, and payroll processing, must be thoroughly mapped to ensure the ERP system can effectively manage the organization’s human capital management needs.Project Management:
For project-based organizations, mapping project management processes, including resource allocation, task tracking, and billing, is essential to integrating these functions within the ERP system.
By focusing on these mission-critical processes, organizations can create a comprehensive process map that serves as a solid foundation for a successful ERP implementation. This strategic approach ensures the ERP system is configured to support the core operations of the business, leading to greater efficiency, visibility, and overall success.
How Creately Helps Process Mapping for ERP Implementations
Creately is a powerful tool that supports organizations in effectively mapping processes for ERP implementation by providing an intuitive and visual workspace. Here’s how Creately can streamline and enhance ERP business process mapping:
1. Collaborative Workspace for Cross-Functional Teams
ERP implementations require input from various departments. Creately’s collaborative environment allows team members across departments to work together seamlessly. By offering real-time editing, commenting, and feedback capabilities, Creately ensures that each stakeholder can contribute to the process map, making it both comprehensive and inclusive. This transparency helps eliminate potential gaps or misunderstandings, aligning everyone around a unified ERP vision.
2. Ready-to-Use Templates for Quick Mapping
Creately provides a variety of templates tailored to ERP business process mapping, including options for documenting critical processes like Order-to-Cash, Procure-to-Pay, and Inventory Management. These templates provide a structured starting point that teams can adapt to specific business requirements, saving time while ensuring no essential details are overlooked.
3. Visualization and Documentation of Current and Future States
Mapping the “As-Is” and “To-Be” processes is simplified through Creately’s visual capabilities. Users can map out existing workflows in a clear, organized format, making it easy to spot inefficiencies and bottlenecks. The tool’s drag-and-drop functionality, shapes, and connectors allow for straightforward depiction of each process, decision point, and role involved. This visual clarity supports better planning and makes future state reengineering more intuitive.
4. Integration of Technology Requirements
With Creately, organizations can document their technology requirements directly on the process map. By associating each process step with specific technical needs, Creately helps organizations ensure that these requirements align with ERP functionalities. This documentation helps prevent costly post-implementation changes and supports a more seamless ERP system selection.
5. Support for Continuous Improvement Post-Implementation
Process mapping does not end with ERP implementation. Creately’s dynamic workspace allows for ongoing updates and adjustments as business needs evolve, making it easy to revisit and refine process maps. This adaptability enables teams to document changes, optimize workflows, and identify further improvements after the ERP system is live, supporting continuous operational enhancement.
6. Enhanced Data Migration Planning
Data migration is a complex yet critical part of ERP implementation, and Creately can aid in planning this by visualizing how data flows across different stages of a process. This structured visualization allows teams to outline precise data requirements, identify dependencies, and ensure that all necessary data is correctly mapped and transferred into the ERP system.
Successfully implementing an ERP system hinges not just on software selection but also on the vital groundwork of ERP business process mapping. This essential step ensures that organizations are well-prepared to harness the full potential of their ERP solutions. Thorough process mapping is indispensable for identifying the specific functionalities required, which streamlines the selection of an ERP system that aligns with your business strategy. This preparatory work mitigates risks associated with missed functionalities, inefficient processes, and potential costly adjustments post-implementation. Employing ERP business process mapping templates during this stage can aid in translating business needs into actionable insights, enhancing the overall ERP implementation process. Moreover, process mapping supports seamless data migration and effective training strategies, maximizing organizational efficiency and engagement. By embracing best practices in business process mapping, such as regular updates and stakeholder alignment, businesses can achieve a more effective configuration and integration of ERP systems. In this way, process mapping is not just a prelude to a successful ERP journey but a continuous guide toward optimization and innovation.
Sources
“Business Process Mapping & ERP.” ACC Software Solutions, 12 Apr. 2018, www.4acc.com/article/business-process-mapping-and-erp/.
Focus ERP. “ERP Business Process Mapping during the Selection.”-, www.erpfocus.com/erp-process-mapping.html.
FAQs Related to ERP Business Process Mapping
What is ERP Business Process Mapping?
Why is business process mapping important in ERP implementation
How can process mapping impact ERP system costs?
There are several tools available for issue mapping, including:
Mapping highlights necessary functionalities early, avoiding costly customizations and ensuring budget-friendly system choices.